Reference no: EM131200166
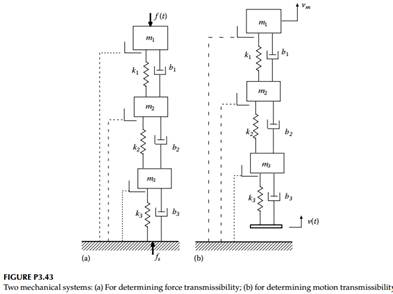
Figure P3.43 shows two systems (a) and (b), which may be used to study force transmissibility and motion transmissibility, respectively. Clearly discuss whether the force transmissibility Fs /F (in the Laplace domain) in system (a) is equal to the motion transmissibility Vm/V (in the Laplace domain) in system (b), by carrying out the following steps:
1. Draw the linear graphs for the two systems and mark the mobility functions for all the branches (except the source elements).
2. Simplify the two linear graphs by combining branches as appropriate (series branches: add mobilities; parallel branches; inverse rule applies for mobilities) and mark the mobilities of the combined branches.
3. Based on the objectives of the problem, i.e., determination of the force transmissibility of system (a), and motion transmissibility of system (b), for applying Thevenin's theorem, determine which part of the circuit (linear graph) should be cut (Note: The variable of interest in the particular transmissibility function should be associated with the part of the circuit that is cut).
4. Based on the objectives of the problem, establish whether Thevenin equivalence or Norton equivalence is needed (specifically: use Thevenin equivalence if a through variable needs to be determined, because this gives two series elements with a common through variable. Use Norton equivalence if an across variable needs to be determined, because this gives two parallel elements with a common across variable).
5. Determine the equivalent sources and mobilities of the equivalent circuits of the two systems.
6. Using the two equivalent circuits determine the transmissibility functions of interest.
7. By analysis, examine whether the two mobility functions obtained in this manner are equivalent.
Figure P3.43
|
Describe evolution of problem and emergence of ug business
: Present a brief background and some history - Describe the evolution of the problem and the emergence of the UG business. Discuss the mechanics of operation of this UG activity, as well as the ways in which payments are made.
|
|
One -way analysis of variance anova
: Practice Exercise 13: One -way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), When is it appropriate to use a one-way ANOVA to analyze data? What letter is use the designate the test statistic used in the one-way ANOVA?
|
|
How the total effective tax burden change
: How did the total effective tax burden change for the lowest and highest deciles of the population between 1979 and 2006?
|
|
Fifo page removal algorithm
: Using the FIFO page removal algorithm, indicate the movement of the pages into and out of the available page frames (called a page trace analysis) indicating each page fault with an asterisk (*). Then compute the failure and success ratios.
|
|
Draw the linear graphs for the two systems
: Draw the linear graphs for the two systems and mark the mobility functions for all the branches (except the source elements).
|
|
What are the geographic locations
: What is the required skill set to qualify for the position you want to apply in each company? Do you have the necessary experience? If not, what is your plan to get it?
|
|
Employers protect their data on employees devices
: How Should Employers Protect Their Data on Employees’ Devices? Companies are finding it increasingly difficult to manage their intellectual property now that employees have Smartphone and tablets many times which are not owned by the company. When a ..
|
|
Find average growth rate for each country over that period
: Find the average growth rate for each country over that period. What are some of the differences between those countries that have led to their different growth rates?
|
|
Use the simplex method to find the optimal solution
: Use the simplex method to find the optimal solution to the following problem. Show all of your tableaus. (Note: Keep 4 decimals in your calculations.). In addition, use Gurobi to solve the problem and provide the code and the output of Gurobi.
|