Reference no: EM13744270
Question 1: A second-price sealed-bid auction is a strategic game with n ≥ 2 bidders as players, where the set of actions for each player is the set of possible bids (nonnegative numbers).
Bidders have a valuation vi for the object. Assume v1 > v2 > . . . > vn > 0.
Denote by bi the bid of player i and by b' the highest bid submitted by a player other than i. Then, if bi > b, player i's payoff is vi b, if bi < b, player i's payoff is zero, and if bi = b' to break the tie, we assume player i's payoffis vi - b if i is smaller than the index of any other player bidding b (that is the object goes to the bidder with the highest valuation).
(a) Show that, with perfect information, a player's bid equal to her valuation weakly dominates all her other bids.
(b) Find a Nash equilibrium of a second-price sealed-bid auction in which player n (the bidder with the lowest valuation!) obtains the object. [Hint. Show first that the strategy profile (v2, v1, 0, . . . , 0) is a Nash equilibrium.]
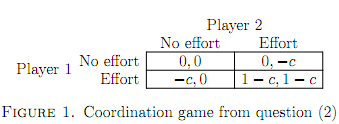
Question 2: Consider the following coordination game. Two people can perform a task if, and only if, they both perform effort. They are both better offif they both exert effort and perform the task than if neither exerts effort (and nothing is accomplished), the worst outcome for each person is that she exerts effort and the other person does not (in which case again nothing is accomplished). Specifically, the players' preferences are represented by the expected value of the payofffunctions in Figure 1, where c ∈ [0, 1] is the cost of effort. Find all the mixed strategy Nash equilibria of this game. How do the equilibria change as c increases? Explain the reasons for the changes.
Question 3: Consider the following take-over game. Firm A (\the acquirer") is contemplating taking over firm T (the \target"). It does not know firm T's value, it believes that his value, when firm T is controlled by its own management, is uniformly distributed on the interval [$0, $100]. Firm T will be worth 50% more under firm A's management than it is under its own management. Suppose that firm A bids y to take over firm T, and firm T is worth x (under its own management). Then if T accepts A's offer, A's payoffis 3/2x - y and T's payoffis y, if T rejects A's offer, A's payoffis 0 and T's payoff is x.
(a) Find the Bayesian Nash equilibrium (equilibria?) of the game in which firm A chooses how much to offer and firm T decides the lowest offer to accept.
(b) Explain why the logic behind the equilibrium is called ad- verse selection.
Question 4: Consider a credit market with two types of firms, i = a, b. Each firm has the opportunity to undertake a project, which requires a fixed amount of investment normalised to I = 1. The return to firm i's project is given by a random variable e Ri, which takes value 0 with probability θi and value Ri with probability 1 - θi. Assume that R'b corresponds to greater risk than R'a in the sense that E[R'a] = E[ R'b] > I and θa < θb.
Assume that firms are born with a type and cannot choose it. Assume that firms can observe their type but banks cannot. Denote by λ the exogenous probability that a firm is born as type a. Assume λ to be small.
Firms have no liquid wealth and finance their projects by borrowing the full investment amount I = 1 from perfectly competitive banks. They have, however, illiquid wealth that they can supply as collateral to a bank. Let a loan contract specify an interest rate r charged and an amount of collateral C required by the bank. Firms face costs to collateralisation. For simplicity, these costs will be assumed to be proportional to the amount of collateral by a factor k > 0.
A firm defaults if its project returns zero. If this happens, the bank becomes the owner of the investment project and the collateral. Therefore, the profits of firm i from undertaking the project under a loan contract specifying r and C are given by Ri (1 + r) - kC if it does not default and by (1 + k)C if it defaults. Hence, a firm's expected return is given by
Πi(r,C) = (1 - θi)(Ri - (1 + r)) - θiC - kC.
On a loan specifying r and C to a firm of type i, the bank receives a rate of return of r if the firm does not default and a return of (C - 1) if the firm defaults. Denote by r0 the banks' cost of funds. Hence, its expected return, net of the cost of funds, on a loan specifying r and C to a firm of type i is given by
Ρi(r,C)= (1 - θi)r + θi(C - 1) - r0.
[Hint. If it helps, assume k = 1/5 , r0 = 1/10 , Ra = 5, Rb = 7.5, θa = 2/5 , and θb = 3/5 , leading to E[ R'a] = (1 - 2/5) x 5 =3 and E[ R'b] =(1 - 3/5) x 7.5 = 3. The numerical values suggested below are derived using these values.]
(a) Show that the banks' break-even lines for loans to borrowers of type a is given by
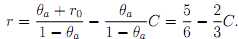
and that for loans to borrowers of type b is given by
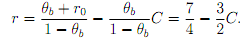
Draw the banks' break-even lines for loans to both types of borrowers in a C - r - diagram. [Hint. both break-even lines start at full collateral of C = (1 + r0) and an interest rate of r0.]
(b) Show that an iso-profit line at expected profit level Π' for a firm of type a is given by and that for a firm of type b is given by
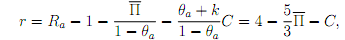
Are they steeper or atter than the banks' zero-profit lines? Are the iso-profit curves for borrowers of type a or those of borrowers of type b steeper? Why?
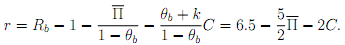
(c) Show that the (efficient) full-information loan contracts to the two types of borrowers are given by
and identify them in your diagram.
(d) Draw the iso-profit curves of borrowers of types a and b that go through their respective full information contract in your diagram. If the banks offered the two full-information contracts without being able to distinguish the two types of borrowers, what would happen?
(e) Assume now that banks could use collateral to screen the two types of firms. In your graph, identify the two contracts banks would be offering in a pure strategy separating equilibrium candidate. Who would be providing more collateral in equilibrium? Who would be paying a higher interest in equilibrium? Why?