Reference no: EM133021767
ENRG2702 Electrical Circuits and Machines
Q1:
Explain the difference between an electric field and an electro-magnetic field. Write down the expression for the Lorentz force and explain the meaning of it.
Q2:
Write down:
a) the expression for Ampere's circuital law and explain the meaning of it.
b) the expression for Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction (including Lenz's law) and explain the meaning of it.
Q3:
State the meaning of permeability, write down the expression for the permeability of free space, and indicate how it was developed from the Biot-Savart Law.
Draw the B-H characteristic for:
a) a ferromagnetic material,
b) a non-ferromagnetic material and show how the permeability may be calculated from them.
Q4:
Draw the fringing of a magnetic field between two poles and explain how it changes the effective area of the air-gap?
How does this change affect Φ(t) and B(t)?
What is a leakage flux and how could be eliminated?
Q5:
For the accompanying diagram mark and identify the areas of:
a) stored energy,
b) co-energy of the magnetic core and explain their physical meanings.
Q6: Write down the expression that describes the relationship between mutual and self- inductances (including the coefficient of coupling k). What is the physical meaning when:
a) k=1
b) k=0?
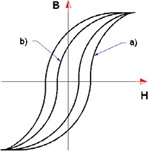
Q7: Draw the static and dynamic hysteresis loops of a ferromagnetic material and explain their differences.
Q8: Which of the two hysteresis loops a) and b) in the picture below is preferable in the construction of a power transformer and why?
Q9: By using the equivalent circuit of an iron core transformer referred to the primary side, draw the phasor diagram for:
a) a purely capacitive load,
b) a load which is 50% resistive and 50% inductive including all current and voltage phasors. Assume E1and E2 are in phase.
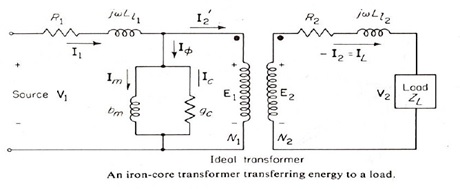
Q10: For an iron-core transformer, state the purpose of:
a) an open circuit test,
b) a short circuit test,
c) a load test.
Q11: Where is the field winding of a DC-machine situated and what is its purpose? What are the principal types of field coil construction?
Explain why the field poles and armature of a DC machine are laminated? What is the load current of a DC generator and where does it run through?
Q12: Where is the armature winding of a DC machine situated and what is its purpose when this machine runs as a generator?
What is the armature reaction of a DC-generator and how can it be reduced?
Q13: What is the main use of stepper motors?
What is the difference between a reluctance and a permanent magnet stepper motor? Describe the construction of a hybrid stepper motor.
Q14: A stepper motor advances1.8 degrees per step. How many pulses are needed to complete 2 revolutions? Explain what is meant by normal drive, wave drive and half-step drive.
Why is viscous damping employed in stepper motors?
When a stepper motor is ramping or slewing properly, every pulse corresponds to a precise angle of rotation. True or false?
Q15: What is the advantages of using a stationary armature in large synchronous generators? Why is the stator always connected in wye?
Q16: State the main differences between steam-turbine generators and salient-pole generators. For a given power output, which of these machines is larger?
Q17: Why does the rotor of an induction motor turn slower than the revolving stator field?
Q18: What happens to the rotor speed and rotor current when the mechanical load placed on the shaft of an induction motor increases?
What is the slip of a 3-phase induction motor?
In what condition is a 3-phase induction machine operating if: a) s>0%
b) s<0%
c) s=0?
Q19: Draw the torque/speed characteristics for a 3-phase:
a) wound-rotor induction motor, with variable external resistance, and
b) squirrel-cage induction motor
and state what you can conclude about the starting torque for each of them?
Q20:
What has to be done to reverse the direction of rotation of:
a) a 3-phase induction motor,
b) a shunt connected DC-motor and
c) a 3-phase synchronous motor?