Reference no: EM132612541
Article 1: Org Lett_2008: Biomimetic Synthesis and Structural Revision of (±)-Tridachiahydropyrone; Org. Lett., 2008, 10, 4025.
Article 2: Tetrahedron Lett_2003: I2 as an efficient catalyst in ionic Diels- Alder reactions of α,β-unsaturated acetals, Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 3001.
Please read article 1_Org Lett_2008 provided and answer the following questions
The paper discusses the synthesis of a γ-pyrone natural product, Tridachiahydrapyrone (2) from its putative precursor 1 under photochemical irradiation to give the required cis product (Scheme 1).
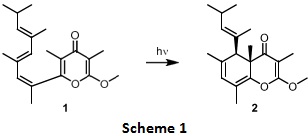
Question 1. i) Identify all the double bonds participating in the electrocyclic process in substrate 1 to give the product 2 and assign E/Z geometry (wherever applicable).
Draw the π-molecular orbitals for the participating conjugated triene in 1 above.
In your diagrams show all the possible nodes and electron distributions (both ground state and excited state).
Indicate which MOs constitute the ground state HOMO and excited state HOMO.
Question 2. The natural product 2 undergoes a sigmatropic rearrangement [i,j] to give product 3 as shown in scheme 2.
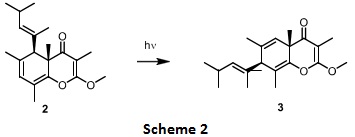
Draw the structure of the starting material (2) and number it appropriately to define the sigmatropic rearrangement occurring and identify what numbers i and j correspond to?
Identify the reaction as either suprafacial or antarafacial under photochemical conditions.
Using electron flow arrows provide a mechanism for the conversion of the starting material 2 shown to the corresponding product 3.
When to a mixture of compound 2 and 3, acrolein(propenal) is added, it leads to the isolation of tricyclic product(s). Predict which of the two substrate, 2 or 3, will undergo a pericyclic reaction with acrolein. Classify what kind of the cyclisation reaction is this and provide the structure of the product formed indicating the exo/endo stereochemistry, if any.
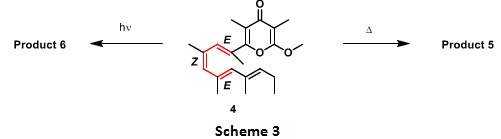
Question 3. For an analogous pyrone substrate 4, as shown in scheme 3, draw the products 5 and 6 for the thermal and photochemical electrocyclisation. Label the pathways as conrotatory/disrotatory and show the stereochemistry in the products. (Hint: bond shown in red is participating in the electrocyclic reaction).
Please read the article 2_Tetrahedron Lett_2003 provided and answer the following questions
Question 4. In the article several substrates were shown to take part in Diels- Alder reaction to give various cyclic products. For the example shown in scheme 4, answer the following questions.
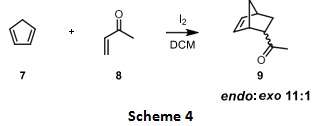
Indicate the diene and dienophile in the above reaction scheme.
The reaction indicates an endo:exo product ratio of 11:1. Draw the structure showing the stereochemistry for both exo and endo products. Explain why endo is the major product.
What conditions (thermal or photochemical) was this reaction carried out? Explain your answer fully using frontier molecular orbital theory as it is applied to cycloaddition reactions (hint: use diagrams showing the interactions between MOs).
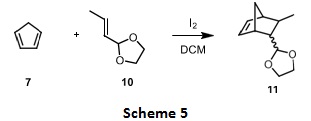
For the corresponding acetal substrates (an example shown in scheme 5), the Diels-Alder cycloaddition reaction is proposed to involve a cationic intermediate of substrate 10 under iodine catalysis leading to improved cycloaddition reaction rates. Propose a structure for the cationic intermediate and explain how formation of the intermediate speeds up the Diels-Alder reaction with the diene. (hint: use MOs energy diagram).