Reference no: EM133138914 , Length: word count:1500
CIS049-2 Microwave and Optical Communications - University of Bedfordshire
Microwave communications
Learning outcome 1: Understand and contrast fundamental concepts, terminology and techniques in modern microwave and optical communications
Learning outcome 2: Use appropriate tools to design and analyse microwave and optical communication systems based on real-world problems.
Aim
Study and analysis of the performance of wired and wireless microwave communication syst ems.
Learning Objective: This assignment is designed to let you carry out a practical measurement of radio wave propagation using a modern microwave network analyser, the R&SZVL6. The experiment will benefit you in the following two aspects:
- To learn how to use a network analyser to measure the S-parameters;
- To reinforce your understanding of the principle of radio wave propagation.
- To demonstrate radio wave propagation in wired and wireless media.
Task
PART A: Wired Communication Link
1. Measure the reflection coefficient (S11) and transmission coefficient (S21) for a standard coaxial cable.
2. Measure the transmission coefficient (S21) for the above set-up using a 10 dB and 20 dB attenuator.
3. Replace the attenuator with a band pass filter and measure the transmission coefficient (S21) response and bandwidth.
Explain the test set-up including labelled photos. Arrange the observed values of S11 and S22 in steps 1-3 in a table and include it in your report. Analyse the results discussing impact of the attenuators and filter on the performance of this wired communications channel.
PART B: Wireless Communication Link
1. Use a pair of monopole antennas and measure their operating frequencies using the Vector Network Analyser (VNA).
2. Connect the two monopole antennas to the two ports of the VNA through two coaxial cables forming a wireless link.
3. Place the antennas in vertical orientation on top of the two tri-pods using polystyrene form and paper tape for the support.
4. Place the antennas at minimum distance (in such a way that they are touching each other with no gap). Note down the transmission coefficient (S21) that represents the path gain.
5. Increase the distance between the two antennas in steps of 10 cm up to a maximum of 1.0 m and record the corresponding path gain results. Plot the path gain as a function of the antenna separation.
6. Place one of the antennas in horizontal orientation while keeping the other in vertical orientation. Measure the path gain values for different separations for this antenna set-up as done in Step 5.
Analyse the results and discuss the effects of antenna polarisation on the link performance.
7. Reconnect the apparatus as shown in Figure 1 and note down the path gain response.
8. Place a metal sheet between the two antennas and take an account of the path gain.
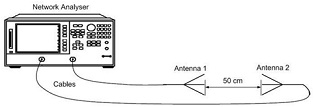
Figure 1
Which of the above links exhibit stronger microwave link? Discuss giving scientific reasons.
Explain the test set-up including labelled photos. Plot THREE graphs for your observations made in Steps 4-8 and include them in your report. Analyse the results discussing impact of the distance, antenna orientation and environment on this wireless communications channel.
Write a formal technical report on your findings, and in particular compare and contrast the performance of the link in wired and wireless modes. Your report should contain an abstract, the problem statement, methodology and equipment configuration, results and analysis, and conclusions.