Reference no: EM13213774
You are considering the purchase of one of two large presses. The key financial characteristics of the existing press and the two proposed presses are summarised below.
Old press: Originally purchased three years ago at an installed cost of $400 000, it is being depreciated under prime cost (straight-line) using a 10-year recovery period. The old press has a remaining economic life of five years. It can be sold today to net $420 000 before taxes
Press A:
This highly automated press can be purchased for $830 000 and will require $40 000 in installation costs. It will be depreciated under prime cost (straight-line) using a five-year recovery period. At the end of the five years, the machine could be sold to net $400 000 before taxes. If this machine is acquired, it is anticipated that the following current account changes would result.
Cash +$25400
Accounts receivable + 120 000
Inventories -20000
Accounts payable + 35 000
Press B: This press is not as sophisticated as press A. It costs $640 000 and requires $20 000 in installation costs. It will be depreciated under prime cost (straight-line) using a five-year recovery period. At the end of five years, it can be sold to net $330 000 before taxes. Acquisition of this press will have no effect on the firm's net working capital investment.
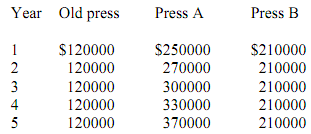
The firm estimates that its earnings before depreciation and taxes with the old press and with press A or press B for each of the five years would be as shown in Table 1.
The firm is subject to a 33 per cent tax rate on both ordinary income and capital gains. The firm's cost of capital, k, applicable to the proposed replacement is 14 per cent.
EARNINGS BEFORE DEPRECIATION AND TAXES COMPANY'S PRESSES
Required
1. For each of the two proposed replacement presses, determine:
a) Initial investment.
b) Net present value.
c) Internal rate of return.
2. Draw NPV profiles for the two replacement presses on the same set of axes, and discuss conflicting rankings of the two presses, if any, resulting from use of NPV and IRR decision techniques.
3. Recommend which, if either, of the presses the firm should acquire
|
How to predict the freezing point of a solution
: Predict the freezing point of a solution of 10.0 g of carbon tetrachloride, CCl4, in 100.0 g of benezene, C6H6. For benezene
|
|
Show banks balance sheet, and calculate excess reserves
: The balance sheet of a bank follows. Suppose that the reserve requirement is 3 percent on the f rst $30 million of checkable deposits and 10 percent on checkable deposits in excess of $30 million. (Amounts on the balance sheet are in millions of d..
|
|
Compute the average molar mass of the sample
: If a sample is composed of 39% of the lighter isotope (with the balance being 7Li), calculate the average molar mass of the sample.
|
|
Calculate the dividend yield and the capital-gains yield
: A stock was priced at $150 per share at the end of 2007. The following table shows dividends per share paid during each year and the price of the stock at the end of the year for the following four years: Dividends Paid Stock Price at Year During ..
|
|
Discuss conflicting rankings of the two presses
: Draw NPV profiles for the two replacement presses on the same set of axes, and discuss conflicting rankings of the two presses, if any, resulting from use of NPV and IRR decision techniques.
|
|
How to complete the reaction in a dinitration
: Why can a first nitration be done at 0 degrees Celsius but the ice bath is removed to complete the reaction in a dinitration
|
|
How much the account earns interest per year
: How much must you deposit in your retirement account each year for 10 years starting now (i.e., years 0 through 9) if you want to be able to withdraw $50,000 per year forever beginning 30 years from now Assume the account earns interest at 10% per..
|
|
What push-pull theory issues
: What push-pull theory issues pushed the people effected by the khmer regime out of their country and what reasons pulled them into the united states.
|
|
Explain the same woman climbing a mountain needs
: A 120 pound woman working in an office consumes about 2200 kcal/day, whereas the same woman climbing a mountain needs 3400 kcal/day.
|