Reference no: EM133320
QUESTION 1
(a) Name five significant activities involved in a digital forensic investigation.
(b) Why is computer forensic possible? Give an instance to support your answer.
(c) How is computer forensic dissimilar from data recovery?
(d) Briefly explain the three types of data that a forensic examiner has to work with. Which one of the three is more tricky to obtain?
(e) Computer crimes pose new challenges for investigators. Give two causes why?
QUESTION 2
(a)Describe the term "computer security incident". Give one instance for each of the subsequent grouping of security incident:
(a) Low level,
(b) Mid Level, and
(c) High Level.
(b)First Response carry out by a forensic staff involves six stages. What are the six stages?
(c)
i. What is the Trojan Defence?
ii. Explain whether this defence is successful or not in court? Clarify your reasoning.
iii. Describe how the Trojan Defence can be used as an anti-forensics technique?
iv. Why is this anti-forensics technique often unbeaten?
QUESTION 3
(a)Data acquisition is often chased by the evidence authentication process.
(i) Briefly illustrate the data acquisition process.
(ii) Why is data acquisition executed?
(iii) What is the purpose of the authentication procedure?
(iv) How is the authentication of evidence frequently done?
(b)Throughout data acquisition, data spoliation can occur.
(i) Put in plain words why data spoliation can occur when using a computer to perform data acquisition of a hard-drive.
(ii) How can this data spoliation be avoided?
(c)(i) What is the "chain of custody"?
(ii) What is the point of the chain of custody?
(iii) When does the chain of custody start?
(d)Data can be covered on a computer system. Data hiding study can be useful in detecting and recovering such data. Discuss three ways of how a suspect can hide data on a computer.
QUESTION 4
(a)Name two sorts of File System.
(b)(i) Where is the metadata concerning files/folders stored in a FAT file system?
(ii) Give four instances of typical metadata stored.
(c)The FAT entry for non-addressable cluster 1 in FAT 16 is used to store the worth for the "dirty status" of file system.
(i) When is the dirty status set?
(ii) What take places when the dirty status is set?
(d)(i) Explain the 8 dot 3 DOS naming convention.
(ii) Write the 8 dot 3 alias for the subsequent file names:
a. SQLOracleHacks.txt
b. SQLOracleAttacks.txt
c. SQLInjection.html
(e)Why does NTFS have better performance with regard to read capability than the FAT file structure?
QUESTION 5
(a)Mull over a company involved in research where all work is strictly confidential. The company's network enforces strong access control and is equipped with a content based filtering firewall which checks all data that leaves the network. In some way, the CEO is concerned that confidential information about their research has been leaked out of the company's network. As a forensic expert, you are asked to investigate. Portray how you will proceed to find evidence, if any, to prove that there may be data leakage.
(b)Judge the following email header: Based on the information in the email header, Based on the information in the email header, depict the path the email takes from source to destination by means of a diagram. Indicate on the diagram the different protocols in use.
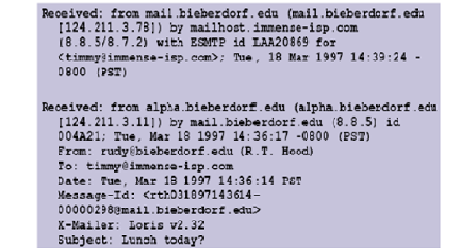
(c)Detail three email forensic tools.
|
Turtle shell architecture
: Turtle Shell Architecture, zero-byte representation, Access Control List, DNS Cache Poisoning attack, 16-pass iterative and 9-pass recursive PHP function
|
|
Symmetric encryption algorithms
: block cipher and a stream cipher, Caesar cipher, cryptanalytic attacks, mono alphabetic cipher and a poly alphabetic cipher, Mix Columns, Add Round key, PGP services, traffic padding, contrast link and end-to-end encryption
|
|
Discretionary and mandatory access control
: Logic bombs, War dialing, Ping of death attack, steganography, RSA scheme, digital signature, A chain of certificates, A certificate revocation list, A trust anchor, asymmetric algorithm used by PGP, IPSec mode, IP virtual Private Networks
|
|
Network security
: SLE, ARO, and ALE, behavioural biometric technology, Enterprise Information Security Policy, Issue Specific Security Policy, System Specific Security Policy, firewalls protect network, creating a DMZ during firewall implementation, use of SSL to se..
|
|
Digital forensic investigation
: computer security incident, Trojan Defence, anti-forensics technique, chain of custody, FAT file system, SQLOracleHacks.txt, SQLOracleAttacks.txt, SQLInjection.html
|
|
Computer security incident
: Locard's Exchange Principle, electronic crime scene, modules or DLLs a process, router forensics, Configuration and user, Local logs process and memory, Network Information, File system, Portray the NTP vulnerability of some Cisco IOS routers
|
|
Security vulnerabilities of vc
: single access point (AP), wireless network, CSMA/CA, goals of information security, Wireless LANs, wireless hacking process, Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), Open System Authentication and Shared Key Authentication, Initialisation Vector (IV), RADIU..
|
|
Owasp top 10 web application security risks
: Reflected XSS and Stored XSS attack, threat Modeling methodologies, Extended Stack Pointer (ESP) and the Extended Base Pointer (EBP), Canary-based defense to buffer overflow attacks in C language, admin.aspx, Index hijacking, cross-site request fo..
|
|
Cryptosystem
: Block cipher, Primitive root, Confusion, Diffusion, Digital signature, Conventional Symmetric-Key Encryption
|