Reference no: EM13864447
Refering to figure below: You are the network administrator for the network depicted in the diagram. You have been assigned the address space 10.1.16.0/21 to create the LANs you need, and the 172.16.1.0/28 space for your WAN links.
LAN: 10.1.16.0/21
WAN: 172.16.1.0/28
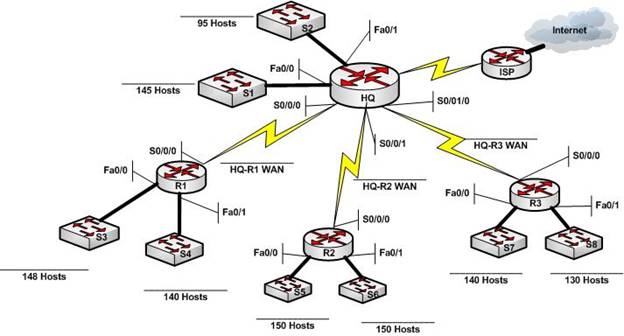
LAN Subnets
Begin by creating and assigning the LAN subnets you will use. In order to make the most efficient use of your address space you should start by creating the subnet needed for the LAN with the most hosts and then work you down to the smallest LAN.
Using the address space 10.1.16.0/21, create subnets for the LANs shown in the diagram and fill in the table 1 below. Notice that the first 7 subnets are all basically the same size and all subnets are all factors of 2 (remember 2n-2 where n is the number of host bits tells you the subnet size). Also remember for the most efficient addressing you should use the smallest size subnet that provides you the needed number of hosts.
TABLE 1: (Questions 1-8)
|
Question
|
LAN
|
Subnet Address
|
Subnet Mask
|
|
1.
|
R1 LAN S3
|
|
|
|
2.
|
R1 LAN S4
|
|
|
|
3.
|
R2 LAN S5
|
|
|
|
4.
|
R2 LAN S6
|
|
|
|
5.
|
R3 LAN S7
|
|
|
|
6.
|
R3 LAN S8
|
|
|
|
7.
|
HQ LAN S1
|
|
|
|
8.
|
HQ LAN S2
|
|
|
WAN Subnets
For the WAN links, you have been assigned the 172.16.1.0/28 address space. Fill in the subnets in Table 2 below by subnetting the assigned WAN space.
TABLE 2: (Questions 9-11)
|
Question
|
WAN
|
Subnet Address
|
Subnet Mask
|
|
9.
|
HQ-R1
|
|
|
|
10.
|
HQ-R2
|
|
|
|
11.
|
HQ-R3
|
|
|
Assign addresses
Use Table 3 below to document the IP addresses for the indicated interfaces following the guidelines below:
1. Assign the first IP address for all LANs to the router interface.
2. Assign HQ the first IP address for all WAN links to Branch routers.
Table 3: (Questions 13-27)
|
|
Device
|
Interface
|
Address
|
Mask
|
|
13
|
HQ Router
|
Fa0/0
|
|
|
|
14
|
|
Fa0/1
|
|
|
|
15
|
|
S0/0/0
|
|
|
|
16
|
|
S0/1/0
|
|
|
|
17
|
|
S0/0/1
|
|
|
|
18
|
R1 Router
|
Fa0/0
|
|
|
|
19
|
|
Fa0/1
|
|
|
|
20
|
Bonus
|
n/a
|
n/a
|
n/a
|
|
21
|
|
S0/0/0
|
|
|
|
22
|
R2 Router
|
Fa0/0
|
|
|
|
23
|
|
Fa0/1
|
|
|
|
24
|
|
S0/0/0
|
|
|
|
25
|
R3 Router
|
Fa0/0
|
|
|
|
26
|
|
Fa0/1
|
|
|
|
27
|
|
S0/0/0
|
|
|
EIGRP Metric Calculation
| |
List the values used in the EIGRP composite metric to calculate the preferred path (4):
|
|
28
|
|
|
29
|
|
|
30
|
|
|
31
|
|
Routing concepts- Questions
32. What is the default formula for the EIGRP composite metric?
33. What command can be used to view the current K value being used by EIGRP?
34. What command can be used to see the actual values of the EIGRP metric?
35. The _____________ metric is displayed in Kbps?
36. The default value used by most serial interfaces is based on T1 connections and is______________bps?
37. The measure of the probability a link will fail based on its history (downtime, errors) is referred to as ____________ and is measured with a value between 0 and 255.
38. ____________represents the amount of traffic using the link with a value between 0 and 255.
39. What is the main difference between a parent route and an ultimate route?
40. What is the relationship between parent and child routes?
41. Provide a brief description of a level 1 route:
42. What are the types of level one routes?
DUAL Concepts
|
List at least 3 advantages that DUAL offers:
|
|
43
|
|
|
44
|
|
|
45
|
|
|
Dual Concept
|
Definition
|
|
46
|
Successor
|
|
|
47
|
Feasible distance (FD)
|
|
|
48
|
Feasible successor
|
|
|
49
|
Feasibility condition (FC)
|
|
|
50
|
Reported Distance
|
|