Reference no: EM131243588
Q1. For Fig 1, the input voltage is dc and positive with the polarity shown. Specify how to implement the switches using a minimal number of diodes and transistors, such that the converter operates over the entire range of duty cycles. The switch states should vary as shown in Fig. 2. You may assume that the inductor current ripples and capacitor voltage ripples are small.
a) Realize the switches using SPST ideal switches, and explicitly define the voltage and current of each switch.
b) Express the onstate current and offstate voltage of each SPST switch in terms of the converter inductor currents, capacitor voltages, and/or input source voltage.
c) Solve the converter to determine the inductor currents and capacitor voltages.
d) Determine the polarities of the switch onstate currents and offstate voltages. Do the polarities vary with duty cycle?
e) State how each switch can be realized using transistors and/or diodes, and whether the realization requires singlequadrant, currentbidirectional twoquadrant, voltagebidirectional two quadrant,or fourquadrant switches.
2. A switching converter operates with a switching frequency of 150 kHz. The converter waveforms exhibit damped sinusoidal ringing, initiated by the transistor turnoff transition, which decays slowly but eventually reaches zero before the end of the switching period. This ringing occurs in a series resonant circuit formed by parasitic inductances and capacitances in the circuit. The frequency of the ringing is 10 MHz. During the first period of sinusoidal ringing, the ac inductor current reaches a peak magnitude of 0.5 A, and the ac capacitor voltage reaches a peak magnitude of 150 V. Determine the following quantities:
(a) The value of the total parasitic inductance,
(b) The value of the total parasitic capacitance,
(c) The energy lost per switching period, associated with this ringing, and
(d) The switching loss associated with this ringing.
(e) Derive a general expression for the switching loss, as a function of the switching frequency, ringing frequency, and the ringing voltage and current peak magnitudes during the first period of ringing.
3. In Fig 3 , the switching transition for a switch are shown with following switching characteristics
tri = 80ns
tfv = 80ns
trv = 120ns
tfi = 200ns
Vd = 300V
I0 = 4A
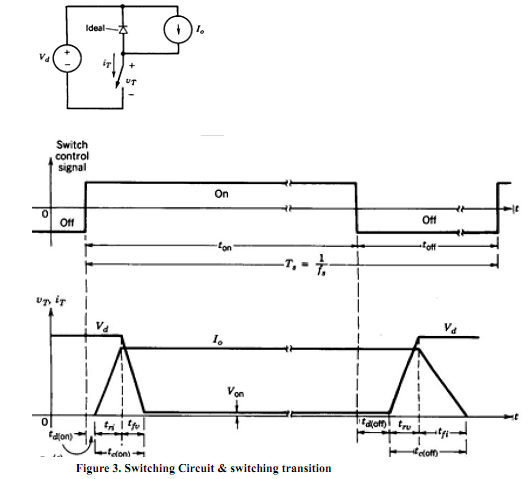
a. Using Fig 3, sketch the instantaneous switching loss for the switch as a function of time.
b. Calculate the switching power loss as a function of the switching frequency in a range 25 100 kHz, assuming Vd = 300V and I0 = 4A.
c. Calculate and plot the total losses as a function of the switching frequency in a range 25 100 kHz in the switch when the onstate voltage is Von =1.5V at 4A and the duty ratio of the switch is D = 0.4 (assume tdon=tdoff).
Assumption for Q4:
A transistor having an onresistance of 0.5 ohm is used. To simplify the problem, you may neglect all losses other than the transistor conduction loss. You may also neglect the dependence of MOSFET onresistance on rated blocking voltage. These simplifying assumptions reduce the differences between converters, but do not change the conclusions regarding which converter performs best in the given situations.
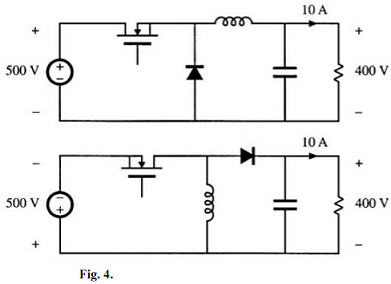
4. It is desired to interface a 500 V dc source to a 400 V, 10 A load using a dcdc converter. Two possible approaches, using buck and buckboost converters, are illustrated in Fig. 4. Use the assumptions described above to:
(a) Derive equivalent circuit models for both converters, which model the converter input and output ports as well as the transistor conduction loss.
(b) Determine the duty cycles that cause the converters to operate with the specified conditions.
(c) Compare the transistor conduction losses and efficiencies of the two approaches, and conclude which converter is better suited to the specified application.
5. To reduce the switching harmonics present in the input current of a certain buck converter, an input filter is added as shown in Figure 5. Inductors L1 and L2 contain winding resistances RL1 and RL2 respectively. The MOSFET has onresistance Ron and the diode forward voltage drop can be modeled by a constant voltage VD plus a resistor RD. All other losses can be ignored.
(a) Derive a complete equivalent circuit model for this circuit.
(b) Solve your model to find the dc output voltage V.
(c) Derive an expression for the efficiency. Manipulate your expression into a form similar to the below equation.
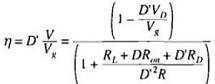
6. In the Cuk converter shown in Figure 6, the MOSFET has onresistance Ron and the diode has a constant forward voltage drop VD. All other losses can be neglected.
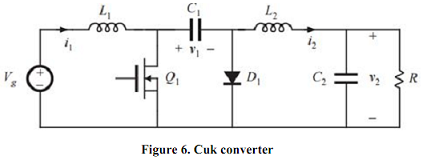
(a) Derive an equivalent circuit model for this converter. Suggestion: if you don't know how to handle some of the terms in your dc equations, then temporarily leave them as dependent sources. A more physical representation of these terms may become apparent once dc transformers are incorporated into the model.
(b) Derive analytical expressions for the converter output voltage and for the efficiency.
(c) For VD = 0, plot V2/Vg vs. D over the range 0 ≤ D ≤ 1, for (i) Ron/R = 0.01, (ii) Ron/R = 0.1, (iii) Ron/R = 1. Conclude from the result.
(d) For VD = 0, plot converter efficiency vs. D over the range 0 ≤ D ≤ 1, for (i) Ron/R = 0.01, (ii) Ron/R = 0.1, (iii) Ron/R = 1. Conclude from the result.