Reference no: EM132174502
Question 1: (a) A silicon dioxide gate insulator of an MOS transistor has a thickness of tox = 120 Å. (i) Calculate the ideal oxide breakdown voltage. (ii) If a safety factor of three is required, determine the maximum safe gate voltage that may be applied. (b) Repeat part (a) for an oxide thickness of fox = 200 Å.
Question 2: In a power MOS transistor, the maximum applied gate voltage is 24 V. If a safety factor of three is specified, determine the minimum thickness necessary for the silicon dioxide gate insulator.
Section - Transistor dc Analysis
Question 3: In the circuit in Figure P3.26, the transistor parameters are VTN = 0.8 V and Kn = 0.5 mA/V2. Calculate VGS, ID, and VDS
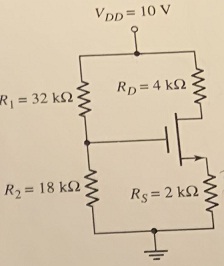
Figure 3.26
Question 4: The transistor in the circuit in Figure P3.27 has parameters VTN = 0.8 V and Kn = 0.25 mA/V2. Sketch the load line and plot the Q-point for
(a) VDD = 4 V, RD = 1 kΩ and (b) VDD = 5 V, RD = 3 kΩ. What is the operating bias region for each condition?
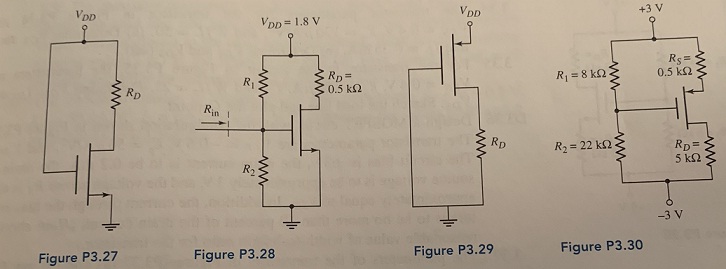
Question 5: The transistor in Figure P3.28 has parameters VTN = 0.4 V, kn' = 120 μA/V2, and W/L = 80. Design the circuit such that IQ = 0.8 mA and Rin = 200 kΩ.
Question 6: The transistor in the circuit in Figure P3.29 has parameters VTP = -0.8 V and Kp = 0.20 mA/V2. Sketch the load line and plot the Q-point for
(a) VDD = 3.5 V, RD = 1.2 kΩ and (b) VDD = 5 V, RD = 4kΩ. What is the operating bias region for each condition?
Question 7: Consider the circuit in Figure P3.30. The transistor parameters are VT? = -0.8 V and Kp = 0.5 mA/V2. Determine ID,VsG, and VSD.
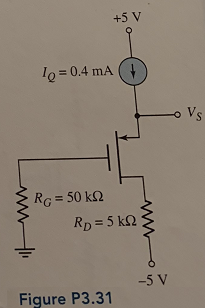
Question 8: For the circuit in Figure P3.31, the transistor parameters are VTP = -0.8 V and Kp = 200 μA/V2. Determine Vs and VSD
Question 9: Design a MOSFET circuit in the configuration shown in Figure P3.26. The transistor parameters are VTN = 0.4 V and k'n = 120 μA/V2, and RD = 5kΩ. The circuit parameters are VDD = 3.3 V and RD = 5 kΩ. Design the circuit so that VDSQ ≅ 1.6 V and the voltage across Rs is approximately 0.8 V. Set VGS = 0.8 V. The current through the bias resistors is to be approximately 5 percent of the drain current.
Question 10: Consider the circuit shown in Figure P3.33 The transistor parameters are VTN = 0.4 V and k'n = 120 μA/V2. The voltage drop across Rs is to be 0.20V. Design the transistor W/L ratio such that VDS = VDS (sat) + 0.4 V, and determine R1 and R2 such that Rin = 200kΩ.
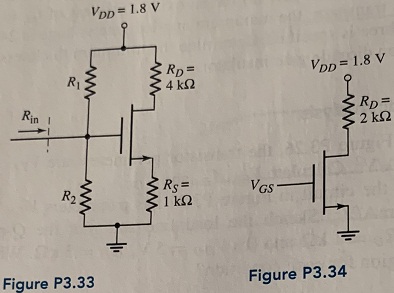
Question 11: The transistor parameters for the transistor in Figure P3.34 are VTN = 0.4 V, kn' = 120 μ,A/V2, and W /L = 50.
(a) Determine VGs such that ID = 0.35 mA. (b) Determine VDS and VDS (sat).
Question 12: For the transistor in the circuit in Figure P3.35, the parameter are VTN = 0.4 V, k'n = 120 μA/V2, and W/L = 25. Determine VGS, VDS. Sketch the load line and plot the Q -point.
Question 13: Design a MOSFET circuit with the configuration shown in Figure. The transistor parameters are VTp = -0.6 V, kp' = 50 μ A/V2, and λ = 0. The circuit bias is ±3 V, the drain current is to be 0.2 mA, the drain to source voltage is to be approximately 3 V, and the voltage across RS is to be approximately equal to VSG. In addition, the current through the bias resistors is to be no more than 10 percent of the drain current. (Hint choose a reasonable value of width-to-length ratio for the transistor)
Question 14: The transistor in the common-source amplifier in Figure P4.20 has parameters VTN = 0.8 V, k'n = 100 μA/V2, W/L = 50, and λ = 0.02 v-1. The circuit parameters are V+ = 5 V, V- = -5 V, IQ = 0 5 mA, and RD = 6 kΩ.
(a) Determine VGSQ and VDSQ.
(b) Find the small-signal voltage gain for RL = ∞.
(c) Repeat part (b) for RL = 20 kΩ.
(d) Repeat part (b) for RL = 6 kΩ.
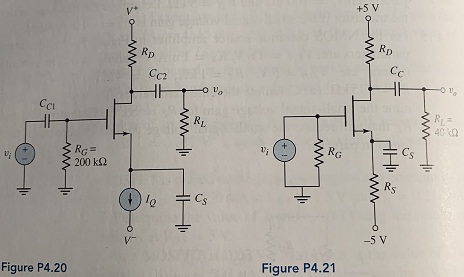
Question 15: The parameters of the MOSFET in the circuit shown in Figure P4.21 are VTN = 0.8 V, Kn = 0.85 mA/V2, and λ = 0.02 V-1. (a) Determine RS and RD such that IDQ = 0.1 mA and VDSQ = 5 5 V. (b) Find the small-signal transistor parameters. (c) Determine the small-signal voltage gain.