Reference no: EM131154003
Question 1. Consider the example network shown in Figure 1. It is easy to see that the shortest paths from A to all other nodes are: (i) A ↔ B for reaching B, (ii) A ↔ B ↔ C for reaching C (tie broken arbitrarily), (iii) A ↔ D for reaching D, and (iv) A ↔ D ↔ E for reaching E. If you 'join' (think set union) all these edges, you get the shortest path tree (SPT), also shown in Figure 1, with a total cost of 6. Referring to the SPT, node A is known as the root of the tree (we also say that the tree is rooted in A). Of course, this is not the only possible shortest path tree. For example, you can replace the edge B ↔ C with D ↔ C without increasing the cost of the SPT. Coincidentally, the SPT for this network is also a minimum spanning tree (MST). You can verify using Prim's algorithm that the cost of the MST is also 6.
Now consider the network shown in Figure 2.
(a) Using Dijkstra's algorithm, find the shortest paths from node A to all other nodes. Include a table showing the minimum distance vector and the predecessor vector at each iteration, as shown in slide 38 of Chapter 5 notes.
(b) Using the results in (a), sketch the SPT rooted in A. What is the toal cost of the SPT?
(c) Using Prim's algorithm, find and sketch the MST rooted in A. What is the total cost of the MST?
(d) Would the MST change if you were to root it in D (this tree structure would be needed if node D were to broadcast to everybody else)? Irrespective of whether the MST changes or not, sketch the MST rooted in D.
(e) Based on (b) and (c), what can you infer regarding the SPT vis-a-vis the MST? Which tree would node A prefer to use if it wants to broadcast a message to all other nodes in the network?
(f) Suppose node A is the source (or root) and it has the MST pre-computed and stored. Explain how it can quickly construct a multicast tree from the MST if it wants to initiate a multicast session with C and D only. Note that node A is free to use any node it doesn't want to reach (i.e., nodes B and E) purely as a relay node. Sketch the multicast tree rooted in A.
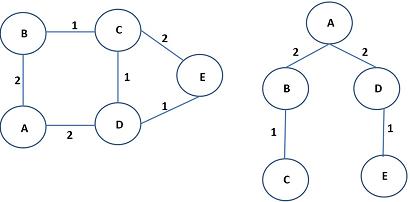
Figure 1: (a) Left: example network for Problem 1. (b) Right: shortest path tree, rooted in
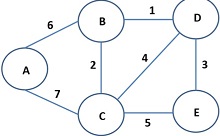
Figure 2: Network for Problem 1. This is the network you should use for answering the questions.
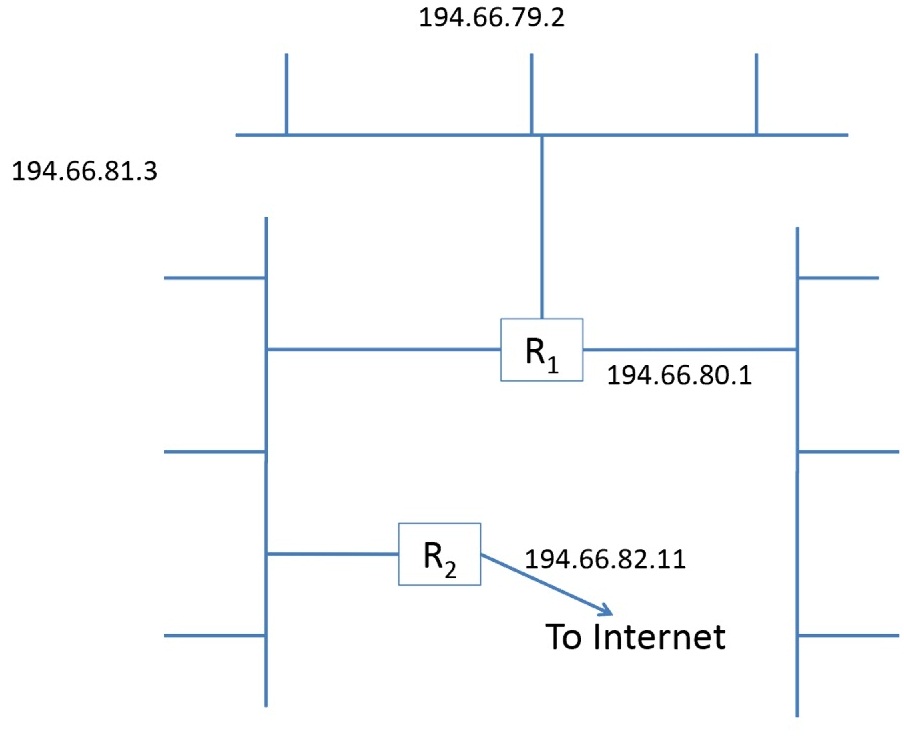
Question 2. Some of the network interfaces in Figure 3 have been assigned IP addresses. R1 and R2 are routers.
(a) Provide suitable IP addresses for the rest of the interfaces. Assume that a class C addressing scheme is used.
(b) Given the addressing scheme in part (a), group all the interfaces into suitable 'IP networks' from an addressing perspective. Then, indicate the IP addresses of each of those networks.
(c) Given the addressing scheme in part (a), determine the routing table of the de-vice/interface with an IP address of 194.66.79.2. You might want to take a look at slide 68 of Chapter 5 notes.
Question 3. Slides 13 and 14 in Chapter notes illustrate through an example how message segmentation can reduce end-to-end delay. In this problem, you are being asked to derive generalized results. Drawing diagrams would help you answer this problem correctly.
One flip side of message segmentation which was ignored in slides 13 and 14 is the effect of overhead bits. In practice, when a message is segmented into several packets, each packet incurs an overhead because some header and trailer bits need to be appended. Let us define the following parameters:
- M = the size of a message (before segmentation) in bits,
- N = the number of packets the message is segmented into, and
- H = the number of overhead bits per message (no segmentation) or per packet (with segmentation).
The actual number of bits transmitted when the message is not segmented is therefore M + H. Conversely, when the message is segmented, the number of bits in each packet is * + H, where we have assumed that * (number of data bits in each packet) is an integer. The total number of bits transmitted is therefore N (1.14 + H) = M + N H.
(a) Calculate the end-to-end delay when the message is sent without segmentation over L hops, the data rate of each hop being R bps. Assume negligible propagation delay over each hop. Your answer should be in terms of M, H, R and L. In the context of slide 13, M = 3 x 106 bits, H = 0 bits, R = 106 bps, L = 3 hops and the end-to-end delay is 9 seconds.
(b) Calculate the end-to-end delay when the message is segmented into N packets and each packet is transmitted over L hops, the data rate of each hop being R bps. Assume negligible propagation delay over each hop. Your answer should be in terms of M, N, H, R and L. In the context of slide 14, M = 3 x 106 bits, N = 3 packets, H = 0 bits, R= 106 bps, L = 3 hops and the end-to-end delay is 5 seconds.
(c) We can now define an end-to-end throughput measure, y (in bps), as follows:
γ = number of data bits delivered/end-to-end delay
where the numerator is M irrespective of message switching or packet switching. Next, define an end-to-end efficiency measure, q, as follows:
η = γ/R.
Write down an expression for η when packet switching is used.
(d) Using your result in part (c), superimpose the plots of i (in %) vs. N for H = 0 and H = 100 bits in one figure (use different line types). Other parameters are as follows: (i) M = 2 Kb, (ii) N = 2 : 2 : 100 in MATLAB notation, (iii) R = 1 Kbps and (iv) L = 10. Be sure to label the axes and provide an appropriate legend. The y-axis should be from 0 to 100. When H = 100, what do you think is the best choice of N from an efficiency standpoint?
(e) Using your result in part (b), plot the end-to-end delay vs. N for H = 100 bits. Other parameters are identical to part (d), i.e., (i) M = 2 Kb, (ii) N = 2 : 2 : 100 in MATLAB notation, (iii) R =1 Kbps and (iv) L = 10. Be sure to label the axes. What do you think is the best choice of N from an end-to-end delay standpoint? Using engineering judgement, what value of N would you choose considering both efficiency and end-to-end delay?