Reference no: EM132581515
Questions -
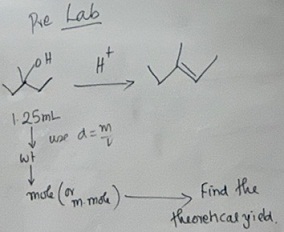
Q1] Find the theoretical yield.
Q2] Determine the pH during the titration of 193 ml of 0.4 M HBr with 193 ml of 0.4 M KOH.
Q3] Choose the option below that is a characteristic of BOTH ketones and aldehydes.
a. They each contain a carbonyl group that exhibits sp2 hybridization around both atoms.
b. They contain a carbonyl group with a nonpolar carbon oxygen bond.
c. The functional group of both of these types of compounds must always be on the end of a carbon chain.
d. They each contain a carbonyl group that may be found in the middle of a carbon chain.
Q4] It has been estimated that >90% of US paper currency is contaminated with illicit drugs. Yikes!
This occurs because most drug exchanges involve cash, possibly with the use of dollar bill counting machines that are prone to contamination. In addition, some drug consumer use dollar bills as a means to ingest drugs.
The illicit drug that is most prevalently found on US currency binds to the green dye on dollar bills. Luckily, mass spectrometry can detect the drug!
The mass spectral data for this drug is shown below. By interpreting the data, identify the drug in Question. (Hint: Using the chemical formulas provided, calculate the molecular weight for each compound and look for "M+1").
1] Heroin 2] Cocaine 3] Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) 4] Tetrahydrocannibinol (THC)
Q5] The gallbladder is an intriguing if often overlooked organ that stores bile for the liver in a variety of vertebrates. A biochemically interesting aspect of the gallbladder is that it is one of the few places in the body that regularly has a basic pH. To study enzymatic processes that occur there, appropriate pH conditions must be replicated. The complicating aspect is that the pH is not uniform throughout the entirety of the gallbladder system, where it can range from pH 7.6 to pH 8.5. Conveniently, the buffer range of the H(Tris)+/Tris conjugate pair overlaps well with this system, having a pKa of 8.02. This pKa is convenient to many biological systems, hence its use as a buffer for many experiments.a)What is the full buffer range of the H(Tris)+/Tris system?b)Describe the preparation of two Tris buffer solutions, one for the high end and one for the low end of the gallbladder pH. Make both buffers to a total buffer concentration of 0.110 M with a volume of 1 liter.
Q6] A balloon filled with air at a pressure of 0.994 atm has a volume of 1.88 L. What will be the volume of the balloon if the pressure is changed to 0.732 atm? Assume that the temperature and the amount of the gas remain constant.
Q7] In lab I used GCMS to analyze a blood sample and now I have to determine the percent ethanol in the sample. I made six different standards. So how do I use this data to determine the percent ethanol? Are there any graphs I need to make and how would I make them? Specifically what would be in each axis and what would be my line equation?
Data:
at retention time = 1.53 minutes for ethanol. Confirmed via GCMS
Concentration (v/v%)/ Trial 1 peak area. /Trial 2 peak area
0.00 /117. /125
0.01 /992626. /1000001
0.02 /2041326. / 2039235
0.05 /5180645. /5179359
0.10. /10188347. /10179225
0.15. /15177192. /15189424
unknown sample. /6343657. /6338241
sample known to be 0. /145. /152
Q8] List five possible water purification processes that are associated with the tertiary treatment of wastewater, including one that removes phosphate ion.