Reference no: EM131281750
Problem 1 - Systematic Treatment of Equilibrium
Given the equilibrium reactions below and relevant constants, calculate the solubility of lithium fluoride at any pH. Plot p[Li+] vs. pH (minimum of 25 points on this plot). Ignore Activities.
LiF ? Li+ + F- Ksp = 1.7 x 10-3
F- + H2O ? HF + OH- Kb = 1.5 x 10-11
LiF(s) LiF(aq) K1 = 0.591
H2O ? H+ + OH- Kw = 1.0 x 10-14
Problem 2 - Diprotic Weak Acids
In Harris, equation 10-19 (fractional dissociation of a weak acid in H2A form) was given. In a similar matter, demonstrate the derivation of equations 10-19, 10-20, and 10-21 (these equation numbers are from the 9th edition of Harris!) INCLUDING ACTIVITIES.
Problem 3 - Systematic Treatment of Equilibrium and Diprotic Weak Acids
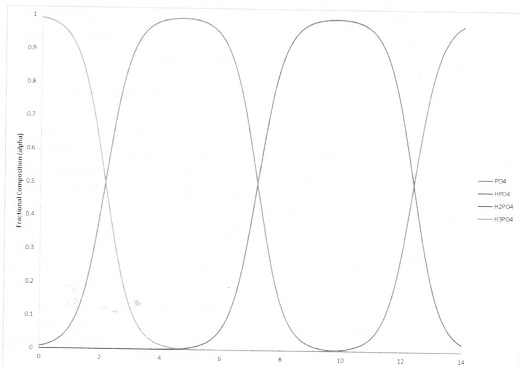
Given the Ka values below, plot mole fraction of each possible carbonate species vs. pH (minimum of 25 points on this plot. It should look similar to the figure below for phosphate) for a solution of carbonic acid with a formal concentration of 0.100 M. Ignore the equilibrium of carbonic acid with CO2 and Ignore Activities.
H2CO3 ? HCO3- + H+ Ka1 = 4.46 x 10-7
HCO3- ? CO32- + H+ Ka2 = 4.69 x 10-11
H2O ? H+ + OH- Kw = 1.0 x 10-14
Problem 4 - Buffers
Using the pKa values in Appendix G and activity coefficients from Table 8-1, calculate the pH of each of the following buffer solutions (a) without activity and (b) with activity.
1. 0.025 M NaHCO3 and 0.0030 M Na2CO3
2. 0.050 M NaHCO3 and 0.015 M Na2CO3
3. 0.0050 M disodium hydrogen citrate and 0.050 M sodium dihydrogen citrate.
4. 0.050 M citric acid and 0.0050 M sodium dihydrogen citrate
5. 0.050 M NaF and 0.040 M HF
Problem 5 - Buffers
For each buffer system from problem #4, calculation the pH of the resultant solution when (a) 15.00 mL of 0.005000 M HCI are added, (b) 15.00 mL of 0.0400) M NaOH is added, and (c) 5.00 mL of 0.02500 M HCl and 8.00 mL of 0.03500 mL of NaOH are added. Assume a 100 mL sample of your buffer, made fresh for each part. Ignore Activities.
Problem 6 - Acid/Base Titration
Plot a titration curve of a 30.00 mL aliquot of 0.05000 M sodium hypochlorite with 0.07250 M HCl. Your plot should include a minimum of 10 points prior to the equivalence point and 10 points after the equivalence point.
Problem 7 - Diprotic Acid/Base Titration
Plot a titration curve of a 25.00 mL aliquot of 0.1000 M diprotic weak acid (pK1 = 2.00, pK2 = 6.50) with 0.05000 M NaOH. Your plot should include a minimum of 10 points in each variable range of the titration curve and both equivalence points. Do NOT calculate the Is' (acid only in solution) point (0.00 mL NaOH added). This plot has the same issue as the one in class.
Problem 8 - Acid/Base Titration
When titrating a weak, unknown base with HC1, you performed the following series of standardizations. Initially, you made a solution of approximately 0.1000 M NaOH and standardized this solution with KHP. You then diluted stock HCl to make a solution of approximately 0.1000 M. In an acid/base titration, you took a 25.00 mL aliquot of your HCI solution and titrated it vAh the standardized NaOH. Due to a bad day in lab, this standardization took more than 4 trials. Throw out any outliers. Finally, a pH titration was performed with a 25.00 mL aliquot of your unknown weak basenThis solution was made by dissolving 3.4581 grams of your unknown in 250.0 mL of water. Determine the pKb of your weak base (Don't worry about error in this value!). In addition; determine the molecular mass of the base and the error in this value. This error will be slightly flawed, you only did ONE titration of your unknoWics-o-illai your error will come from the standardizations. Data will be provided in an Excel file emailed from the Instructor after this exam has been assigned.
Attachment:- q.xlsx
|
Drive the general format of the transient state
: Drive the general format of the transient state temperature profile (i.e. use symbols, not numbers) along the radius of the bar and Plot the cross sectional temperature profile of the cylinder
|
|
Calculate the pv of the individual cash flows
: Calculate the PV of the individual cash flows using the algebraic method. The value in the yellow cell will calculate on its own. Treat each valuein row 7 as if it was a single cash flow.
|
|
Write essay on in dreams surrealism and the human condition
: Write an essay about "In Dreams: Surrealism and the Human Condition". Focus your attention on the Surrealists-an early 20th-century group of artists who created fantastical, bizarre, and irrational art.
|
|
Determine the conditional probability of sending symbol
: Determine the conditional probability of sending symbol A0 given that symbol B0 was received posteriori probabilities:
|
|
Determine the molecular mass of the base
: determine the molecular mass of the base and the error in this value. This error will be slightly flawed, you only did ONE titration of your unknoWics-o-illai your error will come from the standardizations.
|
|
Determining the moral hazard
: "Moral hazard" is a term often used in the context of peoples' behavior once they have insurance. Szuchman and Anderson explore the idea of moral hazard in personal relationships. How would you define moral hazard? Provide an example of moral h..
|
|
Investments in the economy
: Beth plans to manage the business, which means that she will have to quit her current job. Suppose that the interest rate (or rate of return) on investments in the economy is 6%.
|
|
State the name of exhibition in which the work was displayed
: State the title, artist, date, dimensions, and medium of the work of art. State the name of the exhibition in which the work was displayed. Introduce the reader to the work of art by writing a brief, overall description of it.
|
|
Define the in phase component and the quadrature component
: Define the in-phase component and the quadrature component HQ(f) the frequency response of the complex low-pass equivalent model of a band-pass system of impulse response h(t).
|