Reference no: EM13867070
Problem 1: A 10 m3 rigid tank has two sections separated by a membrane. Each section contains nitrogen gas. The nitrogen gas in section A has initial density of 1.6 kg/m3 and the nitrogen gas in section B has a mass of 6 kg. At a certain time, the membrane is punctured. The final density of the nitrogen gas in the tank is found to be 1.8 kg/m3.
Determine the initial density (kg/m3) of nitrogen gas that existed in section B.
Problem 2: A diver is snorkeling 10 feet under water in coral reefs off the east coast of Florida. At this location, the water density is 62 lbm/ft3, the atmospheric pressure is 14.7 psia, and local acceleration due to gravity is 32 ft/s2.
The pressure on the ear-drums of the diver is:
(a) 616.65 lbf/ft2 (absolute)
(b) 616.65 lbf/ft2 (gauge)
(c) 4.28 psia
(d) 4.28 psig
(e) 18.98 psia
(f) 18.98 psig
Note: You must show all work to get credit.
Problem 3: Fresh water and sea water flowing in parallel horizontal pipelines are connected to each other by a double U-tube manometer, as shown in the figure. Assume that the density sea water is 1035 kg/m3.
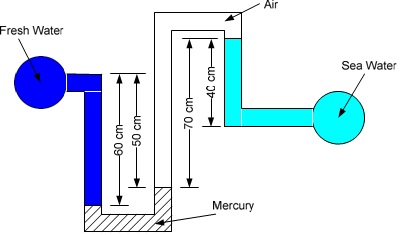
(a) Determine the pressure difference (kPa) between the two pipelines.
(b) Can the air column be ignored in your analysis?
(c) If the air is replaced with oil of specific gravity 0.72, then what is the pressure difference (kPa) between the two pipelines? Can the oil column be neglected?
Problem 4: A damaged 1200-kg car is being towed by a truck. Assume that friction, air drag, and rolling resistance are negligibly small.
(a) Determine the power required (kW) for constant velocity on a level road.
(b) How much power is required (kW) for constant velocity of 50 km/hr on an uphill road at 30° with respect to horizontal?
(c) Calculate the power required (kW) when accelerating on a level road from rest to 90 km/hr in 12 seconds.
Problem 5:
A 25-kg piston in the piston-cylinder system shown in Figure SP 5 is initially at rest on the bottom stops and the gas inside the cylinder has an initial pressure of 70 kPa and an initial temperature of 10oC (State 1). The gas inside the cylinder is heated until the piston just leaves the bottom stops (State 2). Additional heat is added to the cylinder until the piston just hits the top stops (State 3) The pressure surrounding the cylinder is 101 kPa and the volume of the stops and the piston can be neglected. The gas inside the cylinder can be considered an ideal gas, pV = mRT, where p = pressure, V = volume, m = mass of the gas, R is a constant and T = absolute temperature of the gas.
(a) Calculate the work in going from State 1 to State 2, in kJ.
(b) Find the work in going from State 2 to State 3, in kJ.
(c) Determine the temperature at State 2, in K.
(d) Obtain the temperature at State 3, in K.
(e) Draw the process on a p-V diagram.
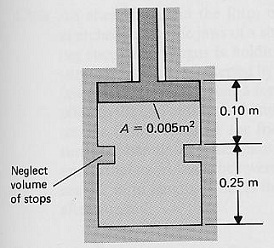
Problem 6:
Hydrogen gas is contained in a vertical piston-cylinder device at 14.7 psia and 15 ft3. At this state, a linear spring with a spring constant of 12,000 lbf/ft touches the top of the piston but exerts no force on it. The cross-sectional area of the piston is 2.5 ft2. Heat transfer occurs to hydrogen gas, pushing the piston upwards against the spring, and the hydrogen gas expands until its volume doubles.
(a) Show the process on a p-V diagram.
(b) Determine final pressure (psia) of the hydrogen gas.
(c) What is the total work done (Btu) during the expansion process?
(d) What fraction of the above work (Btu) is done against the spring?
Problem 7:
A piston-cylinder device initially contains 0.6 m3 of water vapor at 250 kPa. The specific volume and specific internal energy of water vapor at the initial condition are 0.72 m3/kg and 2537 kJ/kg, respectively. At this condition, the piston is resting on a set of stops and the mass of piston is such that a pressure of 300 kPa is required to move it. Heat transfer is allowed to occur slowly so that the water vapor volume doubles. The specific internal energy at the final condition is 3410 kJ/kg.
(a) Show the entire process on a P-V diagram.
(b) What is the work done (kJ) during the process?
(c) Determine the total amount of heat transfer (kJ) during the process.