Reference no: EM131213880
Preamble
An existing mining company wants to a build a dam for their processing facilities and is seeking a suitable site that will ensure a permanent water supply of about 10000 ML. Their choice of locations is limited to roughly a 28km x 19km region, the visible area of the regional Geology Map.
A) Regional Geology Task: You are required to establish a geological column and determine the geology history of the region in order to help identify 3 potential dam sites to ensure a permanent water supply (Regional Geology Map; Topographic Map; Appendix 1). Therefore, a brief summary (2 pages) of the geological history of the region should be discussed, including a note on the tectonic setting. The brief summary includes a geological column that has the oldest unit at the base and the youngest at the top. It may be helpful to also identify structural features, such as the thrust fault on the western side, within this column.
Factors that should be identified within the geological history include aspects such as unconformities, igneous events, deformational events and metamorphic grade. Faults should be identified along with the movement along these faults. The plate tectonic settings need to be identified, where possible, and placed within the geological history. Evidence needs to be included regarding the principle of superposition for the geological history and appendices may be used.
B) Cross Sections:
Two cross sections, with no vertical exaggeration, need to be constructed that best highlighted the geology of the region, particularly focusing on where the potential dam sites could be located (1 page):
1. An initial cross section needs to be constructed running east - west.
2. A second cross section running north - south should be constructed.
C) Potential Dam Sites:
Identify three potential dam sites along any of the water ways found within the map for a dam of approximately 10000 ML. Each potential dam site should be on a different geological unit to ensure that a range of geological factors are considered and the best potential site is chosen. An analysis of each site should be conducted and a comparison of the various sites should detail the strengths and weaknesses of each site.
There needs to be a final selection of the best dam site based on an evaluation of the three selected sites that considers all of the data presented. Further site investigation recommendations to verify the viability of the site need to be included (1 page) prior to seeking tenders to actually construct the dam.CIV2403 - Geology and Geomechanics
Question 1:
A long sheetpile wall is embedded 3 m into a permeable soil, as shown in Fig 1. Dimensions are in meters. The soil is silty sand. A falling head test was performed to find the hydraulic conductivity of the soil. In this test, the head in the standpipe dropped from 450 mm to 270 mm in 120 sec. The soil sample is 200 mm long and has a diameter of 40 mm. The diameter of the standpipe is 7.1 mm.
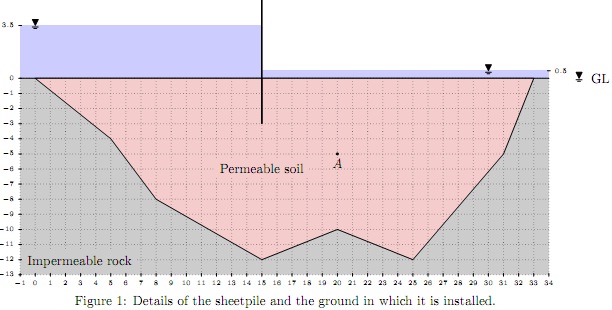
1. Determine the hydraulic conductivity of the soil in mm /min (per meter run).
2. Produce a flow net on the provided sketch sheet (Fig 2).
3. Calculate the seepage rate in lit /min (per meter run).
4. Calculate the porewater pressure at point A (the downstream water level is at +0.5 m).
5. Assuming that we are going to use one pump in every 25 m along the sheet pile in downstream side, determine the capacity of the pumps in lit/min to dry the downstream side (keep water level at the ground level).
Question S2
In order to reduce the seepage rate in the previous question, a 6 m-wide impermeable block is installed next to the sheet pile as shown in Fig. 3. Numerical analysis is performed to find the head loss along the impermeable block, and equipotential lines are drawn in Fig. 3.
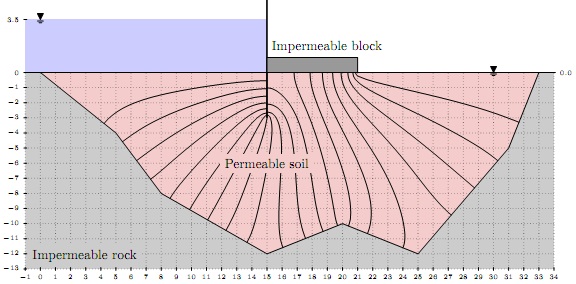
1. Complete the flow net using the provided sketch sheet (Fig 4).
2. Assuming that we are going to use one pump in every 25 m along the sheet pile in downstream side, determine the capacity of the pumps in lit/min to keep the downstream side dry.
3. Compare the result in question S2.2 with that of question S1.5 and write a brief discussion.
4. Determine the required mass for the impermeable block in kg/m in order to achieve a factor of safety of 3 (FS = 3) against uplifting. Factor of safety against uplifting is defined as the ratio between the weight of the block (W ) to the uplifting force acting on them (F ), i.e. FS = W.
Attachment:- Assignment Topography.rar