Reference no: EM132536542
Problem 1: A method used for data transmission that uses aknowledgements and timeouts to achieve reliable data transmission.
Select one:
a. Automatic Repeat Request
b. Turbo coding
c. All of these options
Problem 2: A process by which cells in areas of high usage can be divided into smaller cells.
Select one:
a. Cell sectoring
b. Cell splitting
c. None of these options
Problem 3: A ___ is a network of devices connected using Bluetooth technology.
Select one:
a. Piconet
b. Scatternets
c. Bluetooth
d. None of these options
Problem 4: Adjacent cells assigned different frequencies to avoid ____.
Select one:
a. Interference
b. Frequency use
c. None of these options
Problem 5: Cells are divided into a number of wedge-shaped sectors, each with their own set of channels
Select one:
a. Cell sectoring
b. Cell splitting
c. None of these options
Problem 6: Critical technology used for broadband wireless access is ____
Select one:
a. WiFi
b. WiMAX
c. Bluetooth
Problem 7: Determine the amplitude, frequency, time period and phase from the below equation.
s(t)=3sin(400Πt+3Π/2)
Select one:
a. 3. 200, and 3Π/2
b. 3. 200Π. and 3Π/2
c. 3. 400Π. and Π/2
d. 3, 400. and Π.
Problem 8: Determine the equation for the waveform with Amplitude A=4, frequency f= 150 Hz & Phase angle = 90°
Select one:
a. S(t) = 4 sin (300Πt + Π/2)
b. 5(t) = 4 sin(180Πt + 90)
c. 5(t) = 4 sin(150t+ Π/2)
d. S(t) = 4 sin(150t+Π)
Problem 9: Find the binary data stream from the BFSK waveform. ( consider one bit = 3 cycles)
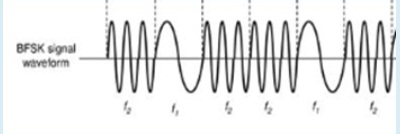
Select one:
a. 100110
b. 101101
c. 110111
d. 111011
Problem 10: Find the binary data stream from the BFSK waveform.
Select one:
a. 10100110
b. 10010110
c. 11001001
d. 10010001
Problem 11: Find the equation for the following waveform.
Select one:
a. Sin(t+2Π)
b. Sin(t)
c. Sin(t+Π)
d. Sin(2t+2Π)
Problem 12: Find the modulation scheme from the following transmitted signal:
s(t) = 5 cos(2Πf1t, binary 0
s(t) = 5 cos(2Πf2t, binary 1
Select one:
a. BFSK
b. MFSK
c. BPSK
d. DPSK
Problem 13: Function of MAC layer includes ____
Select one:
a. Assemble data into frame with address &: error detection fields.
b. Disassemble frame and eprform address recognition
c. All of these options
Problem 14: In this technique entire band of frequencies is divided into multiple RF channels ______
Select one:
a. FDMA
b. TDMA
c. None of these options
Problem 15: In transport layer. application layer data has been converted into ______
Select one:
a. sockets
b. segments
c. packets
d. datagrams
Problem 16: It connects calls between mobile unit and BS.
Select one:
a. MTS0
b. Base station
c. None of these options
Problem 17: It is used to transfer data between station on IEEE 802.11 LAN and station on integrated IEEE 802.x LAN
Select one:
a. Distribution service
b. Integration service
c. None of these options
Problem 18: It provides an interface to higher layers and perform flow control and error control.
Select one:
a. MAC Layer
b. LLC Layer
c. IP Layer
d. None of these options
Problem 19: It provides link between cellular network and public switched telecommunications networks.
Select one:
a. Network subsystem
b. BSS (1)
c. BTS (1)
d. None of these options
Problem 20: Signal propagation effects may disrupt the signal and cause errors and it is called
Select one:
a. Signal strength
b. Fading
c. None of these options
Problem 21: Simplest form of error detecting code is called
Select one:
a. Parity bit
b. Check bit
c. All of these options
Problem 22: Station moving from BSS in one ESS to BSS within another ESS.
Select one:
a. No transition
b. BSS transition
c. ESS transition
d. None of these options
Problem 23: THE concept of using N oscillators for N different subcarrier frequencies is called ____
Select one:
a. DFT
b. IFFT
c. FFT
d. OFDM
Problem 24: The functional areas covered by MAC layer includes _____
Select one:
a. Reliable data delivery
b. Access control
c. Security
Q d. All ofthese options
Problem 25: The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is a communication protocol for electronic mail transmission. This protocol belongs to _____ layer in TCP/IP protocol suite.
Select one:
a. Network layer
b. Data link layer
c. Application layer
d. Transport layer
Problem 26: The _____ assigns a Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity (TMSI) and maintains the information about subscribers currently and physically located in the cellular region.
Select one:
a. VLR
b. HLR
c. EIR
d. None of these options
Problem 27: The ______ controls the synchronization, flow control, and error-checking functions.
Select one:
a. Medium access control layer
b. Transport layer
c. Physical layer
d. Logical link control layer
Problem 28: What is the period (wavelength) for the function y = -5cos(3t + 2Π)?
Select one:
a. T= 3
b. T= 1/3
c. T= 3/2Π
d. T= 2Π/3
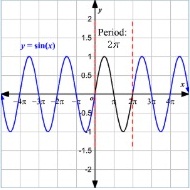
Problem 29: What is the period (wavelength) for the waveform shown in blue?
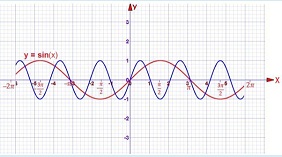
Select one:
a. Π/2
b. 2
c. 2/Π
d. 2Π
Problem 30: _______ is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC) for use as a network address in communications within a network segment.
Select one:
a. MAC address
b. IP address
c. Transport port address
d. Port number
Problem 31: You are communicating between two satellites. The transmission obeys the free space law. The signal is too weak. Your vendor offers you two options. The vendor can use a higher frequency which will be 6 times current frequency OR can 6 times the effective area of both of the antennas. Which will offer you more received power or will both offer the same improvement, all other factors remaining equal? How much improvement in the received power do you obtain from the best option?
Pt/Pr = (cd)2/f2ArAt
c = speed of light = 3 x 108 m/sec
d = propagation distance between antennas
Pr = signal power at the receiving antenna
Pt = signal power at the transmitting antenna
Ar = effective area of the receiving antenna
At = effective area of the transmitting antenna
ENTER YOUR ANSWER AS A WHOLE NUMBER: Now much improvement in the received power do you obtain from the best option? (Example: if it increases as double or two times the received power, then enter the answer as 2).
Answer:
Problem 32: A Wireless Communication channel has a loss of 30 dB. At the transmission end the signal power is measured as 0.5 W. and the receiving end output noise level is measured as 5 p.W. Using this information, calculate the output signal-to-noise ratio at the receiving end.
Note: Enter your answer in 2 decimal points only.
Answer:
Problem 33: Calculate the attenuation loss (in dB) of a communication link operating in free space at a frequency of 3.4 GHz over a distance of 13.0 Km? Hint use the equation:
L = 10 log (4Πd/λ)2
Note: Enter your answer with two decimal points
Problem 34: What is the maximum distance (i.e. distance to radio horizon) for a terrestrial microwave wireless link where the sending antenna is on a hilltop 204 meters above sea level and the receiver is a mobile car radio with antenna 9 meters above sea level?
Note Enter your answer in 2 decimal places. Answer:
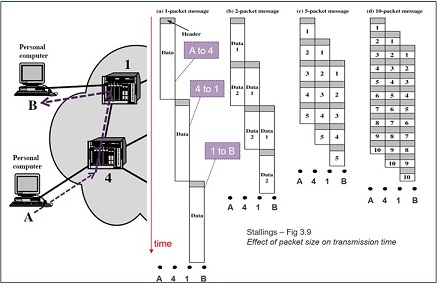
Problem 35: In packet switching. line efficiency varies for different packets sizes. As seen in the figure below a single node-to-node link can be dynamically shared by many packets over time. Use the scenarios in figure (a), (b), (c) & (d) below to calculate the most efficient octet-times. Assume that the standard packet size is 450 octets (un-fragmented packet) and the header size is 47 octets. Enter the result in whole number.