Reference no: EM131092396
Classifying types of adjustments
Classify the following items as (a) prepaid expense, (b) unearned revenue, (c) accrued revenue, or (d) accrued expense.
1. A three-year premium paid on a fire insurance policy...
2. Fees earned but not yet received.
3. Fees received but not yet earned.
4. Salary owed but not yet paid.
5. Subscriptions received in advance by a magazine publisher.
6. Supplies on hand.
7. Taxes owed but payable in the following period.
8. Utilities owed but not yet paid.
Adjusting entries
Econo Company, an electronics repair store, prepared the unadjusted trial balance shown below at the end of its first year of operations.
|
Econo Company
|
|
Unadjusted Trial Balance
|
|
April 30, 2012
|
|
Debit Credit
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash ........................................................................................ 13,800
|
|
Accounts Receivable................................................................ 90,000
|
|
Supplies.................................................................................... 21,600
|
|
Equipment.............................................................................. 454,800
|
|
Accounts Payable...................................................................................................... 21,000
|
|
Unearned Fees .......................................................................................................... 24,000
|
|
Randy Huntsinger, Capital....................................................................................... 312,000
|
|
Randy Huntsinger, Drawing...................................................................................... 18,000
|
|
Fees Earned............................................................................................................. 543,000
|
|
Wages Expense...................................................................... 126,000
|
|
Rent Expense........................................................................... 96,000
|
|
Utilities Expense....................................................................... 69,000
|
|
Miscellaneous Expense............................................................ 10,800
|
|
|
For preparing the adjusting entries, the following data were assembled:
a. Fees earned but unbilled on April 30 were $10,000.
b. Supplies on hand on April 30 were $8,150.
c. Depreciation of equipment was estimated to be $13,800 for the year.
d. The balance in unearned fees represented the April 1 receipt in advance for services to be provided. Only $19,000 of the services was provided between April 1 and April 30.
e. Unpaid wages accrued on April 30 were $1,770.
Instructions
1. Journalize the adjusting entries necessary on April 30, 2012.
2. Determine the revenues, expenses, and net income of Econo Company before the adjusting entries.
3. Determine the revenues, expense, and net income of Econo Company after the adjusting entries.
4. Determine the effect on Randy Huntsinger, Capital of the adjusting entries.
Adjusting entries and errors
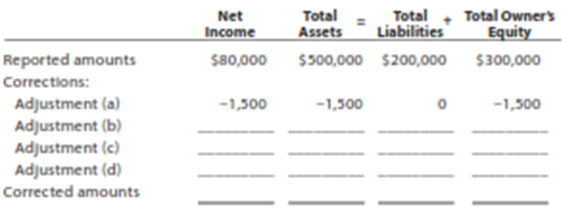
At the end of June, the first month of operations, the following selected data were taken from the financial statements of Beth Cato, an attorney:
Net income for June $ 80,000Total assets at June 30 500,000Total liabilities at June 30 200,000Total owner's equity at June 30 300,000
In preparing the financial statements, adjustments for the following data were overlooked:
a. Supplies used during June, $1,500.
b. Unbilled fees earned at June 30, $18,000.
c. Depreciation of equipment for June, $3,000.
d. Accrued wages at June 30, $1,200.
Instructions
1. Journalize the entries to record the omitted adjustments.
2. Determine the correct amount of net income for June and the total assets, liabilities, and owner's equity at June 30. In addition to indicating the corrected amounts, indicatethe effect of each omitted adjustment by setting up and completing a columnar tablesimilar to the following. Adjustment (a) is presented as an example
|
Constant factor in both in our personal and work lives
: Change is a constant factor in both in our personal and work lives. There seems to be resistance to change whether the change will be good or bad. Why do people resist change?
|
|
When designing an organizational structure
: There are many elements to consider when designing an organizational structure. Pick one of the six key elements and discussing why that element is important to the overall success of the design.
|
|
During the history of social science research
: During the history of social science research, according to Kristen Luker , date analysis has changed. How it has changed?
|
|
What is her effective annual internal rate of return
: Katherine Lim purchased a condominium for $50, 000 in 1987. Her down payment was $20, 000. She financed the remaining amount as a $30, 000, 30-year mortgage at 7%, compounded monthly. Her monthly payments are $200. It is now 2007 (20 years later) and..
|
|
Determine the correct amount of net income for june and the
: Econo Company, an electronics repair store, prepared the unadjusted trial balance shown below at the end of its first year of operations. Determine the correct amount of net income for June and the total assets, liabilities, and owner's equity at Jun..
|
|
Deficits and investment
: Deficits and investment: Suppose the government decides to reduce taxes today by 1% of GDP, financed by higher borrowing, with the borrowing to be repaid 10 years from now with higher taxes. Discuss the various arguments about what effect this will h..
|
|
Consider the model of land assembly
: Consider the model of land assembly (under the topic Eminent Domain). Suppose, at each stage of negotiation between the property owners and the buyer, the owner can extract α fraction of the net total surplus/gains from transaction at hand. (Note: th..
|
|
Major manufacturer of the world consumer goods
: For decades the U.S. has been a major manufacturer of the World consumer goods. Nowadays, many items we buy from the United States are made in China. What are the economic implications of this practice to both countries?
|
|
The economy is operating above full employment
: Draw the appropriate graph assuming that the economy is operating above full employment. Assuming the aggregate demand excess is $1328B and MPC is .87, calculate the amount of desired fiscal restraint. Which type of government intervention (from scen..
|