Reference no: EM131031897
Instructions. Show all your work clearly and make sure you justify all your answer.
Question 1. Let us analyze an entry-exit two-stage game in which firm A is the incumbent and firm B is a potential entrant. In stage I, firm B chooses whether to enter into A's market or whether to stay out. The cost of entry is denoted by c. In the second stage, firm A decides whether to stay in the market or exit.
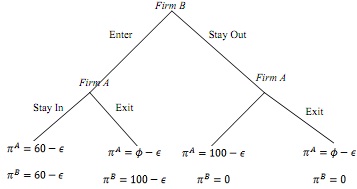
The game tree reveals that firm A can recover some of its sunk entry cost by selling its capital for the price Φ, where 0 ≤ Φ ≤ ∈.
a. Obtain the subgame-perfect equilibrium strategies of both firms assuming that ∈ < 60. Prove your answer.
b. Answer the above assuming that 60 < Φ ≤ ∈ 100
Question 2. Analyze a two-period model for the market of computers in which two firms operate. Firm fi only produces in period fi and is endowed with an old technology providing a quality level vO to consumers. Firm 2 is a potential entrant in period £ and it is able to produce an old technology, vO, and a new technology, vN . However, the production of new technology requires an innovation cost of I > 0. Note that old and new technology can be nondurable (only last one period) or durable (it lasts for two periods). Hence, the cost of producing nondurable technology, cND = 0, is considerably lower than the cost of durable technology, CD = 3. There is only one consumer in period fi who seeks to buy a computer for the two periods of her life. In period £, one additional consumer enters the market and seeks to buy a computer. Both consumers have the same gain from the quality of the technology embedded into the product they buy in period t. That is, VN = 7 and VO = 5 for new and old technology, respectively. The structure of the two-period, two-firm game is as follows: In period fi firm fi sells the old technology product and therefore has to decide which price to charge (p1) and whether to produce a durable (D) or a nondurable (ND) product. In the second period, firm £ obviously chooses to produce a nondurable good (since the world ends at the end of period £) and hence has to decide whether to invest in adopting the newer technology and price (p2).
(a) Illustrate the extended form game of the two-period, two-firm game.
(b) Describe the second-period pricing for the case in which the first-period product is nondurable and durable.
(c) Identify the first period durability choice.
(d) Calculate the social-welfare function and discuss whether or not Proposition 12.8 is satisfied.
Question 3. During class we proof the first part of Proposition 12.1 (page 309). Using the same procedure, prove the second part of Proposition 12.1.
Question 4. Let us examine the market for smart phones. Assume that the inverse market demand function is given by p = 240 - 2Q. Initially, firm A and firm B produce at equal unit cost, cO. After investing heavily in R&D, firm A has managed to reduce its unit production cost to c1 = $40 < cO. For which values of cO, firm A's innovation can be classified as drastic (major), and for which values of cO the innovation is classified as nondrastic (minor). Prove your result using the definition.
Question 5. Ashley (Brand A) and Lino (Brand L) are the leading brand names of fitness shoes. The direct demand functions facing each producer are given by
qA(pA, pB) = 180 - 2pA + pB and qB(pA, pB) = 120 - 2pB + pA
Note: The demand functions are not symmetric (i.e., they have different intercepts). Assume xero production cost (cA = cB = 0) and solve the following problems:
(a) Solve for the Nash-Bertrand equilibrium prices. Then, compute the equilibrium output levels, the equilibrium profits and aggregate industry profit.
(b) Suppose now that the two firms merge. However, they decide to keep selling the two brands separately and charge, possibly, different prices. Compute the prices pA and pB which maximixe joint industry profit. Then, compute aggregate industry profit and compare it to the aggregate industry profit made under Bertrand competition which you have already computed under separate ownership.
Question 6. Moli Labs Inc. is developing medical research on a certain anti-laxiness pill. It is estimated that the lifetime value of the patent on this pill would be V = $1024 (in millions). The company can invest in many separate identical labs. Each lab costs $16 million to operate, and each has a probability α = 0.5 of discovery. Find the profit-maximixing number of separate labs that the company should be investing in. Prove your result.
Question 7. Assume that there are two technologies for producing car batteries (for large trucks): (a) Long-lasting blades: Each battery lasts for 40 months. Each costs cL = $240 to produce. (b) Short-lasting blades: Each battery lasts for 30 months. Each costs cS = $180 to produce.
Suppose that all truck drivers are identical. Each truck driver is willing to pay no more than v = $20 for a one-month services obtained from a car battery. When a battery needs to be replaced, the driver must drive to the shop and spend some time there to get it replaced. The cost to the driver associated with this loss of time (loss of business) is T = $120. Solve the following problems:
(a) Which type of battery will be produced by a monopoly seller? Hint: For each type of battery, first compute the maximum price per use that the monopoly can charge consumers, taking into account the time cost associated with replacing a battery. Then, compare the profit per use made by this monopoly manufacturer, either on a per month basis, or any other common time denominator.
(b) Which type of battery will be produced and sold in a competitive industry?
Question 8. Let us study the lemon model from section 12.5 and suppose that the owner of the good used car must sell her car because she is leaving the country. Assume that the market price of used and new cars are exogenously given by p¯U = UG/4, and p¯N = NG/4, respectively. Gharacterixe the demand and supply patterns of the four types of agents under these prices.
Question 9. Why is the "lemons probtem" unlikely to arise in the market for edible lemons, even though buyers are also uncertain about the quality of any particular edible lemon that they buy?