Reference no: EM132325386
Assessment Task 1
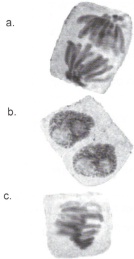
1. Identify the stages of mitosis
2. A fat present in a vegetable oil has the structure shown below:
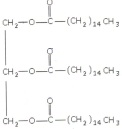
a) Circle an ester functional group.
b) Is this fat saturated or unsaturated? Explain.
3. Draw a line to match the term and its definition:
| Alleles |
Alleles paired together that are different |
| Dominant |
An allele that is masked by another is |
| Genotype |
An organism's expressed physical trait |
| Heterozygous |
Characteristics passed onto offspring |
| Homozygous |
Different forms of a gene for any given trait |
| Phenotype |
The genetic make-up of an organism |
| Recessive |
Identical alleles |
| Traits |
One allele masks the presence of another |
4. The structure of lactose is shown below. Lactose undergoes hydrolysis in the digestion process.
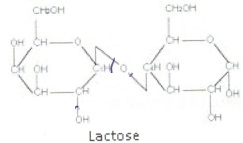
a) What is meant by hydrolysis?
b) Circle a hydroxyl group and a glycosidic link in the molecule
c) Draw the structures of the hydrolysis products.
5. Explain what is meant by the primary, secondary and tertiary structures of proteins.
Clearly outline the bonding type involved at each level.
Use labeled diagrams.
6. Circle the peptide linkages in the part of the protein chain shown below.
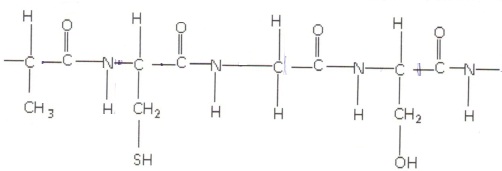
Write the formulas of the amino acids that made up the above part of the chain and identify them.
7. What two functional groups are present in all amino acids?
8. A segment of DNA includes the base sequence GATTATCAA.
List the base sequence on the complementary strand of the molecule.
9. Explain the main function of the following types of molecules:
Carbohydrate:
10. Describe the process of translation.
Include diagrams
11. Explain the biological role of each of the following ions:
Ion Biological Role
Calcium
Chloride
Iron
Magnesium
Phosphate
Potassium
Sodium
12. The following is a pedigree of a sex-linked recessive trait haemophilla.
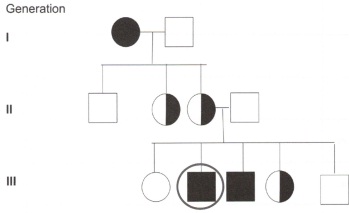
What is the chances of the circled person having children that are haemophiic?
13. Round seeds are dominant over wrinkled seeds. A pure round seed and pure wrinkled seed are crossed. Draw punnet squares to determine the traits of the F2 generation.
14. Using diagram, describe the events that occur during meiosis.
15. What is meant by the term karyotyping?
16. List three ways the generation of waste can be minimised in a biological testing laboratory
17. Why is there an importance for confidentiality when working in a biological testing laboratory?
Assessment Task 2
1. There are 160 bacteria per 500mL of water. From this, how many bacteria would you estimate to be in 1 L? (Estimate do not calculate)
2. A water laboratory technician was performing a total suspended solids test. The filter paper was weighed before use. 1L of water was filtered through the filter paper. The filter paper was air dried and then re-weighed. Which will be heavier, the filter paper before the water was filtered, or the filter paper after filtration.
3. According to Beer's law, concentration and absorbance are directly proportional. As such if a technician got the following results, what would you expect the absorbance to be for the 0.24mg/dL7
| Conc mg/dl |
Absorbance |
| 0 |
0 |
| 0.04 |
0.069 |
| 0.08 |
0.145 |
| 0.16 |
0.296 |
| 0.2 |
0.379 |
| 0.24 |
|
4. According to Beer's law, concentration and absorbance are directly proportional. As such if a technician got the following results, which of the following results is clearly not correct?
Conc mg/d Acetylsalicylic Acid
0 0
100 0.096
200 0.186
300 0.364
400 0.370
5. Correct any mistakes in the reported results using the correct enterprise procedure
| Sample |
Instrument Reading |
| 201605038 |
20.3 |
| 201605039 |
76 |
| 201605045 |
0.1 |
| 201605068 |
64.5 |
| 201605089 |
Fe present |
| Sample |
Reported Result |
| 201605038 |
203 |
| 201605039 |
76 |
| 201605045 |
1 |
| 201605068 |
64.5 |
| 201605089 |
Ge present |
6. A laboratory technician needs to dispense 0.625 mL of reagent using a micropipette. How many pL would he set the micropipette to?
7. The lab assistant needs to weigh out 250.0 mg of a sample, the balance only weighs in grams. How many grams should she weigh out of the sample?
8. Complete the following units of measurement table (use scientific notation when necessary):
| kg |
g |
mg |
| 5.9 |
5900 |
5900000 |
|
6.8 |
|
|
|
790 |
| 1.5 |
|
|
|
2.75 |
|
|
|
1050 |
9. How many significant figures are expressed in the following?
1. 24.5mL
2. 200. g sodium chloride
3. 0.0040mm wire
10. Round off each of the following numbers to three significant figures:
1.2983
2.0.00457
3.1.009
11. Fill in the following table:
| Fixed Notation |
Scientific Notation |
| 9 608 |
|
|
1.315 x 104 |
| 0.00005629 |
|
|
3.14 x 10-6 |
|
|
12. A 12.5% w/v sodium hypochlorite was diluted to be a 1.25% w/v concentration. What is the new concentration in %v/v?
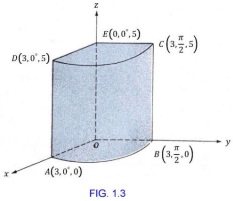
13. Calculate the area of the top of a can using the formula Πr2 if the radius (r) is 3.00cm
14. Calculate the volume of the can in question 13. if the height of the can is 13.0cm
15. A microbiology lab technician takes a 1mL sample of milk and performs a serial dilution as shown.
A 1 mL sample of the 10-3 dilution was dispensed into each of two sterile petri dishes. Molten agar was added and mixed with the diluted sample. Once set, the plate was incubated upside down for 24 hours at 37°C. The technician then counted the number of colonies on each plate and averaged the number, 126 colonies was the resulting answer. Calculate the amount of colonies in the original 1 mL sample.
16. In a haematology laboratory a white blood cell, red blood cell or platelet can be performed manually using a neubauer haemocytometer under a microscope.
The neubauer haemocytometer consists of two identical counting chambers. Each chamber contains an etched grid constructed to have a total surface area of 9mm2.
The count from each chamber should be within 10% of each other to ensure an accurate count.
A dilution of yeast cells is used and a small amount of diluted sample is allowed to flow between the coverslip and haemocytometer chamber.
The size of each large cell in the grid is 1mm x 1mm.
The distance between the coverslip and the surface of the haemocytometer is 0.1mm.
After counting the number of cells in both chambers the number of cells per mL of suspension needs to be calculated:
• Overall calculation:
Cell count/L = Average cell count x 1/volume x dilution factor x 103
Calculate the total cell count/mL if:
The cell suspension was diluted 1 in 2 with trypan blue. Trypan blue is taken up by
dead cells only, viable cells appear colourless as they do not take up the trypan blue.
125 cells on average per large cell in grid 1 and 131 cells on average per large cell in grid 2.
17. Calculate the viable cell count/mL if:
Of the cells in grid 1 of question 16, 23 were blue.
Of the cells in grid 2 of question 16, 26 were blue.
18. What amounts are required to make 250.0mL of a 6.00% (w/v) sodium hydroxide (NaOH) aqueous solution?
19. There are 25g in 300.0mL of solution. What is its percent concentration? Is this w/w, w/v or v/v concentration?
20. How much 20% (w/v) solution can be made from 50g sodium chloride (NaCI)?
21. A laboratory technician needs to make 500.0mL of the following chromatography solvent. How many millilitres of each will be required:
Butanol : Acetic Acid : Distilled water (3 : 5 : 2)
22. A solution of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) contains 3.50g per litre.
How many litres of the solution contain 1.50g of CaCO3?
How many grams of CaCO3 are in 5.00mL of this solution?
23. How much 20% (w/v) solution can be made from 50g sodium chloride (NaCI)?
24. A laboratory technician needs to make 500.0mL of the following chromatography solvent. How many millilitres of each will be required:
Butanol : Acetic Acid : Distilled water (3 : 5 : 2)
25. A solution of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) contains 3.50g per litre.
a. How many litres of the solution contain 1.50g of CaCO3?
b How many grams of CaCO3 are in 5.00mL of this solution?
26. A laboratory technician separated an unknown mixture into its components. The original sample was 3.600g. The final weights of the components were as follows:
| Component |
Weight |
| Sodium Chloride |
0.600g |
| Ammonium Chloride |
1.200g |
| Sand |
1.800g |
Calculate the percentage, proportion. fraction and ratio for each and fill in the table below.
| Component |
Percentage (1 decimal place) |
Proportion (simplest form) |
Fraction (simplest form) |
Ratio |
| Sodium Chloride |
|
|
|
|
| Ammonium Chloride |
|
|
|
|
| Sand |
|
|
|
|
What type of percentage are here? (w/w, w/v. v/v)
Express the final mixture results as a ratio.
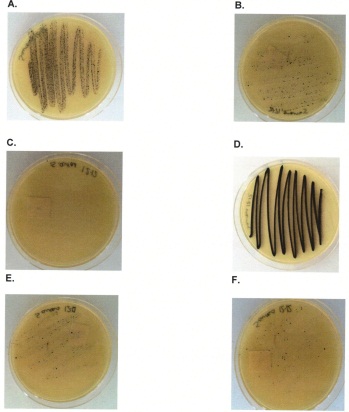
27. A sample of food gave a Staphylococcus aureus count of 54 typical and 16 atypical colonies per gram.
5 typical colonies were selected for confirmation and 4 of these confirmed as S.aureus.
3 atypical colonies were selected for confirmation and 2 of these were confirmed as S.aureus.
What is the confirmed bacterial count per gram?
28. Report the following results using a semi-quantitative scale
29. What is the minimum length of time calibration records should be stored?
30. In a laboratory, who should have access to client details and reports?
Cleaner
Clients
Laboratory technician
Payroll officer
Assessment Task 3
1. The following request form has come in.
What type of sample has been taken?
What needs to happen to the sample after it has been registered, but before the test can be performed?
What is the name of the method that should be followed?
What equipment will be required to prepare the sample for testing and to perform the test? (list at least 3 equipment for sample preparation and 3 for performing the test)
2. List two different hazards involved with using microscopes and how can they be controlled
3. What type of hazard category is associated with a sample of blood for performing a
blood cell count?
Biological hazard
Chemical Hazard
Indirect Hazard
Physical Hazard
4. List 2 different types hazards involved in performing a Gram stain on a prepared (unfixed) bacterial sample?
For each hazard listed, identify the control measures that should used/followed/implemented to minimise the chance of these occurring?
5. How would you clean up a spill of E.coli that is being used as a Gram stain control? Your answer must include:
Chemical/spill kit used
How the chemical is applied
Who needs to be notified?
Waste disposal?
6. List two different chemicals used in microscope slide preparations; such as in Gram stains, blood films, cell counts; and the hazards associated with them.
7. How would a spill of iodine stain, for staining onion cells, be cleaned up? Your answer must include:
Chemical/spill kit used
How the chemical is applied
Who needs to be notified?
Waste disposal?
8. Give two examples of how you can help to reduce the amount of waste that is produced in a microscope laboratory.
9. If the microscope was found to have a faulty light globe, who in the laboratory is the most appropriate person to report this to:
Laboratory supervisor
OHS representative
Laboratory Manager
All of the above
10. What two things would you do with a microscope that was found to have a fault; to ensure the fault is dealt with AND so that everyone knows not to use its.
11. List three items that must be checked on sample receipt prior to microscopic examination.
Two that will ensure traceability
One not to do with traceability
12. Who should be notified if a sample for processing arrives and the sample container is found to have been leaking (about 5% leakage)?
Notification not required, the sample should not be affected.
Laboratory supervisor
Laboratory manager
OHS representative
13. How would you dispose of a blood specimen?
Biohazard bag
Microscope Slide Discard
Sharps Bin
Sink with copious water
14. How would you dispose of a Gram stain slide?
Biohazard bag
Microscope Slide Discard
Sharps Bin
Sink with copious water
15. Just before the lab is shut for the day a bacterial sample comes into the laboratory requiring a Gram stain to be performed. Unfortunately due to being so late, the Gram stain cannot be performed till tomorrow. Under what conditions should the bacterial sample be stored till tomorrow?
16.
Looking at the following picture, fill in the table below:
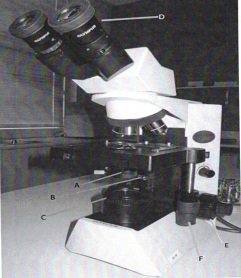
Label Name of Part
B
D
F
Label Function of microscope Parts
D
E
F
17. Which type of microscopic technique would you use for viewing specimens that have undergone immunohistochemistry staining?
Stereomicroscope
Darkfield microscope
Electron microscope
Fluorescent microscope
Polarising microscope
18. Which type of microscopic technique would you use for viewing cell culture specimens?
Stereomicroscope
Compound light microscope
Electron microscope
Phase contrast microscope
Polarising microscope
19. Which type of microscopic technique would you use for viewing a drosophila larvae specimen while removing its salivary glands?
Stereomicroscope
Compound light microscope
Electron microscope
Phase contrast microscope
Polarising microscope
20. Which type of microscopic technique would you use for viewing a gram stain preparation of Escherichia coli?
Stereomicroscope
Compound light microscope
Electron microscope
Phase contrast microscope
Polarising microscope
21. Count the number of cells in the following haemocytometer grids. The sample was diluted 1 in 10 with trypan blue.
Calculate the number of cells/L in the sample.
The formula to calculate the number of cells per mL:
Average cell count x 1/v x dilution factor x 103
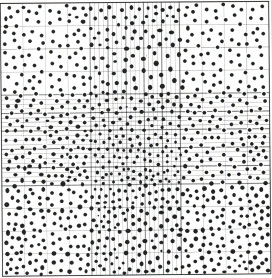
22. List two factors that must be considered when releasing test results.
- One ensuring it is the correct results being released
- One who results are released to or by
23. What is the measurement on the following Vernier scale?
24. A laboratory technician performed a Gram stain of their Escherichia coli reference culture; he wrote the following description for this specimen.
Gram Negative Rods
2um
What is wrong with this report?
25. How would you report the following specimen (three identifiers)?
26. The laboratory technician has come in first thing in the morning to use the microscope after the overnight shift. The technician lifts the cover off the microscope.
Is microscope 1 ready for use?
Why/Why not?
27. The laboratory technician is viewing a histology specimen under 40x power. There is something wrong with the image, you realise it is caused by the microscope set up. What is wrong with the microscope 2 set up for viewing?
28. What part of microscope 3 is causing the image to appear dirty?
29. What part of microscope 4 is causing the image to appear dirty?
Lab - Prepare practical science classes and demonstrations
Assessment 1
1. What is the difference between a hazard and a risk?
2. List the five steps in hierarchy of risk control in order of most effective to least effective.
Give a laboratory example for each
3. Define the term physical hazard.
Give three examples of physical hazards
For each of the examples given, how should the hazards be addressed using the hierarchy of control?
4. Give three different examples of biological hazards in a laboratory
For each of the examples given, how should the hazards be addressed using the hierarchy of control?
5. Give three different examples of indirect hazards in the workplace
6. What is the problem with the storage of the following equipment?
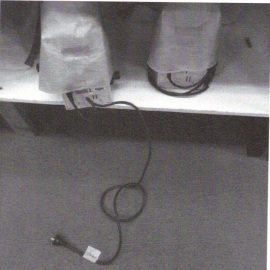
How would you address this?
How would you prevent this from happening again?
7. What is the problem with the following piece of equipment?

How would you address this?
How would you prevent this from happening again?
8. A laboratory Technician was incubating a set of standards a 00°C water bath; after 5 minutes the tubes were pulled out of the waterbath. The technician ended up with burns on her hands.
What two control measures need to be put in place to address this hazard?
9. The waste xylene drum is being transported to the waste collection area by one of the lab technicians, through a corridor to the back of the facility.
In addition to the laboratory, several offices with many staff, open into this corridor.
As the technician heads back to the laboratory through the same corridor as before; he notices wet patches on the floor and a strong overpowering xylene smell.
What should the technician do now?
10. Identify the following signs and symbols and their purpose


11. Chemical Activity
Fill in the table below for each substance
| Substance |
Disposal |
Storage/Transport Conditions |
| |
ONE OF |
Light? |
Temperature/ Humidity |
Dangerous Goods Code |
|
Biohazard Waste |
ONE OF |
ONE OF |
ONE OF |
|
Heavy metal waste |
(Dark, Light, N/A) |
(Freezer, Fridge, Room Temp, cool, 37C) |
(3, 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 5.1, 5.2, 6.1, 6.2, 8, 9, N/A) |
|
Neutralise |
|
ONE OF (dry, moist) |
|
|
Organic Waste |
|
|
|
|
Sink with copious Water |
|
|
|
| Silver Nitrate |
|
|
|
|
| Sodium Hydroxide |
|
|
|
|
| Hydrochloric Acid |
|
|
|
|
| Escherichia coli |
|
|
|
|
| Butanol |
|
|
|
|
| Copper Sulphate |
|
|
|
|
12. Explain the terms risk assessment and risk management, including how they relate and how they differ.
13. Explain the four key steps in risk management. Use an example to assist with the explanation.
14. What is Good Laboratory Practice?
Describe at least three principles of Good Laboratory Practice
15. Before using a chemical or reagent, what documents should you gather information from?
16. What three items must be included on a hazard report form?
17. Give two examples that would constitute a notifiable incident
18. What steps should be taken after a notifiable incident occurs to make sure the incident is investigated correctly?
19. List two ways to minimize the amount of chemical waste generated in a laboratory
20. List two ways to minimise the amount of general waste generated in a laboratory
21. What is the name of the standard/guideline/code that covers storage, handling and transport of dangerous goods.
22. What are the levels of physical containment? What standard/guideline/code covers this?
23. List eight Australian safety standards relating to safety in laboratories (include the reference number for each)
1 must cover lab design and/or construction
1 must cover PPE
1 must cover labelling of chemical substances
24. What is the name of the regulation/legislation/standard in Australia that regulates each of the following:
Chemical Labelling
Storage and Transport of chemicals
Occupational Health and Safety:
Waste Management:
25. What are three environmental standards or compliance that need to be adhered to through the EPA that may relate to laboratories?
26. A colleague tells you that the emergency shower is not functioning properly. What should you tell them to do?
27. List two ways you can help your fellow worker with OHS issues.
28. You are made responsible for the OHS training of a new employee in the laboratory. List three different types OHS procedures that the new employee needs to be aware of to be able to work in the laboratory as well as deal with incidents and emergencies
29. The following sign is on the entrance to the laboratory,

is this sign alone appropriate for the following staff. Explain your reasoning.
1. Group of very experienced and qualified staff.
2. Group of unqualified staff
3. Group of staff for who English is an additional language.
30. Under the OHS act which of the following people is/are responsible for workplace health and safety?
Employer
Supervisor
Employee
OHS Rep
Contractor
All of the above
31. Under the OHS act which of the following people is/are responsible for notifying about OHS issues in the workplace
Employer
Supervisor
Employee
OHS Rep
Contractor
All of the above
32. Who would you clarify the following with (area warden, health and safety representative, laboratory supervisor, area manager, OHS manager):
OHS Obligations:
Laboratory Procedures:
Safety procedures:
Work Instructions:
OHS paperwork:
33. List two task that the health and safety representative can assist with/or perform in the workplace.
34. List three functions of an OHS committee in the workplace.
35. If you are working on a task that you consider unsafe or unhealthy, the first thing you should do is:
Report it to Worksafe
Tell a fellow worker
Refuse to do the work
Talk to your supervisor and HSR
36. At a minimum, how often are workplace inspections to be performed?
37. According to the OHS act, what is the name of the group that a health and safety representative represents?
38. Under what circumstances can an employer pass on medical information to health and safety representatives
39. Under the OHS act which pieces of information does an employer NOT have to allow the health and safety representative access to?
Details of hazards in the workplace
Details of incidents occurring in the workplace
Health and Safety of the employees
Personal details of employees
Safety data sheets
Reports of investigations of health and safety issues
40. Explain why information and testing methods and results should be kept confidential.
41. Suggest at least two ways to secure data against accidental damage or loss.
42. What would you do if you overheard two co-workers talking about a well known Aft footballers' test results in the tea room?
43. Create an electronic chemical label as demonstrated below, for your assigned solution and email to Melissa Lockwood
Assessment 2 Questions Satisfactory
1. What would you do if you only had a 2 year old 1M NaOH solution (that doesn't appear to have any signs of deterioration) to titrate with a vinegar sample?
Dispose of it and remake it
Use it
Restandardise against KHP and then use
Not do the titration
2. What would you do if you only had a 2 year old 1M NaOH solution (that has visible precipitate in the bottom of the reagent bottle) to titrate with a vinegar sample?
Dispose of it and remake it
Use it
Restandardise against KHP and then use
Not do the titration
3. How would you store a solution of 1M AgNO3 that you had just prepared using chlorine free water?
Clear reagent bottle with plastic stopper
Amber reagent bottle with plastic stopper
Clear reagent bottle - lid doesn't matter
Amber reagent bottle - lid doesn't matter
4. How would you store a solution of 1M NaOH that you had just prepared?
Clear reagent bottle with plastic stopper
Amber reagent bottle with plastic stopper
Clear reagent bottle - lid doesn't matter
Amber reagent bottle - lid doesn't motter
5. How would you dispose of 1M NaOH?
Sink with copious water
Collect - evaporate
Collect - neutralise
Collect - Waste bottle for chemical disposal company
6. How would you dispose of 1M AgNO3?
Sink with copious water
Collect - evaporate
Collect - neutralise
Collect - Waste bottle for chemical disposal company
7. How would you dispose of 1M Glucose?
Sink with copious water
Collect - evaporate
Collect - neutralise
Collect - Waste bottle for chemical disposal company
8. How would you dispose of 1M NCI?
Sink with copious water
Collect - evaporate
Collect - neutralise
Collect - Waste bottle for chemical disposal company
9. How would you dispose of 1M BaCl2?
Sink with copious water
Collect - evaporate
Collect - neutralize
Collect - Waste bottle for chemical disposal company
10. What is used to clean up an acid spill?
Bicarb Soda
Sand
Sulphur
Vinegar
11. What is used to clean up a spill of a base?
Bicarb Soda
Sand
Sulphur
Vinegar
12. List 2 different ways you can minimize waste generation and environmental impact in a chemical testing laboratory?
13. List two non-sustainable work practices that could occur in a chemical laboratory as a part of a work task
14. From the SDS below, what signal word should be written on a label of this solution.
15. From the SDS in question 14, what pictograms should be on a label of this solution?
16. Correct any mistakes in the reported results using the correct enterprise procedure
| Titre No. |
Initial Burette Reading |
Final Burette Reading |
|
Titre Reported |
| 1 |
0.1 mL |
19.9 mL |
|
19.8 mL |
| 2 |
19.9 mL |
39.6mL |
|
20.3 mL |
| 3 |
0.5 mL |
20.4 mL |
|
19.9 mL |
| 4 |
20.4 mL |
40.2 mL |
|
19.8 mL |
17. What is wrong between the following sample register and laboratory test report?
18. How and where should a volumetric pipette be stored?
19. How and where should a volumetric flask be stored?
20. Station 1
There are four labelled pieces of glassware provided, identify each and record in the table below:
| Item |
Identity |
Size |
Grade of Glassware |
| A |
|
|
|
| B |
|
|
|
| C |
|
|
|
| D |
|
|
|
21. Station 2
At station 2, correctly place the selected glassware away for storage. Get this checked off by the assessor.
| Item |
Observed |
| Beaker |
|
| Volumetric flask |
|
| Pipette |
|
22 Station 3
Identify which of the solutions at station 4 require disposal/using/re-standardising Give at least 1 reason you have come to the decision for each.
| Solution Number |
Dispose |
Reason for decision? |
|
Use |
|
|
Re-Standardise |
|
| A |
|
|
| Potassium Chloride |
|
|
| B |
|
|
| Glucose solution |
|
|
| C |
|
|
| Sodium hydroxide |
|
|
| D |
|
|
| Silver nitrate |
|
|
| E |
|
|
| Glucose solution |
|
|
| F |
|
|
| Silver nitrate |
|
|
| G |
|
|
| Sodium hydroxide |
|
|
| H |
|
|
| Potassium chloride |
|
|
23. Station 4
With the assessor observing, correctly dispose of the solutions at station 3. Write in the table below how you disposed of each.
Time allotted is 10 minutes
| Solution Number |
Disposal Procedure |
Assessor sign off |
| A |
|
|
| Glucose solution |
|
|
| B |
|
|
| Sodium chloride |
|
|
| C |
|
|
| Sodium hydroxide |
|
|
| D |
|
|
| Silver nitrate |
|
|
| E |
|
|
| Hydrochloric Acid |
|
|
| F |
|
|
| Lead nitrate |
|
|
24. Station 5
With the assessor observing, correctly clean up spills of the solutions at station 5. Write in the table below how you cleaned each.
Time allotted is 10 minutes
| Solution Number |
Spill Procedure |
Assessor sign off |
| A |
|
|
| Glucose solution |
|
|
| B |
|
|
| Sulphuric acid |
|
|
| C |
|
|
| Sodium hydroxide |
|
|
| D |
|
|
| Silver nitrate |
|
|
| E |
|
|
| Hydrochloric Acid |
|
|
| F |
|
|
Sodium Chloride
|
|
|