Reference no: EM13733102
Understanding impact behaviour of various materials
The design and manufacturing of engineering structures capable of absorbing energy during impact is highly required in the automotive industry since it is directly related to the passenger safety requirements. For this reason, any potential new automotive components (side panels, crash cores etc) needs to fulfil a number of impact properties requirements to be implemented. It is also widely known now that the energy absorptioncapabilities under impact loading conditions of composites, are, in general,superior to metallic materials. The aim of this demonstration is to test the impact properties of unidirectional Carbon Fibre Reinforced Composites (CFRC) as well as a number of metal samples using a Charpy type of methodology.
Charpy impact testing involves striking a standard notched or un-notched specimen with a controlled weight pendulum swung from a set height. The specimen is supported at its two ends and struck by the pendulum. The amount of energy absorbed in fracturing the test-piece is measured and this gives an indication of the notch toughness of the test material. The pendulum swings through during the test, the height of the swing being a measure of the amount of energy absorbed in fracturing the specimen.
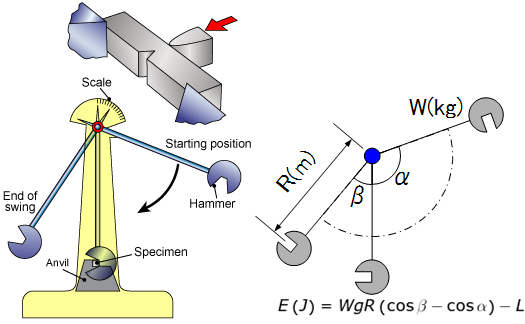
With W and R the mass and length of the hammer, Angles at the end of the swing (β), Angle of fall (α), the energy loss is L.
Charpy tests show whether a metal can be classified as being either brittle or ductile. A brittle metal will absorb a small amount of energy when impact tested, a tough ductile metal absorbs a large amount of energy. The appearance of a fracture surface also gives information about the type of fracture that has occurred; a brittle fracture is bright and crystalline, a ductile fracture is dull and fibrous.
Governing equations:
The Charpy impact strength of un-notched specimen, AcUis expressed in kJ per m2
AcU= 1000*E /(h*b)
E is the absorbed energy, h and b being the width and thickness of the specimen.
The Charpy impact strength of notched specimen, AcNis expressed in kJ per m2
Acu= 1000*E /(h*bN)
E is the absorbed energy, h and b being the width and remaining thickness of the specimen.
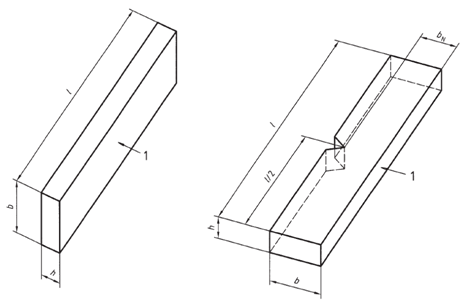
For this class, Charpy impact tests will be carried out using a 7.5Joules pendulum (W and R=)with an impact velocity of 3.8 m/s and a specimen span of 40 mm. The width and thicknesses will be measured accordingly for each specimen.
Questions
1. Evaluate the energy loss is L by recording α and β without any sample.
2. Measure the impact energy of 0, 90 and 45 degree oriented CFRC samples. Report the data (width and thickness of the samples, energy in Joules and Charpy impact strength kJ/m2). Comment on the trends and results.
3. Measure the impact energy of notched steel and aluminium samples. Report the data (width and thickness of the samples, energy in Joules and Charpy impact strength kJ/m2). Comment on the trends and results.
Understanding thermal oxidation of steel
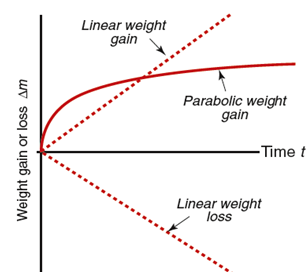
The aim of this demo is to demonstrate the thermal oxidation of steel samples when exposed to air in a furnace at either 500 degrees of 800 degrees. Samples placed in a furnace will be taken out of at given intervals and weight loss/gain will be determined.
Questions
4. Plot the mass difference Δmversus time (10 minute intervals, 3 to 4 measurement depending on time restriction) for the steel sample exposed to high temperature. Describe the kinetic of oxidation from the curve (i.e. weight loss or gain etc)
5. For both oxidation temperatures, visually describe the oxide layer deposited on the surface of the samples (after the samples have cooled down!!) i.e. is it cracked/porous/smooth? Does it stick to the surface? etc)
6. Does the visual observation of the oxide layer fits in with what you have seen in class when discussing oxidation kinetics
Understanding creep properties of a CFRC using Dynamic Mechanical Analysis.
The aim of the demonstration is to illustrate the creep behaviour of an epoxy resin (automotive grade) with and without carbon fibre reinforcement (0 and 90 degree orientation). Creep is defined as the tendency of a material to distort under external loads over time, especially as temperature increases. For polymer in particular it is the result of their dynamic visco-elastic properties.
The creep behaviour and creep recovery tests will be performed in single cantilever mode under constant stress of 5 MPa at room temperature and at 50°C. Creep time will be 5 minutes and recovery time will be 3 minutes to ensure enough recovery time.
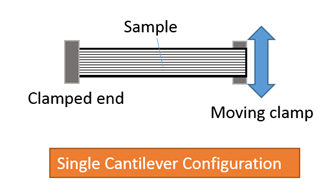
Below is the illustration of a strain vs time creep experiment; 3 regions can be seen. In the first region, strain has suddenly increased once the load is applied at t=5 minutes and is related to the elastic response of the samples. The second region is transient region in which the strain increases non-linearly. The last region is recovery region in which the load is removed and strain decreases (recovery). Recovery can be calculated by J = γ1 - γ2/γ1 , where γ1 is the maximum strain in the creep zone, γ2 is the recovered strain.
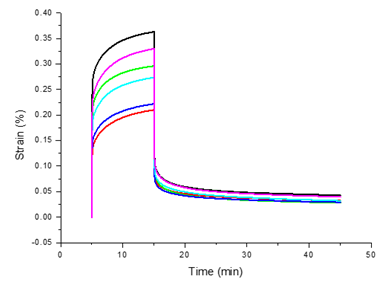
Questions
1. Plot the strain versus time for the plain resin sample and unidirectional (0 and 90 degree orientation) sample tested at room temperature and at 50 degrees.
2. Calculate the creep recovery J for each types of sample.
3. Comment on the effect of fibre and fibre orientation on the creep behaviour and recovery. Try to be quantitative (fibre have improved/reduced the creep properties by X %).
4. Comment on the effect of temperature on the creep behaviour and recovery. Try to be quantitative (an increase in temperature has improved/reduced the creep properties by X%).