Reference no: EM133198191
Assignment:
1.Keynes' ideas drew many economists _______________ the classical view of the economy. One of the main differences between the Keynesian and classical views of the economy is that Keynes asserted that wage rates can be _____________________ while the classical
economists believed that wage rates are ____________.
a.away from, inflexible in a downward direction, flexible
b.toward, inflexible in a downward direction, flexible
c.away from, flexible, inflexible in an upward direction
d.toward, flexible, inflexible in a downward direction
2.Most of her ____________ is tied up in real estate. How much _______ did Jones earn last year at his job? How much ___________ do you have in your pocket?
a.money, income, wealth
b.wealth, money, money
c.wealth, income, money
d.money, money, money
e.wealth, wealth, money
3.According to Keynes, a decrease in _______________ and subsequent increase in ___________ may not be matched by an equal increase in _________________.
a.consumption, investment, saving
b.consumption, saving, investment
c.aggregate demand, aggregate supply, investment
d.investment, consumption, saving
e.none of the above
4.If we say that a dollar is being used to trade for some good, then here the dollar, as money, is serving as a ______________
a.store of value
b.medium of exchange
c.unit account
d.none of the above
e.There is not enough information to answer the question
5. Exhibit
Taxable Income Income Taxes
$0 - $9,000 10% of taxable income
$9,001 - $52,000 $900 + 15% of everything over
$9,000 $52,001 - $300,000 $7,350 + 20% of everything over $52,000
Greater than $300,000 $56,950 + 30% of everything over $300,000
$56.950+30%(X-300000)
Refer to exhibit 11-1. The tax structure depicted in this tax schedule is a ______________ tax structure.
a.regressive
b.progressive
c.proportional
d.flat
6.An aggregate demand (AD) curve shows the:
a.real output (Real GDP) people are willing and able to buy and to sell at different price levels, ceteris paribus.
b.amount of a particular good people are willing and able to buy at a particular price, ceteris paribus.
c.real output (Real GDP) people are willing and able to sell at different price levels, ceteris paribus.
d.real output (Real GDP) people are willing and able to buy at different price levels, ceteris paribus.
7.Which of the following functions of money best describes the function of savings deposits?
a.store of value
b.medium of exchange
c.unit of account
d.none of the above
8.If M1 rises, then _____________
a.M2 will decline.
b.M2 will rise.
c.checkable deposits will decline.
d.checkable deposits will rise.
9.The Federal Reserve is a __________________ agency and the U.S. Treasury is a _______________ agency.
a.budgetary, monetary
b.monetary, budgetary
c.monetary, monetary
d.budgetary, budgetary
e.none of the above
10.If people move money from their checkable deposits into their savings accounts, it follows that
a.M1 will decline and M2 will rise.
b.M1 will decline and M2 will remain unchanged.
c.M2 will decline and M1 will rise.
d.Both M1 and M2 will decline.
e.none of the above
11.The ___________ is the change in the interest rate due to a change in the supply of loanable funds.
a.income effect
b.expectations effect
c.liquidity effect
d.price-level effect
12.Refer to exhibit 11-1. Arya earns $420,000 of taxable income. Arya's income taxes equal
a.$92,950.
b.$126,000.
c.$165,865.
d.$117,750.
13. Which one is not an element explaining the aggregate expenditure Model:
Y= C+I+G+NX
a) If any of these types of spending increases, aggregate expenditures will also increase.
b) Increased production could help alleviate unemployment.
c) An increase in aggregate expenditures will lead to an increase in real GDP.
d) Businesses increase price level in order to maximize cost.
14. Jack earned an income of $500. He spent $200 with his friends on a picnic. Calculate marginal propensity to consume (MPC).
a) 0.7
b) 0.8
c) 0.6
d) 0.4
15. The fraction of each additional dollar of income that Jack is saved supposed to be equal:
a) 0.5
b) 0.8
c) 0.9
d) 0.6
16. Jose buys a jacket for $100. If his MPC is 40%, the expenditures multiplier:
a) 1.67.
b) 2.5.
c) $250 Increase in real GDP
d) MPC+MPS=1
17. When real GDP is below the equilibrium of full-employment level of output or above with a hot economy. What is the best fiscal policy government can do in both cases?
a) Reduce regulation to facilitate market failures.
a) Government can apply the consumer price index adjustment budget.
c) Increase government spending and decrease tax or increase tax and decrease government spending.
d) Government can reduce recession and increase inflation instead.
18. There are three types of unemployment which one is considerably reduced to zero with potential output or full-employment level of output.
a) Frictional unemployment
b) Structural unemployment
c) Natural rate of unemployment
d) Cyclical unemployment
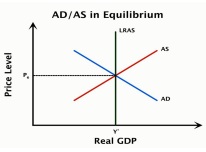
19. Look at the above graph. Explain the difference between Long Run AS and Short Run AS.
a) LRAS and SRAS differ in fixed price level and GDP is below output level of full-employment.
b) In SRAS, resource prices are sticky while in LRAS they are flexible.
c) AD differs LRS below AS.
d) All answers
20. Which one is not a determinant of aggregate demand?
a) Consumption
b) Net exportation
c) Price level
d) More Taxes