Reference no: EM13719394
Question 1: Application of 2D Solid Elements
Simplification of complex geometry to perform an efficient analysis of a mechanical or structural problem is a critical step the Computer Aided Engineering analyst must make. In particular, simplifying complex 3D problems into 2D can be beneficial, reducing setup, solve times and allowing for rapid design optimisation.
For this task you are required to identify a series of physical problems which lend themselves to being simplified to the use of a 2D solid element.
You are required to:
- Describe and discuss the differences of the 2D Solid Element types:
o Plane Stress;
o Plane Strain; and
o Axisymmetric.
- Provide 4 realistic case studies in which the simplification from 3D to 2D solid elements can be made for each of the 2D Solid Element types proposed above. You must describe and discuss why the simplification is suitable. Include schematics and support mathematically if able to do so. This should be conducted clearly, with clearly defined boundary conditions etc.
- Setup an ANSYS FE model for one of the case studies discussed above for each element type. Therefore, three models: one for the plane stress, plane strain and axisymmetric element assumptions.
- Present the FE setup (element selection, mesh, boundary conditions etc.), results and a detailed discussion of the suitability for the 2D assumption in a clear and structured report. Describe and discuss the critical results for the particular analysis?
Question 2: Bar Element
Considering an aluminium rod under compression, its FE model is an assembly of two bar elements as shown in the figure below. The rod has a square cross-section (30 mm x 30 mm) and the Youngs Modulus of the aluminium is 70 GPa.
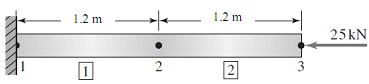
Determine
1) the nodal displacements at nodes 1-3;
2) the reaction at node 1; and
3) the axial stresses and strains in each element.
Question 3: Truss Structure - Update
Consider the three membered planar truss-structure shown in the figure below. All members of the truss have identical square cross-sectional area (A) of 25 mm x 25 mm, and Youngs Modulus (E) = 210 GPa. The hinged joints, A, B and C allow free rotation of the members about the z-axis.
Determine:
1) the horizontal and vertical displacements at joint C;
2) the reaction forces at each support;
3) the stress and strain of each member.
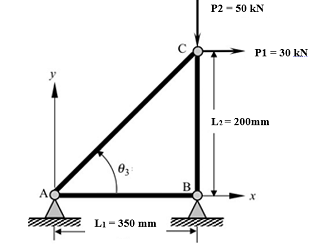
|
Compare and contrast the house and the senate
: Compare and contrast the legislative/ governmental structure and performance in the United States and the countries of the Gulf Cooperation Council.
|
|
Find the expectation value of the potential energy
: For the harmonic oscillator, find the expectation value of the potential energy for the lowest energy state
|
|
Assume that the density remains the same
: Blue and yellow streams of paint (each with a density of 825 kg/m3 and a viscosity 1000 times greater than water) enter a pipe with an average velocity of 4 m/s as shown in the figure. The pipe has a diameter of 2 inches and length of 25ft. would you..
|
|
Determine the quality of the steam at the turbine exit
: Consider a 210-MW steam power plant that operates on a simple non-ideal Rankine cycle, where the isentropic efficiency for both the turbine and the pump is 85%. Steam enters the turbine at 10 MPa and 500C and is cooled in the condenser at a pressure ..
|
|
Describe the differences of the 2d solid element types
: Identify a series of physical problems which lend themselves to being simplified to the use of a 2D solid element - Describe and discuss the differences of the 2D Solid Element types
|
|
Assume the drainpipes are the same height as the building
: Galvanized iron drainpipes of diameter 50 mm are located at the four corners of a building, but three of them become clogged with debris. Find the rate of downpour (cm/min) at which a single functioning drainpipe can no longer drain the roof.
|
|
Rocket propellant chamber is filled with combustion gases
: A 1m3 rocket propellant chamber is filled with combustion gases at 3000 K and 7 Mpa at the instant combustion ceases. The throat area of the nozzle is 0.1m2. Estimate the time it takes for the chamber pressure to drop to 0.7 MPa. Assume that the inst..
|
|
Converted to thermal energy due to the collision
: Consider a mass M is a distance L above the ground at constant temperature, TR. The mass is released, falls, and hits the ground. The kinetic energy just before it hits is converted to thermal energy due to the collision and is transferred to the gro..
|
|
Determine the thermal efficiency and propulsion efficiency
: A ramjet is to propel an aircraft at Mach 3 at high altitude where the ambient pressure is 8.5Kpa and the ambient temperature Ta is 220 k. The turbine inlet temperature T is 2540 k.if all components of the engine are ideal - that is frictionless.
|