Reference no: EM132343045
Case Study: Oligopoly
Please address the following case study relating to the commercial airliner production industry. This case study relates to Chapter 13 of the textbook.
Note: There are videos of hand-worked problems to accompany sections 1-3 but not section 4 because the questions in section 4follow from the reading.
Please submit your work as a single Word document. When I request calculations, you can write them by hand and incorporate a photograph into the document or you can type up the calculations in the document. Similarly, you can create any tables by hand, in Word, or other ways, but your tables should be clear. The document should be approximately 2-4 pages (counting each side of the paper as a page) in length. Please indicate in some way which part of the document responds to each question. The assignment will be graded based on correctness, effort, and presentation.
Section 1. Normal Form Games (pages 509-525)
For each of the following normal-form games, identify any dominant and any dominated strategies. Attempt to solve the normal-form game using successive elimination of dominated strategies and describe or illustrate your process. Attempt to solve the normal-form game finding the Nash Equilibrium using best-responses and describe or illustrate your process. Describe the Nash Equilibrium actions and payoffs.
a) Two firms must decide whether or not to lobby the government for reduced regulation. The payoffs are as follows:
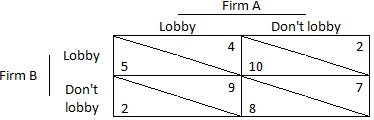
b) An established firm and a new firm are competing for a contract. Each can choose either an aggressive strategy or a conservative strategy in their presentation. Only one firm can win the $20 million dollar contract. If they choose the same strategy, the established firm wins the contract but if they choose different strategies, then they each have a 50% chance at the contract.

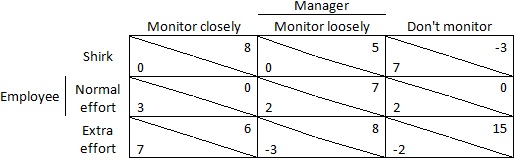
c) A manager must choose how much effort to put into monitoring his employees and his employees must choose how much effort to put into their jobs. The change in profits (payoffs) for the firm and the net value of the effort and bonuses (payoffs) for the employees can be depicted in the following table:
Section 2 Continuous-choice Games (pages 525-531, also consider 570-572)
There are 2 firms in an identical-product Cournot duopoly. Demand for their product is characterized by the demand curve:
p=50-q_A-q_B
The cost for firm A is:
C(q_A )=60+14q_A
and the cost for firm B is:
C(q_B )=60+14q_B
- Find each firm's best-response curve.
- Graph these best-response curves.
- Find the equilibrium quantities and prices.
- Find the equilibrium profits of each firm.
Section 3. Sequential Games (pages 531-539)
Now let's focus on the market for modern large, long-distance jets. Boeing entered this market first with its 787 Dreamliner. Suppose that gave Boeing the opportunity to commit to its production to which Airbus had to respond. There are three possible outputs for each firm in this market and the payoffs for each combination of outputs produced by each company are as follows:
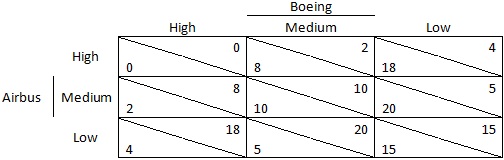
a) Solve this game as a simultaneous-action (Normal-form) game using the best-responses method.
b) Create a decision tree representing this game as a sequential game with Boeing acting first.
c) Solve the sequential game using backward induction.
d) In roughly 5 sentences describe why the solutions to the simultaneous-action and the sequential-action game are different. Be sure to use appropriate vocabulary.
Section 4. Repeated Games (pages 539-553)
Now, let's consider a longer time frame in the modern large, long-distance jet market. Suppose that instead of acting sequentially, Boeing and Airbus interact simultaneously, but repeatedly. The payoff table is the same as in Section 3.
a) Identify a cooperative set of actions and outcomes that the companies would prefer to the Nash Equilibrium.
b) Describe a trigger strategy that would help support this cooperative outcome.
c) Describe a Nash Equilibrium (including the relevant trigger strategies) that features a cooperative outcome.
Attachment:- Oligopoly Case Study.rar