Reference no: EM131227152
Q1: Demand for a good is given by: QD = 100 - P and supply by QS = 0.5P - 20, where P is the market price of the good. In equilibrium, price and output under perfect competition will be
A. $100 and 30 units respectively
B. $120 and 35 units respectively
C. $70 and 30 units respectively
D. $60 and 10 units respectively
E. $80 and 20 units respectively
Q2: The price of fresh fish rose and the quantity sold fell. Other things remaining the same, which of the following is consistent with this observation?
A. The price of meat, which is a substitute for fish, rose.
B. The number of consumers that have a preference for fish increased.
C. The cost of fishing increased.
D. The fishermen learned to fish more efficiently.
E. The supply of fresh fish increased.
Q3: Other factors being unchanged, the supply curve for eggs will shift downward and to the right if
A. The price of chicken feed falls
B. A virus spreads through poultry farms through the country and kills millions of chickens
C. The government introduces a new tax on poultry suppliers
D. The average income level in the country falls due to a recession
E. New research establishes that cholesterol, found in egg yolks, is found to cause heart disease
Q4: The demand curve faced by an individual firm in a competitive market, implies that the firm
A. Can increase its profits by raising the price of the good it sells
B. Should reduce its price in order to increase sales
C. Can raise the market price of the good by lowering its sales
D. Takes the market price as given
E. Can influence the market price
Q5: In order to maximize profits, a perfectly competitive firm will continue producing until
A. Its total sales revenue is maximized
B. The average cost is minimized
C. The marginal cost equals the market price
D. The profit per-unit is at its highest possible point
E. It utilizes its full production capacity
Q6: The height of an individual demand curve at each level of output shows
A. The value of producer surplus
B. The revenue earned by the firm from an additional unit consumed
C. The value of consumer surplus
D. The marginal cost of producing the good
E. The marginal benefit from consuming an extra unit of the good
Q7: Suppose that demand for and supply of a commodity in a market are shown on a graph with price on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis. The y-intercept of the demand curve is equal to $30. The equilibrium price and quantity are $20 and 300 units respectively. What is the total consumer surplus in the market?
A. $1,300
B. $1,500
C. $2,000
D. $3,000
E. $9,000
Q8: Which of the following is true of a competitive market?
A. Competitive markets provide significant economic profits to producers in the long run.
B. Competitive markets promote business by allowing producers to gain at the expense of consumers.
C. The outcome of a competitive market is fair and equitable.
D. Competitive markets yield efficient outcomes.
E. Competitive markets allow consumers to gain at the expense of producers.
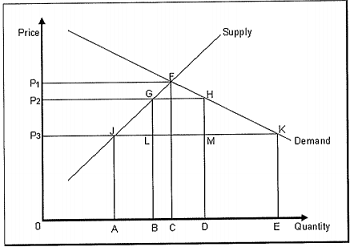
Q9: The following figure shows the domestic demand and supply curves for a good. With free trade, the price of the good in the domestic market is P3. The government introduces a 5% tariff in the market which raises the domestic price to P2.
Refer to Figure With the imposition of the tariff, the change in consumer surplus is equal to
A. A gain measured by the area of P2G1P3
B. A loss measured by the area of P1FGP2,
C. A gain measured by the area of P1FJP3
D. A loss measured by the area of P2GIP3
E. A loss measured by the area of P2HKP3
Q10: The following figure shows the domestic demand and supply curves for a good. With free trade, the price of the good in the domestic market is P3. The government introduces a 5% tariff in the market which raises the domestic price to P2.
Refer to Figure. With the imposition of the tariff, the change in producer surplus is equal to
A. A gain measured by the area of P2GJP3
B. A loss measured by the area of P3JA0
C. A gain measured by the area of P2FC0
D. A loss measured by the area of P3FGP2
E. A gain measured by the area of P3FJP3
Q11: The following figure shows the domestic demand and supply curves for a good. With free trade, the price o the good in the domestic market is P3. The government introduces a 5% tariff in the market which raises the domestic price to P2.
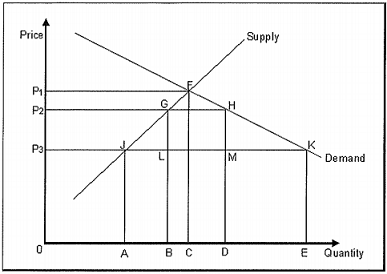
Refer to Figure. The increase in the government's revenue due to the imposition of a tariff is equal to
A. The area of P1FKP3
B. The area of GHML
C. The area of GHKJ
D. The area of GFHML
E. The area of P2HKP3
Q12: In a given market, demand is described by the equation QD = 1,800 - 10P and supply is described by QS = 200 + 10P.
(a) Determine the equilibrium price and quantity.
(b) Determine the surplus or shortage that would exist if the price were $60.
Q13: Explain why the demand curve for a competitive firm is horizontal.
Q14: The marginal cost of a firm under perfect competition is given by the equation MC = 2QF - 20. The market price is $50 per unit. Determine the firm's profit-maximizing level of output. Write down the equation for the firm's supply curve.
Q15: For a perfectly competitive firm, long-run average cost is: LAC = 300 - 20QF + 0.5QF2, where QF denotes the firm's output. Determine the firm's long-run profit-maximizing output and price.
Q16: In a perfectly competitive market, long-run average cost and long-run marginal cost are constant and equal: LAC = LMC = $8 for a typical firm. However, one of the firms discovers a technological innovation lowering its average cost and marginal cost to $7. How will this affect the equilibrium price? If all firms can take advantage of the innovation, what is the impact on the market price and industry profits?
Q17: A perfectly competitive market is described by the demand curve QD = 60 - 2P, and the supply curve QS = 5P - 10. A typical firm has the total cost equation: C = 16 + 2QF + QF2.What is the equilibrium price and quantity in the market? Compute the firm's total revenue, total cost, and total profit.
Q18: A firm has the following cost function: C = 30 - 14Q + Q2. Derive the firm's supply curve from the total cost function.
Q19: A small nation permits free trade in good X. At the good's free-trade price of $8, domestic firms supply 6 million units and imports account for 4 million units. Recently, the small country has erected trade barriers with the result that imports have fallen to zero, price has risen to $10, and domestic supply has increased to 8 million units. Calculate the change in consumer surplus and producer surplus resulting from the trade barrier. What is the deadweight loss?
Note - Just select correct option for MCQ. For other questions, please give step by step solutions.