Reference no: EM132982888
Question: For ONE of the case studies given on the next page, complete the following:
1. Derive at least four concept designs to satisfy the given specification. Use short written descriptions and simple sketches to illustrate your ideas. Show evidence of the use of the following techniques when creating your designs:
- Brainstorming
- Synectics
- Morphological Chart
2. Use the weighted objective method to select your best solution from these concept designs.
3. What other information would be required to be able to write a more complete
Product Design Specification? (Use an objective tree to clarify and expand upon the vague brief given.)
Case Studies
(a) As a keen, but economically challenged, cyclist you need a means of carrying two bicycles whilst travelling between destinations on a touring holiday in your small car which has a tow bar fitted.
Following on from the first TMA in this module, produce a design report for one design of the product based on one of the scenarios covered on the following pages. The report should contain. where appropriate:
Title page
Acknowledgements
Summary
Contents
Introduction
Basic Product Design Specification
Design Parameters
Simple Description of chosen Design Design Evaluation
Detailed drawings of the design. including dimensions, such that its constructional features can be seen*
Conclusions
References
Appendices
Drawings should be submitted as complete engineering drawings done using CAD (or other suitable software). If the maximum size of printing is A4 then several sheets. each showing a different view of the design. will probably be needed to show sufficient detail for the design to be constructed. In this case, all views should be clearly labelled and all sheets numbered. Only computer-produced drawings will he marked; it is not acceptable to submit hand-drawn work. Please submit copies of the drawings within the report (.PDF) and in addition, upload the computer files of the drawings (.DWG).
Note: you may have to invent information to make the design report complete.
(a) Bicycle Rack
When a full design specification was produced and the weighted objective procedure carried out, it was found that a tow bar mounted rack was the best solution.
The rack is to bolt to the tow bar once the tow ball is removed. The dimensions of the tow bar bracket are shown in Figure 1. The 330 mm dimension refers to the distance from the ground to the bottom of the bracket. In order to avoid the bikes fouling the car, it should be assumed that no part of either bike should protrude beyond the face of the tow bar bracket (ie between the bracket and the car).
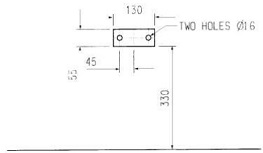
Figure 1
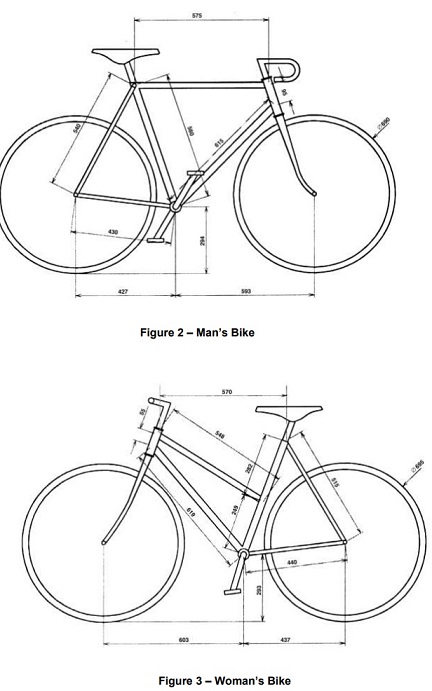
The two bikes to be carried have dimensions shown in Figures 2 and 3. The width of the handlebars of the man's bike is 420 mm, whilst that of the woman's is 630 mm. The width across the pedals is 360 mm in both cases.
Your good friend Fred has offered to help build the bike rack and he has access to the following materials and equipment:
• square section steel tubing, 25 mm x 25 mm x 2 mm thick
• steel plate, 8 mm thick
• steel strips, 25 mm wide by 6mm thick
• brazing and welding gear
• a powered hacksaw
• a pillar drill
Design a suitable rack that can be made using Fred's materials and equipment. It is not necessary to worry about stresses: the materials are capable of exceeding the strength requirements of any design. In addition, the rack should be designed to 'look right'.
As part of the report, you should produce:
(i) An arrangement drawing showing the outline of the bikes on the rack.
This does not need to be very detailed or show any dimensions but should clearly demonstrate that the rack will enable the two bikes to be carried without fouling the car or the ground.
(ii) A detailed engineering drawing of the rack only, comprising front and side elevations with all dimensions required for manufacture shown.