Reference no: EM13144013
1. Two homeowners (indexed by A and B) possess the following demand curves for the consumption of landscaping water.
a) What is the maximum price each consumer is willing to pay for a unit of water? At what quantities is the marginal benefit to each consumer of more water equal to zero?
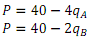
b) Calculate the price elasticities of demand for A and B at P=30, 20 and 10. How does the elasticity change as you move down the demand curve?
c) Assuming these are the only consumers of water, calculate the total ("market") demand curve, making sure to write it in a form where P is on the left hand side of the equation. Graph these equations neatly.
d) Calculate the price elasticities of demand for the market demand curve you calculated in c) at the prices specified in part b).
e) Suppose the local water utility charges consumers P=$10 for each unit of water. How much will be consumed overall? The utility, facing reduced deliveries
from the Bureau of Reclamation due to a wide-scale drought, enlists you to figure out the effect of an increase in rates to $15. What is the new level of consumption and by how much does each consumer alter their consumption?
f) Given the scenario in e), what is the consumer surplus (total benefits net of expenditures) to consumers from the water they consume after the price increase? How is this surplus divided across the individuals?
2. Continuing from question 1, suppose there is a newcomer (indexed by C) to this (very small!) community with the following demand curve for water
What is the new market demand curve (be careful)? Draw this demand curve and represent it in equation form.
3. The elasticity of demand (at currently consumed quantities) for one good is ½ while that for another is 2. Both goods are consumed in identical quantities. Suppose your objective is to raise revenue for education by imposing a 5% tax on purchases of one or the other good.
Assuming you only care about raising the largest amount of money possible, which good would you tax? Why? Does your answer help to explain the high tax rates observed on potentially addictive substances?
4. The price of gasoline spikes by 50% due to a major hurricane wiping out a large amount of US refinery capacity. A week after the price spike, it is observed that Americans reduce their consumption by only 20%. Is demand on this time scale elastic or inelastic (circle
one)? Suppose the price remains at this new level for a period of months and consumers expect it to persist indefinitely. Do you expect the reduction in consumption observed in the first week to increase/decrease/remain the same (circle one)? Briefly in the space below explain your answer in terms of long-run vs. short-run demands.
|
Minimum energy required to break an oxygen-oxygen bond
: The minimum energy required to break an oxygen-oxygen bond in ozone (O3) is 387 kJ/mole. What is the longest wavelength of light
|
|
Computing the noncontrolling interests share
: In computing the noncontrolling interest's share of consolidated net income, how should the sub- sidiary's income be adjusted for intercompany transfers?
|
|
Identify one of the general deductions
: Identify one of the general deductions and explain its current treatment. Then, argue whether or not it should be allowed as a deduction. You can approach this question from an economic, social, revenue, or political perspective.
|
|
How many milliliters would a student need to pour
: Hexane has a density of 0.659 g/mL. How many milliliters would a student need to pour in order to get 49.5 g of hexane?
|
|
Demand curves for the consumption of landscaping water
: Calculate the price elasticities of demand for A and B at P=30, 20 and 10. How does the elasticity change as you move down the demand curve?
|
|
What is o’monica basis in her new residence
: At the time of the sale, O’Monica’s adjusted basis was $50,000. Within two months of the sale, O’Monica moved into a new residence she purchased for $500,000. What is O’Monica’s basis in her new residence?
|
|
Determining balance of the tax owed
: Trent files his tax return 35 days after the due date. Along with the return, Trent remits a check for $8,000, which is the balance of the tax owed.
|
|
Estimate cost of the merchandise destroyed
: Estimate the cost of the merchandise destroyed . Briefly descrive the situations in which the gross profit method is useful
|
|
Calculate the formula of the hydrated crystal
: A 4 g sample of the hydrated crystal Ba(OH)2• χH2O is heated until all the water is removed. The remaining solid weighs 2.17 g. Calculate the formula of the hydrated crystal.
|