Reference no: EM133150581
Reservoir Engineering
Question 1. Fill in the blanks of the hydrocarbon classification shown below,
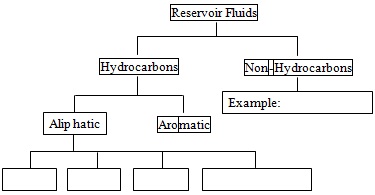
Question 2. Define saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Question 3. Fill in the blanks or select the correct choice:
a. Asphaltene is the (heavy/light) fraction of the crude oil that .............. in light alkanes such as pentane, but is ......... in aromatic solvents such as ........ and
...........
b. Asphaltene and resin molecules have (polar/non-polar) molecular structure.
c. Resins (assist/decrease) the solubility of asphaltenes in the crude oil.
d. The term "sour gas" is used for natural gas samples containing significant amount of .............
Question 4. Draw a typical phase diagram of a pure substance and describe it briefly indicating the critical point.
Question 5. Draw a typical phase diagram of a two-component mixture and describe it briefly indicating the critical point.
Question 6. Describe the classification of reservoir fluids based on their phase diagrams (hint: there are five classes). Plot the phase diagram pointing out the initial and final pressure of the reservoir.
Question 7. Explain briefly what an equation of state (EoS) is.
Question 8. Explain what is meant by:
• Solution gas-oil ratio,
• Oil formation volume factor
• Oil Viscosity
Plot the diagram of these three oil properties against pressure.
Question 9. Consider a gas sample with the composition listed in bellow table:
|
Component
|
Mole fraction
|
|
C1
|
0.45
|
|
C2
|
0.15
|
|
C3
|
0.07
|
|
C4
|
0.03
|
|
C5
|
0.04
|
|
C6
|
0.06
|
|
C7+
|
0.01
|
|
H2S
|
0.01
|
|
CO2
|
0.02
|
|
Total
|
1
|
Calculate the:
• MW and specific gravity of this gas sample
• API gravity of this gas sample
• The pseudo-critical pressure and temperature of this gas based on Sutton's (1985) equations.
Ppc = 756.8 - 131.0γg - 3.6 γg2
Tpc = 169.2 + 349.5γg - 74.0 γg2
Question 10. Consider a gas sample with the following composition; calculate the pseudo-critical pressure and temperature of this gas.
|
Component, i
|
Mole fraction, yi
|
Pci (Psi)
|
Tci (°R)
|
|
C1
|
0.7
|
673
|
344
|
|
C2
|
0.18
|
709
|
550
|
|
C3
|
0.02
|
618
|
666
|
|
C4
|
0.03
|
551
|
766
|
|
C5
|
0.04
|
485
|
847
|
|
C6
|
0.01
|
434
|
915
|
|
C7+
|
0.02
|
361
|
1024
|
|
Total
|
1
|
|
|
Question 11.
(a) Define the gas compressibility factor (z-factor).
(b) Determine the gas compressibility factor for the gas in question 9 at 2500 psi 750°R. (Hint: use the chart developed by Standing and Katz (1954)), you can find this chart at the end of this booklet.
(c) Define the gas formation volume factor
(d) Determine the gas formation volume factor for a reservoir gas sample of part (b)
Question 12. Briefly describe the black oil and compositional reservoir simulation approaches and outline their difference.
Attachment:- Reservoir Engineering.rar