Reference no: EM132918818
MITS5003 Wireless Networks & Communication - Victorian Institute of Technology
Question 1 An electromagnetic signal is made up of many frequencies. For the given electromagnetic signal:
Compute the following:
• The fundamental frequency
• Time Period of the signal
• Spectrum of the signal
• Absolute bandwidth
Question 2
• The ratio is important because the bit error rate is a decreasing function of this ratio. System describes a permissible probability of error. There is a given for a given probability of error that must be achieved. Elaborate, how can we increase the bit rate , while maintaining the same . Hint (How must the signal Power S and Bandwidth W of the channel change to retain the
same. )
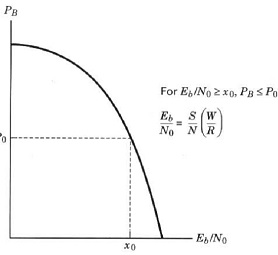
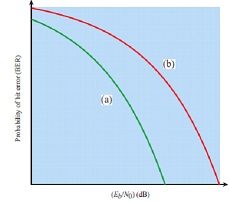
• Identify, which curve [curve (a) or (b)] represents better performance versus the probability of bit error?
Question 3
Differentiate between Datagram Packet switching and Virtual Circuit Packet Switching. What is the principal application that has driven the design of the circuit switched networks?
Question 4
• Compute the bit rate required to transmit data for a channel with a 1-MHz bandwidth. The SNR for this channel is 63.
• For the same channel with a bandwidth of 1MHz and a bit rate 4Mbps, Calculate the number of signaling levels.
Question 5
Compute and compare the path loss in dB for two possible cellular environments operating at a frequency of 1.9GHz at a distance of 2 Km. Assume isotropic antennas. Comment on the results.
• Free space between mobiles and base stations (n=2)
• Urban area cellular radio with (n = 3.1)
Question 6 Draw the transmitted signal using Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum for the following:
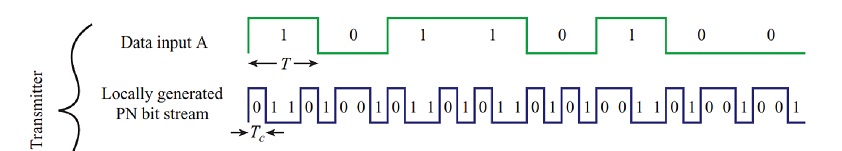
Question 7
• Briefly describe the handoff procedure and discuss the two types of handoff in cellular networks.
• Illustrate the principle of frequency reuse in the context of a cellular network?
• If the calling rate averages 15 calls per minute and an average holding time of 3 minutes. Calculate the traffic intensity in Earlangs?
• Explain in your own words, any two ways of increasing the capacity of a cellular system.
Attachment:- Wireless Networks.rar