Reference no: EM13199974
Question 1
You are the operations manager of a firm that uses the continuous-review inventory control system. Suppose the firm operates 52 weeks a year, 365 days, and has the following characteristics for its primary item:
Demand = 25,000 units/year
Ordering cost = $30/order
Holding cost = $8/unit/year
Lead time = 2 weeks
Standard deviation in weekly demand = 100 units
A normal distribution table is shown below.
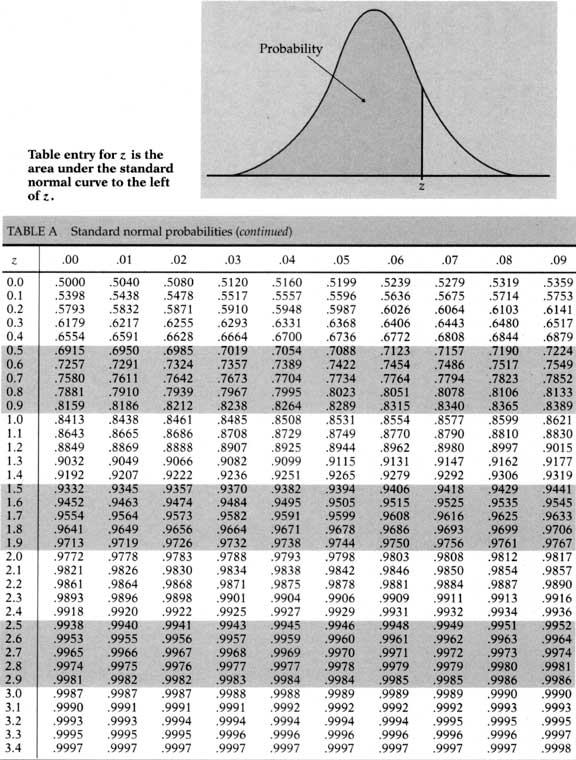
Use the information in Table. What is the economic order quantity for this item?
Fewer than 400 units
Between 400 and 450 units
Between 450 and 500 units
Greater than 500 units
Question 2
You are the operations manager of a firm that uses the continuous-review inventory control system. Suppose the firm operates 52 weeks a year, 365 days, and has the following characteristics for its primary item:
Demand = 25,000 units/year
Ordering cost = $30/order
Holding cost = $8/unit/year
Lead time = 2 weeks
Standard deviation in weekly demand = 100 units
A normal distribution table is shown below.
Use the information in Table 12.4. What is the length of their order cycle if they order the economic order quantity each time?
Less than four days
Between four and five days
Between five and six days
Greater than six days
Question 3
You are the operations manager of a firm that uses the continuous-review inventory control system. Suppose the firm operates 52 weeks a year, 365 days, and has the following characteristics for its primary item:
Demand = 25,000 units/year
Ordering cost = $30/order
Holding cost = $8/unit/year
Lead time = 2 weeks
Standard deviation in weekly demand = 100 units
A normal distribution table is shown below.

Use the information in Table. What is the reorder point for this item if they use a 95% service level?
1,046 units
170 units
1,194 units
68 units
Question 4
You are the operations manager of a firm that uses the continuous-review inventory control system. Suppose the firm operates 52 weeks a year, 365 days, and has the following characteristics for its primary item:
Demand = 25,000 units/year
Ordering cost = $30/order
Holding cost = $8/unit/year
Lead time = 2 weeks
Standard deviation in weekly demand = 100 units
A normal distribution table is shown below.

Use the information in Table. If this form uses an EOQ model for purchase decisions, which change would result in the biggest increase in order quantity over the amount required by the original data?
The cost of ordering rises to $50 per order.
The holding cost drops to $5 per unit per year.
The annual demand soars to 30,000 units per year.
The lead-time increases to three months.
Question 5
Peterson Enterprises uses a continuous review inventory control system. The firm operates 50 weeks per year and has the following characteristics for an item:
Demand = 50,000
Ordering cost $35/order
Holding cost = $2/unit/year
Lead time = 3 weeks
Standard deviation in weekly demand = 125 units
A normal distribution table is shown below.

Use the information in Table. What is the EOQ for this item?
Fewer than 1,100 units
Between 1,100 and 1,200 units
Between 1,200 and 1,300 units
More than 1,300 units
Question 6
1. Cynthia Korinsky, manager of a large medical supply house that operates 50 weeks per year and five days per week, has decided to implement a periodic review system for all class A items. One such item has the following characteristics:
Demand = 10,000 units per year (or 40 units per workday)
Order cost = $50 per order
Holding cost = $5 per unit per year
If Korinsky wishes to minimize total cost (thereby approximating the EOQ), what should be P, the number of workdays between orders?
Fewer than or equal to 10 days
Greater than 10 days but fewer than or equal to 12 days
Greater than 12 days but fewer than or equal to 14 days
Greater than 14 days
Question 7
Demand = 5,200 units/year
Standard deviation of weekly demand = 11 units
Ordering costs = $45/order
Holding costs = $2/unit/year
Cycle-service level = 90% (z for 90% = 1.28)
Lead time = 3 weeks
Number of weeks per year = 52 weeks
Use the information in Table. The firm decided to change to the periodic review system to control the item's inventory. For the most recent review, an inventory clerk checked the inventory of this item and found 500 units. There were no scheduled receipts at the time. How many units should be ordered? (HINT: Use the EOQ model to derive P, the time between reviews.)
0 units
Between 1 and 300 units
Between 301 and 600 units
Above 600 units
1 points
Question 8
Demand = 5,200 units/year
Standard deviation of weekly demand = 110 units
Ordering costs = $45/order
Holding costs = $0.50/unit/year
Cycle-service level = 90%
Lead time = 2 weeks
Number of weeks per year = 52 weeks
A normal distribution table is shown below.

Use the information in Table 12.7. A firm uses the periodic review system to control the item depicted above. It reviews the item's status every three weeks (P = 3). At the most recent inventory review, an inventory clerk found 1,500 units. There were no scheduled receipts and no backorders. How many units should be ordered? (Hint: You must calculate T before answering this question.)
0 units
Between 1 and 3,750 units
Between 3,751 and 4,000 units
Greater than 4,000 units
Question 9
Demand = 5,200 units/year
Standard deviation of weekly demand = 110 units
Ordering costs = $45/order
Holding costs = $0.50/unit/year
Cycle-service level = 90% (z for 90% = 1.28)
Lead time = 2 weeks
1. Number of weeks per year = 52 weeks
A normal distribution table is shown below.
Use the information in Table. What is the EOQ for this item?
Between 1 and 1,500 units
Between 1,501 and 3,000 units
Between 3,001 and 4,500 units
Greater than 4,500 units
Question 10
1. Under a cycle counting system for checking inventory accuracy:
the length of the time between orders determines which items are counted most frequently.
the A items are counted most frequently.
the items with the highest holding cost are counted most frequently.
the items that have been withdrawn last are counted most frequently.