Reference no: EM132608945
ITC513 Wireless Networking Concepts - Charles Sturt University
Learning outcome 1: be able to critically analyse wireless networking concepts and their applications in real life situations.
Learning outcome 2: be able to analyse and describe wireless signalling techniques and radio frequency communications.
Learning outcome 3: be able to compare and contrast different wireless networks in terms of size, speed, limitations and applications.
Assessment - Tasks and Design Project
Task 1: Free Space Propagation and Path Loss
In a free space wireless propagation environment, transmit power between a transmitter and receiver usually decreases due to free space path loss denoted as Lf(dB) and can be expressed as a function of distance d between the transmitter and receiver. Your task is to calculate and plot the path loss Lf(dB) for a distance d = 0to 30km and carrier frequency fc = 200, 500 and 1500 MHz. Assuming that the transmit powerPt is 100 watts, you can calculate and plot the received power Pras a function of distance d (as given above) for the carrier frequencies given above. You can assume transmit and receive antennas gains are the same, i.e. Gt = Gr = 0dB .
Deliverable: You are required to plot path loss Lf(dB) as a function of distance for each carrier frequency, so you will have three curves in the plot. You also need to plot received power Pras a function of distance d for each carrier frequency, so you will have three curves of the received power. You need to submit your executable GNU Octave code along with the plots in a single Word file.
Task 2: Research Project
1. You are working as Network Design Engineer with local service provider and your manager has asked you to propose the design for the below cellular architecture shown in Figure 1. In your design provide the following information with reasons; Base station sites locations, Antenna specification (such as antenna shape, height, gains etc), mention the type of the area considering the cell size (such as suburban, metropolitan, rural etc) and justify you design. Note that the numbers within each cell are representing the traffic density in Erlang.
2. Looking at the figure below, justify the design of this cellular network with appropriate reasoning?
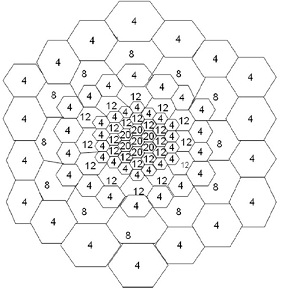
Figure 1: Cellular Architecture
Task 3: Viva Questions
Your lecturer will ask questions from Task 1 and Task 2 in the class or online meetings after the due date of the assignment. Viva will be conducted between 7th and 20th September. Please make an appointment with your lecturer. If you fail to give the viva between the abovementioned dates you may get zero marks for Task 3.
Assessment - Task and Research Project
Task 1: Wireless Channel Capacity Calculation
Task 1(a) - Wireless communication systems are often modeled under the free-space assumption. As a wireless communication expert, you will be required to find the capacity of a given wireless link. One such link is shown in the following figure, which operates in the 3 GHz frequency band using a bandwidth of 20 MHz. The transmitter is at a distance of 3 km from the receiver. Given that the system uses a transmit power of +30dBm, and the receiver has a noise power of +5dBm, calculate the capacity of this wireless link in bps (bits per second).

Figure for Task 1(a): Wireless link under free-space assumption
Task 1(b) - Under the same scenario as given in part (a), now assume that an interferer is also present in the surroundings of the receiver, as shown in Figure 1(b). The interferer is at a distance of 5 km from the receiver, and uses a transmit power of +50dBm. Assuming that the interferer's transmission is treated as noise at the receiver, calculate again the capacity of the wireless link in bps (bits per second).
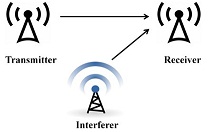
Figure for Task 1(b): Wireless link in presence of Interferer and under free-space assumption
Task 2: Innovative Research Project
A local engineering group has asked you to present your findings of some of the most recent wireless technologies for future communication systems. A list of these potential technologies is given as follows:
• Millimetre Wave (mmWave) Communications
• Enabling Technologies for 6G
• Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IRS)
• Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) for Wireless Communications
• Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC) Systems
• Machine Learning for Wireless Communication
• Simultaneous Wireless Information & Power Transfer (SWIPT) Systems
• Industrial Internet-of-Things (IIoT)
• Tera-Hertz Communication systems
• Autonomous vehicles
• Intelligent Transport system
• Emerging wireless technologies and Dark web
• 5G - Trends and Technologies
• Smart Cities
Research these technologies, paying specific attention to one of them. You should consider their applications in future communication systems, strengths and weaknesses, and their security issues among other details. You should also provide an opinion regarding the popularity and adoption of your chosen technology in the near future.
Deliverable: You need to provide a report on your selected wireless communication technology. The report should include Abstract, Introduction, Body of the report that may include sections such as real life applications, advantages and challenges, security issues etc (body of the report vary for each student), conclusion and references. Your report should not be more than four A4 pages long including everything, i.e. from first page to the last page of references. In general, four A4 pages with the font size of 11 may have 2000 words
You need to provide at least three recent reference articles to your technology of choice.
The report has 6% of the total Task 2 weight-age.
You are also required to give a short upto 10 minutes oral presentation during the online meeting or in the class. Your lecturer will schedule a time for your oral presentation. Your presentation should have a maximum of 10-12 slides. The presentation has 4% of the total Task 2 weight-age.