Reference no: EM13966524
1. A binary adder is shown in Figure 1. The adder, on test inputs may be showing unintended results. Actually, the input values are: A = 1, B = 0, C = 1; and the output values are: D = 0 E = 0.
(a) Construct a weak-failure model of the circuit using PROPOSITIONAL LOGIC, that is a model that allows for faulty components. Explain each formula and its role in the model.
(b) You want to obtain minimal conflicts, that is, sets of components that cannot be all simultaneously working well at the light of the observation. (Minimality means in this case that no proper subset of a conflict is a conflict.)
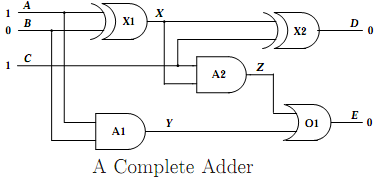
Explain your methodology based on automated reasoning a` la Prover9 for obtaining such conflicts, in particular, how you make sure they are minimal.
(c) Use Prover9 to obtain all possible minimal conflicts. Show the main ingredients of the input file, with an explanation. Do the same with the output file, interpreting and explaining the results.
(d) Assume that a second test is performed (in addition to the first one). Now the values are: A = 1, B = 1, C = 1, and D = 0, E = 0. Now, using both sets of observations, find minimal conflicts through new Prover9 input, run and output.
Explain how and with what results you used the new informa- tion. Analyze the results in comparison with the previous diagnoses.
|
Write a communication plan including all stakeholders
: Write a communication plan including all stakeholders in a cookie bakery where sales was going down because customers started logging complaints in the last 15 days.
|
|
Transition probability matrices
: (a) Xn D the number of sixes obtained up to the nth roll; (b) Xn D the number of rolls, at time n, that a six has not been obtained since the last six. Prove or disprove that each fXng is a Markov chain, and if they are, obtain the transition probabi..
|
|
How tactical analysis can prevent and deter crime
: Tactical Analysis: Explain how tactical analysis can prevent and deter crime. Explain the differences of patterns, series, and trends, and discuss modus operandi
|
|
Subsequences of markov chains
: Suppose fXng is a stationary Markov chain. Let Yn D X2n. Prove or disprove that fYng is a stationary Markov chain. How about fX3ng? fXkng for a general k?
|
|
Construct a weak-failure model
: Construct a weak-failure model of the circuit using PROPOSITIONAL LOGIC, that is a model that allows for faulty components. Explain each formula and its role in the model.
|
|
Explain the hazards of chemical burns
: Explain the hazards of chemical burns other than tissue damage.
|
|
What other factors affect decisions to migrate
: Read: Lee, Everett S. 1966. "A Theory of Migration." Demography 3(1): 47-57. Give an example of a push factor and an example of a pull factor. What other factors affect decisions to migrate?
|
|
Find the range of speed of the governor in the position
: In a porter governor, the mass of the central load is 18 kg and the mass of each ball is 2 kg. The top arms are 250 mm while the bottom arms are each 300 mm long. The friction of the sleeve is 14 N. If the top arm makes 450 with the axis of rotati..
|
|
List some examples of organic solvents
: List some examples of organic solvents, and discuss how they are hazardous and what protective measures can be used to control exposure.
|