Reference no: EM131195027
Biochemistry Assignment-
Q1. Which techniques will be used to separate each of the following proteins from the Crude Cell lysate which contains the mentioned proteins? Take one protein at a time and write down the sequence of events that you will undertake to separate that particular protein and then go onto the next one. Explain why you have used this method as well.
|
Protein
|
Concentration of ammonium sulfate (AS) required for precipitation
|
Molecular Weight (KDa)
|
Isoelectric point (pI)
|
|
1
|
45%
|
38
|
3.7
|
|
2
|
80%
|
22
|
4.8
|
|
3
|
65%
|
4
|
5.3
|
|
4
|
20%
|
75
|
6.8
|
|
5
|
30%
|
55
|
9.50
|
|
β-galactosidase
|
45%
|
115
|
5.3
|
Q2. It is the year 1986 and you have just discovered a new virus. You have also learned that many patient harbor antibodies against this virus, indicant exposure to the virus. Some of these patients have skin lesions and others have malignant lymphoma. You plan to devote a significant amount of time to the study of this virus and will investigate whether the virus is the causative agent of these disorders.
Fun you determine the genome sequence of the virus. Ned you develop a strategy to identify regulatory regions in the viral genome. In the figure below, the thick black line represent the viral genomic DNA the squiggly lines represent viral mRNAs, and the thin lines with letters attached are segment of viral DNA that you have hued to a reporter gene. The thin lines are accurately positioned relative to the DNA sequence of the viral genome above, as much as Word will allow.
In your experiment, you have generated 10 different constructs (plasmids, recombinant DNA) to test. Assume everything is put together correctly. You introduce each of these 10 constructs into human cells and score for relative GFP production along with a control plasmid that has no viral sequence (+++ is high level of GFP, + is low level, - cells are not green). Hence is your data:
|
construct
|
GFP level
|
construct
|
GFP level
|
|
A
|
+
|
F
|
+
|
|
B
|
+
|
G
|
+
|
|
C
|
+
|
H
|
+
|
|
D
|
+++
|
I
|
+
|
|
E
|
+
|
J
|
--
|
|
Control
|
--
|
|
|
For which of the constructs above, if any, do we have evidence for promoter activity:
For which of the constructs above, if any, do we have evidence for enhancer activity:
Q3. Unlike prokaryotic RNA polymerases, eukaryotic RNA polymerase II requires the assistance of transcription factors. In the last century, biochemical approaches were undertaken that allowed for the purification and analysis of General Transcription Factors. These factors assist the various RNA polymerases in transcription initiation, elongation, and termination. TFII is a prefix that is placed before those transcription factors that assist RNA polymerase II.
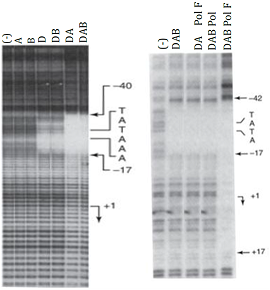
The figure displays some of the DNA foot printing experiments. These experiments made use of purified DNA of known sequence and protein material composed of TFIID, TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIIF and RNA Polymerase II (abbreviated D, A, B, F, and Pol, respectively). The purified proteins that are present in each foot printing reaction are indicated above the gel picture. From the data, construct a model that indicates an ordered binding series. Who binds to what? Who binds first? Who binds second? Does X need Y in order to bind? (I am not asking you to explain how this experiment was done; I am asking you to interpret the data.)
Q4. For the attach paper write down its abstract and highlight the important finding. You also need to explain the experiments being conducted and what will be the nest set of experiments that you will perform.
Attachment:- Paper.rar