Reference no: EM13116389
Following are selected accounts for Green Corporation and Vega Company as of December 31, 2010. Several of Green's accounts have been omitted.
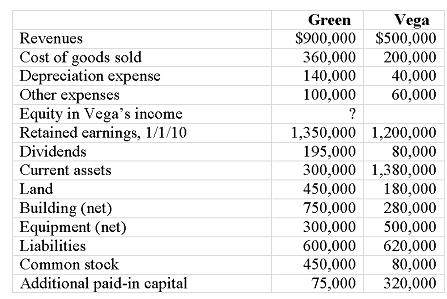
Green obtained 100% of Vega on January 1, 2006, by issuing 10,500 shares of its $10 par value common stock with a fair value of $95 per share. On January 1, 2006, Vega's land was undervalued by $40,000, its buildings were overvalued by $30,000 and equipment was undervalued by $80,000. The buildings have a 20-year life and the equipment has a 10-year life. $50,000 was attributed to an unrecorded trademark with a 16-year remaining life. There was no goodwill associated with this investment.
5. Compute the book value of Vega at January 1, 2006.
A. $997,500
B. $857,500
C. $1,200,000
D. $1,600,000
E. $827,500
6. Compute the December 31, 2010, consolidated revenues.
A. $1,400,000
B. $800,000
C. $500,000
D. $1,590,375
E. $1,390,375
7. Compute the December 31, 2010, consolidated total expenses.
A. $620,000
B. $280,000
C. $900,000
D. $909,625
E. $299,625
8. Compute the December 31, 2010, consolidated buildings.
A. $1,037,500
B. $1,007,500
C. $1,000,000
D. $1,022,500
E. $1,012,500
9. Compute the December 31, 2010, consolidated equipment.
A. $800,000
B. $808,000
C. $840,000
D. $760,000
E. $848,000
10. Compute the December 31, 2010, consolidated land.
A. $220,000
B. $180,000
C. $670,000
D. $630,000
E. $450,000
Difficulty: Medium
11. Compute the December 31, 2010, consolidated trademark.
A. $50,000
B. $46,875
C. $0
D. $34,375
E. $37,500
12. Compute the December 31, 2010, consolidated common stock.
A. $450,000
B. $530,000
C. $555,000
D. $635,000
E. $525,000
13. Compute the December 31, 2010, consolidated additional paid-in capital.
A. $210,000
B. $75,000
C. $1,102,500
D. $942,500
E. $525,000
14. Compute the December 31, 2010 consolidated retained earnings.
A. $1,645,375
B. $1,350,000
C. $1,565,375
D. $2,845,375
E. $1,265,375
15. Compute the equity in Vega's income reported by Green for 2010.
A. $500,000
B. $300,000
C. $190,375
D. $200,000
E. $290,375