Reference no: EM1378282
Question 1:
Martinez Plastics Company makes just two product lines, plastic casings for pens and plastic casings for cell phones.
Based on new information, management has adjusted the percentages that apply to the first stage of the ABC system as shown below.
Requirement
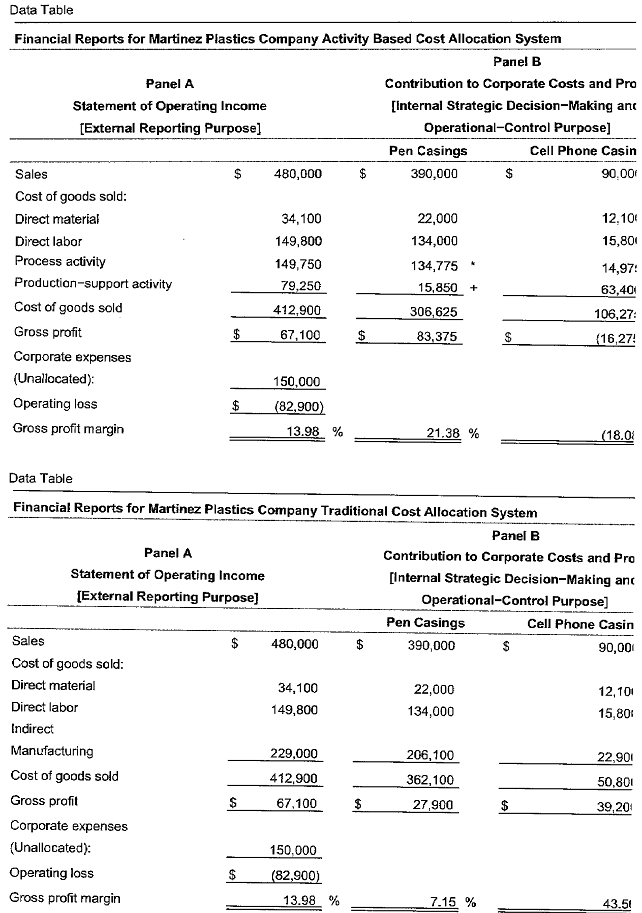
1. Prepare a schedule that shows the gross margin for both products.
Begin by allocating the indirect resources to the cost pods. First identify the formula labels, then compute the activity cost.
Total indirect cost x Percent of indirect resource used =
Plant and machinery 189,000 x 90% =
Engineering costs 40,000 x 30 % =
Processing activity cost
Next, identify the formula labels, then compute the allocated production support cost.
Total indirect cost x Percent of indirect resource used =
Plant and machinery 189,000 x 10 % =
Engineering costs 40,000 x 70 % =
Production support cost
Prepare a schedule that shows the gross margin for both products. (Use parentheses or a minus sign for a d Financial Reports for Martinez Plastics Company Activity Based Cost Allocation System
Question 2:
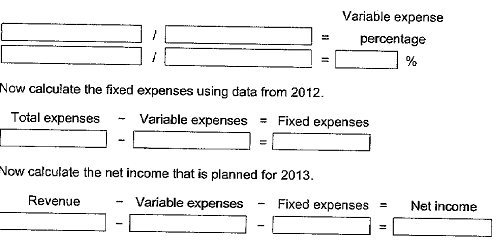
Allendale Prep School, a private high school, is preparing a planned income statement for the coming academic year ending August 31, 2013. Tuition revenues for the past two years ending August 31 were as follows: 2012, $830,000; and 2011, 5870,000. Total expenses for 2012 were $820,000 and in 2011 were $837,600. No tuition rate changes occurred in 2011 or 2012, nor are any expected to occur in 2013. Tuition revenue is expected to be S820,000 for 2013.
Requirement
1. What net income should be planned for 2013, assuming that the implied cost behavior remains unchanged?
Let's begin by determining the variable expense percentage.
Question 3:
Requirement
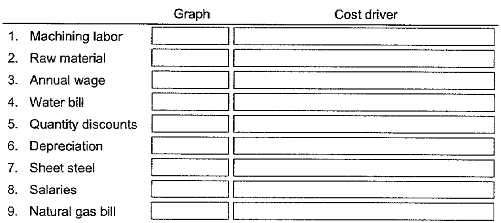
1. Indicate by letter which graph best fits each of the situations described. The graphs may be used more than once. Next to each number-letter pair, identify a likely cost driver for that cost
Situations
1. Cost of machining labor that tends to decrease as workers gain experience
2. Price of an increasingly scarce raw material as the quantity used increases
3. Guaranteed annual wage plan, whereby workers get paid for 40 hours of work per week even at zero or low levels of production that require working only a few hours weekly
4. Water bill, which entails a flat fee for the first 10,000 gallons used and then an increasing unit cost for every additional 10,000 gallons used
5. Availability of quantity discounts, where the cost per unit falls as each price break is reached
6. Depreciation of office equipment
7. Cost of sheet steel for a manufacturer of farm implements
8. Salaries of supervisors, where one supervisor is added for every 12 phone solicitors
9. Natural gas bill consisting of a fixed component, plus a constant variable cost per thousand cubic feet after a specified number of cubic feet are used
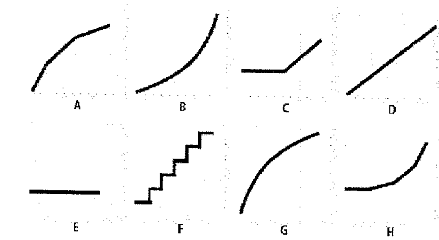
The vertical axes of the graphs represent total dollars of costs incurred, and the horizontal axes represent levels of cost driver activity during a particular time period.