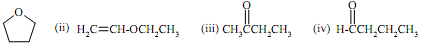Reference no: EM13653
Q1. (a) Write structures for the following molecules:
(i) 2-phenylethanol.
(ii) 2-methyl-2-propen-1-ol.
(iii) trans-2-methoxycyclohexanol.
(b) Explain each of the following observations:
(i) 1-Propanol is completely miscible with water, but 1-hexanol is practically insoluble in water.
(ii) Phenol is more acidic than cyclohexanol.
(iii) 1-Butanol and diethylether have the same molecular weights and similar solubility in water, but the boiling point of 1-butanol is 118oC, whereas that of diethylether is 35oC.
(c) Write a step-by-step mechanism for the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 1-methylcyclopentanol. If more than one alkene is possible predict which one will be formed in the largest amount.
(d) Write equations for the following reactions, showing the products formed:
(i) Reaction of 1-hexanol with thionyl chloride (SOCl2).
(ii) Reaction of 3-pentanol with sodium metal.
(iii) Reaction of CH3CH2CH2O- with CH3CH2Cl.
Q2. (a) Provide reagents for the following conversions:
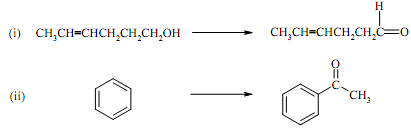
(b) Write an equation for the formation of an acetal from reaction of excess methanol with benzaldehyde in the presence of an acid catalyst, showing all the steps in the mechanism.
(c) Write products for the following reactions:
(i) Addition of hydrazine (NH2NH2) to 3-pentanone.
(ii) Reaction of propanal with methylmagnesium bromide, followed by acid hydrolysis.
(d) Write the structure of the carbanion formed from propanal on treatment with sodium hydroxide, show how it is stabilised by resonance, and write the steps in the aldol condensation reaction of propanal.
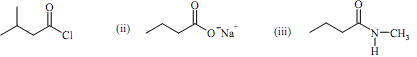
Q3. Name each of the following structures:
(b) The following acid can be prepared from an alcohol, or from a reaction involving a Grignard reagent. Write the steps in both syntheses.
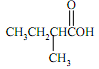
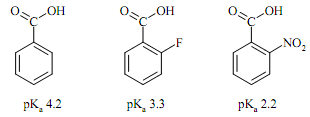
(c) Suggest an explanation for the following pKa values:
Q4. (a) State how the following reaction could be monitored by infrared spectrometry:

(b) A molecule with molecular formula C3H6Br2 shows only a single peak in its 1 H-NMR spectrum. Propose a structure for the molecule.
(c) State the (n+1) rule used for determining splitting patterns in 1 H-NMR and apply it to determine the multiplicity of each absorption expected in the NMR spectrum of the following molecule:
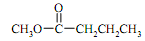
(d) The following 1H-NMR spectrum belongs to one of the isomers (i) to (iv) of formula C4H8O. Assign the spectrum to the correct isomer, explaining the basis of your assignment and why each of the other isomers can be eliminated.