Reference no: EM134657
Use the Black-Scholes option pricing formula to check whether a call option is priced correctly.
Pick any corporation of your choice, whose stock is traded on NYSE (New York Stock Exchange) and which has options written on it.
- There are different sites which give details about companies' options.
- You will find the annualized yield (rate of return) on US Government Treasury bills. The three-month one is the one that is most commonly used to evaluate the annual risk-free rate.
- And current information on the stock.
- Choose any month you like for the option expiration month. Choose any exercise price you like for which the option is in-the-money. The column labeled "Ask" shows the current price at which call options with different exercise prices can be purchased.
- As part of your calculations you will need to calculate σ2, which in the Black-Scholes formula is variance (per year) of the continuous returns on stock. This is the expected stock return volatility between the purchase date and the expiration date. Unfortunately, this represents the future, so there is no way you can know the correct volatility. What traders do instead is estimate this volatility using past data.
Based on the information above, answer the following questions:
1.) What stock (company name) have you chosen? What are the S, E, R, σ2 and T in your Black-Scholes formula? Show calculations, where required, and describe in words how you got each number. Attach print-outs of website pages you used that shows where the information is coming from; highlight the important numbers on your print-outs. (Keep in mind that the information on the websites gets constantly updated, and so if the information is not printed out at approximately the same time the option price results will not be correct.)
2.) Evaluate the intrinsic value of your chosen call option? Calculate and explain.
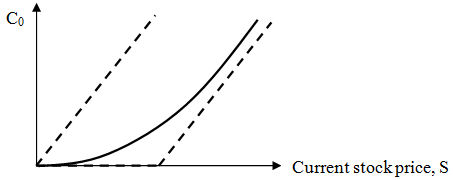
3.)
(a) Is the call option for your stock overpriced or underpriced, according to the Black-Scholes option pricing model? By how much? Calculate and explain. Can you explain why this is the case?
(b) Label on a graph (like the one right below) and put the dollar amounts of
- current stock price for the stock you picked
- exercise price that you picked
- current call option value that you have calculated
- intrinsic value that you have calculated
- time value premium based on your calculations
c.) In order to replicate the payoff of the call option at the expiration date that you selected, how many shares of stock should you buy today, and how much should you borrow at the risk-free rate? Evaluate and explain.
d.) Is the put option for your stock overpriced or underpriced, according to the Black-Scholes option pricing model? Evaluate and explain.