Reference no: EM132306170
Assumptions: Acceleration due to gravity g = 9.81 m/s2
Density of water = 1000 kg/m3
Standard density of air = 1.2 kg/m3
Specific gravity of mercury = 13.63 g/cm3
Question 1. Air passes through a diameter D = 1.5 m ventilation duct at a velocity of 6.5 m/s. Calculate the volumetric flow rate and the mass flow rate. Hint: use assumptions.
Question 2. A ventilation shaft of diameter 5.5 m passes an airflow of 210 m3/sec at a mean density of 1.2 kg/m3 and a mean temperature of 18°. Determine the Reynolds number for the shaft. What the determined Reynolds number will indicate?
Question 3. Air passes through a diameter D=1.5 ventilation duct using a forcing ventilation system. If it is required to deliver 25 m3/s at the end of the duct what is the air velocity in the duct. If the duct has a 15% leakage rate what is the airflow that needs to be developed by the fan supplying the system?
Question 4. During a ventilation survey the cross-sectional area of a mine airway is measured to be 30.25 m2. Anemometer traverses of the airway have been undertaken and the results from four such traverses at the area measuring site indicated that on the first pass a total of 550 m of air was registered on the anemometer. In the second traverse 543 m was measured, in the third 579 m and in the final traverse 556 m. Given that each anemometer traverse was timed over 100 sec, determine the average flow velocity of the air and the air quantity flowing.
Question 5. Measurements of gas concentration at a particular site underground indicate that the concentration of methane in the general body of the air is 0.5%. If 37 m3/s of air is flowing at the site determine the volume of methane present in the airstream?
Question 6. A Pitot-static tube is used to measure air velocity as part of a ventilation survey. At a particular measuring site a velocity pressure of 450 Pa is measured, assuming the air has a density of 1.12 kg/m3 what is the air velocity at that point?
Question 7. A 2 x mech network in Figure 1. A different pressure of 2400 Pa is applied across the circuit and a natural ventilation pressure of 510 Pa acts in the direction of airflow within mash 1. A regulator R6 is constructed in the rightmost branch in order to limit the airflow in branch to 20 m3/s. Given the resistances of all airways, determine the distribution of airflow and the resistance of the regulator.
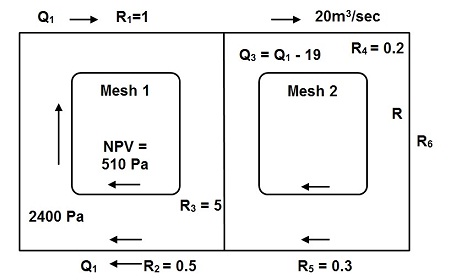
Figure 1. Two-mesh network
Question 8. Describe a method of undertaking a point measurement traverse for airflow in a circular duct using a pitot static tube, are there any standards available for such a traverse?
Question 9. A smoke tube is used to determine the velocity of a slow moving airflow in a drive. The observer has recorded a travel time of 75 sec over a measured distance of 9 m. Calculate the appropriate average air velocity in the drive.
Question 10. The instantaneous liberation rate of methane in a room being advanced by a continuous miner varies from 0.05 m3/s to 0.28 m3/s. Calculate the quantity of fresh air containing no methane that must be delivered to the working place to maintain continuously the methane concentration at the face at less than 0.5%.
Question 11. A tunnel in a mine is 2000m m in length and has a cross-sectional area of 30.25 m2 and a perimeter of 22 m. If the friction factor for the airway is 0.004 kg/m3, determine the resistance of the airway.
Question 12. A rectangular 5 x 5.6 m tunnel is 1050m in length and contains two right angled bends with a centre-line radius of curvature of 3.5 m. The tunnel is unlined but is in good condition with the major irregularities having been trimmed away. The tunnel is required to pass 65 m3/s of air with a density of 1.25 kg/m3. Calculate the airway resistance and the frictional pressure drop.
Question 13. Measurements from a ventilation survey indicate that along a particular tunnel a pressure drop of 0.05 kPa for a flow of 75m3/s. If the tunnel is 600m in length and is a 5.5 x 6 m airway what is the friction factor of the tunnel?
Question 14. Two mine airways with resistances of 0.75 Ns2/m8 and 1.2 Ns2/m8 are connected in series determine the resistance of the series combination. If the airflow through these airways is 36 m3/s, what is the pressure drop in each of the airways and the total pressure drop in the series combination of airways?
Question 15. A mine has a total airflow requirement of 250 m3/s. If the equivalent resistance of the workings is 0.49 Ns2/m8 determine the pressure to be developed by a single mine fan to ventilate the workings.
Question 16. It was proposed to split a part of an underground mine into two ventilation branches connected in parallel across the bottoms of two shafts as shown in Figure 2.
Determine for each airway:
• the airflow
• frictional pressure drop
Hint: assume the Square Law and equivalent resistance for the 2 parallel branches
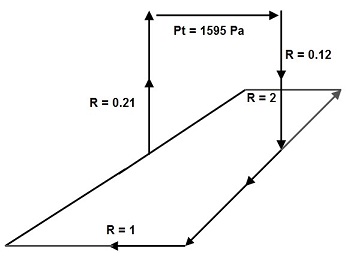
Figure 2.
Question 17. A working area of a mine has diesel equipment operating within it. The maximum diesel loading is 810 kW. The same section of the mine also has a methane inflow of 0.22 m3/s flowing into it. If the maximum permissible methane concentration in the general body of the air is 0.5% and the design diesel air quantity is 6 m3/s per 100 kW of installed diesel power, determine the required ventilation flow rate for the working area.
Question 18. Determine the characteristic curves for the fan shown in Figure 3 for the following cases:
a) Three fans in series
b) Two fans in parallel
c) Four fans in a 2 x 2 series parallel combination
Figure 3. Fan Characteristics Curve
Question 19. For the fan curve for static pressure in Figure 3 determine the
• static pressure
• quantity
• Total efficiency
curves if the fan were working at 1200 rpm.
Question 20. A worker in a development drive is working at a rate of 270 W/m2. If the air velocity passing over the worker is 0.6 m/s, the air dry bulb temperature is 35°C, the air wet bulb temperature is 32°C, radiant temperature of the surroundings is 35°C, and it can be assumed that the worker's skin temperature is 34°C, if the barometric pressure is 110 kPa determine:
• The air-cooling power
• The basic effective temperature
Is the working environment safe?
Question 21. During a 40 hour underground working week radiological monitoring indicates that a miner is subjected to the following levels and periods of exposure to radon daughters
• 20 h at 0.14 WL
• 10 h at 0.20 WL
• 10 h at 0.35 WL
Determine the cumulative exposure in WLM for that week.
Question 22. In a given stope 270 m2 of ore and 210 m2 of barren rock (waste) surface are exposed. The stope also contains 1050 tonnes of broken ore. Assuming the ore has a density of 3000 kg/m3, determine the rate of emanation into the stope given the following:
• J (ore) = 540 pCi/m2s
• B (ore) = 580 pCi/m3s
• J (waste) = 80 pCi/m2s
Question 23. The airflow is 90 m3/s in a 1600m long airway of perimeter 22 m and cross-sectional area 26 m2. If the initial concentration of radon in the airway is 26 pCi/l, there is an initial radon daughter activity of 0.05 WL at the entry and the rate of emanation J = 430 pCi/m2, determine the following:
• The working level of radon daughters at exit due to the initial radon
• The activity of radon daughters at outlet due to radon emitted from the rock surfaces
• The activity of radon daughters at outlet due to decay of radon daughter products available at entry
• The total working level of radon daughters leaving the airway
Question 24. Air enters an airway at the rate of 60 kg/s with a dry bulb temperature of 21 °C and a wet bulb temperature of 17°C at a pressure of 100 kPa. This air flows along the airway initially picking up 320 kW of heat and 120 g/s of moisture from the surrounding strata. The air subsequently flows over a number of items of machinery where it is heated at constant moisture content to a dry bulb temperature of 31.5°C.
Following the machinery, the air is split into two flows. Now 20 kg/s of the total flow passes through an air cooler in which the air-dry bulb temperature is 23 °C with the wet bulb temperature reduced to 14°C. The remainder of the flow is heated at a constant dry bulb temperature to an enthalpy of 71 kJ/kg. The two airflows are then recombined prior to the airflow being passed to another airway. Using the provided psychrometric chart, calculate:
• The dry and wet bulb temperatures of the airstream immediately upstream of the machinery.
• The heat input from the machinery.
• The heat removed and the rate of condensation of water from the airstream passing through the air cooler.
• The wet bulb temperature of the airflow, which does not pass through the air cooler.
• The dry and wet bulb temperature of the recombined airstream at the exit of the airway.
Question 25. A moist airstream with a pressure of 100 kPa has an initial dry bulb of 26°C and a wet bulb of 23°C. Use the 100 kPa psychrometric chart to calculate the end dry/wet bulb to this original airstream when subjected to the following processes from the initial air state in each case:
• Heating at constant moisture content, raising the specific enthalpy by 9 kJ/kg.
• Enthalpy increase of 9 kJ/kg, moisture content increases to 20 g/kg.
• Constant dry bulb cooling to a moisture content of 0.01 kg/kg.
• Constant dry bulb heating to a relative humidity of 90%.
• Constant wet bulb (and sigma heat) process to a relative humidity of 30%.
• Constant wet bulb process to saturation.
• Constant moisture content process to saturation.
Question 26. The following two airstreams mix at the junctions of two roadways. The first airstream has a mass flow of 36 kg/s and a dry/wet bulb of 32/24°C, the second airstream has a mass flow of 16 kg/s and a dry /wet bulb of 31/21 °C. The pressure is 100 kPa. Determine the dry/wet bulb temperatures of the mixed airstream.
Question 27. What methods are available to control dust in mines?
Question 28. What is dpm? What is ndpm? What limits exist in Australia in terms of worker exposure?
Question 29. The conditions at the entrance to a crosscut are temperatures, 29°C wet bulb and 35°C dry bulb and barometric pressure 110 kPa. At the exit of the crosscut the temperatures are 30°C wet bulb and 32°C dry bulb and the barometric pressure 110 kPa. The volume flow at the entrance is 34 m3/s. Determine the following
• the water picked up in litres per day
• the heat picked up by the air in kW
• The increase in relative humidity.
Question 30. A mine has been sealed for some time following a fire. The atmosphere has stabilised and a typical analysis is
CO2 1.0% CH4 3.82%
O2 17.25% H2 0.0%
CO 0.035% N2 77.9%
Determine
- Graham's ratio and its implication
- Trickett's ratio and its implication