Reference no: EM13810108
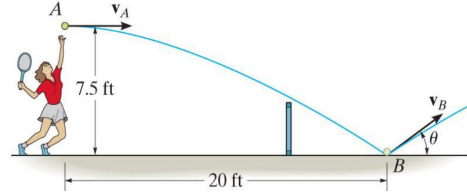
Q1 ) It was observed that a tennis ball when served normontally 7.5 ft above the ground strikes the smooth ground at B 20 ft away. Determine the initial velocity V A of the ball and the velocity v9 (and 0) of the ball just after it strikes the court at Blake e = 0.7.
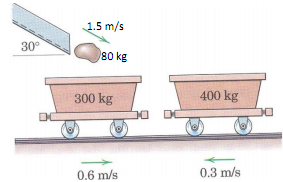
Q2) A 80-kg boulder leaves the delivery chute with a speed of 1.5 m/s (as shown) and lands in a 300-kg mine car (car 1) which was moving on a horizontal track with a speed of 0.6 m/s. Assume the boulder instantly comes to rest relative to the car on impact. Later, the carl-boulder system collides head-on with a 400-kg car 2 moving with a speed of 0.3 m/s (as shown). Calculate the velocity of the cars after collision. Coefficient of restitution, e, for the car-car impact is given as 0.7.
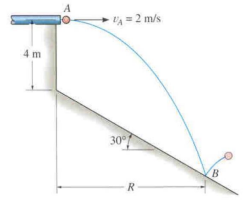
Q3) A 0.5 kg ball is ejected (see figure) from the tube at A with a horizontal velocity v = 2 m/s.
Coefficient of restitution for impact is given as e = 0.6. Find the distance R where the ball strikes the smooth inclined plane and the velocity (i.e. magnitude and direction) of its bounce. Assuming the collision time was 8 milliseconds, compute the average normal force exerted on the ball by the incline during collision.
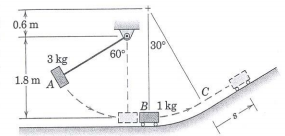
Q4) The 3-kg block A is released from rest in the 60° position shown and subsequently strikes the 1-kg cart at B (direct central impact). If the coefficient of restitution for the collision is e = OS, determine the distance s traveled along the incline past point C before the cart B stops. The incline (i.e. the path C onwards) is rough with a coefficient of friction μk = 0.15. Assuming the collision time was 8 milliseconds, compute i) average force of impact on B ii) average force of impact on A.
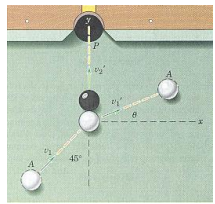
Q5) In a pool game the cue ball A must strike the eight ball in the position shown in order to send it to the pocket P with a velocity 1,1. The cue ball has a velocity vl before impact and a velocity vi after impact. The coefficient of restitution is 0.9. Both balls have the same mass and diameter. Calculate the rebound angle 0 and the % of kinetic energy lost during impact.
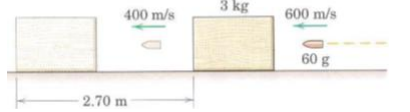
Q6) A 60-g bullet is fired horizontally with a velocity v1 = 600 m/s into the 3-kg block of soft wood initially at rest on the horizontal surface. The bullet emerges from the block with the velocity v2 = 400 m/s, and the block is observed to slide a distance of 2.7 m before coming to rest. Determine the coefficient of kinetic friction ilk between the block and the supporting surface.
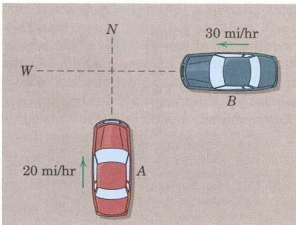
Q7) Car B weighing 3200 lb and traveling west at 30 mi/hr collides with car A weighing 3400 lb and traveling north at 20 mi/hr as shown. If the two cars become entangled and move together as a unit after the crash, compute the magnitude v of their common velocity immediately after the impact and the angle θ made by the velocity vector with the north direction.