Reference no: EM13495448 , Length: 20
Consider such a PAM signal
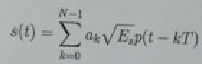
where T is the signaling rate, and E, is the energy per symbol.
In class we chose the at as - I or 41, i.e., binary PAM. but in practice higher levels of
PAM arc used.
1) Use a Nyquist pulse with a = 0.2 can calculate the spectral efficiency. i.e.. the number of transmitted bits per unit bandwidth (or binary PAM, 4-PAM, and I28-PAM
2) The error probability of 2-PAM was computed in the flats on Page 58 in terms of E, and Na. Compute the bit error probability for binary PAM, 4-PAM. and 128-PAM in terms of bit energy Es and Na.
3) In PAM we are sending one symbol per time. rather then two as in DSB. However. nothing prevents us from viewing the even symbols and the odd symbols as two separate channels. Draw a block diagram that interprets this and transmits 64 QAM over the two channels.
4) Now, take your 64 signal points from 3), and eliminate half the points such that for each point its nearest neighbors are removed. Draw the resulting 32-point constellation it is called a 32-dither PAM constellation. Can you compute its bit error rate and compare with those in 2)?