Reference no: EM132955215
Question 1
(i) Write a brief essay (not longer than 2 A4 pages) about the Ethernet.
(ii) A 100-Mb/s Ethernet coaxial cable line is 3-km long. If the signal propagation speed in the cable is 200,000 km/s, calculate how long it takes for a bit to be transmitted from a transmitting host at one end of the network to the receiving host at another end if is there is a 5 ?s one-way total delay in the bus cable equipment?
(iii) Calculate the minimum frame size which is required by the CSMA/CD protocol in the Ethernet described in the part (ii).
Question 2
(i) Calculate the ratio of useful data to the entire frame size in a classic Ethernet frame containing 26 bytes of the data received from the Network Layer.
(ii) Calculate the ratio of useful data to the entire frame size in a classic Ethernet frame containing the largest possible amount of the data.
Question 3
A company is going to undertake a big development project for an air-space industry which will be divided between a few groups, each working on a particular task (e.g. designing a wing, developing an engine, developing cabin equipment, etc.). The project will be managed by a chief designer who will oversee the overall progress, but it also requires intensive interaction within each group. Each group will have its own manager. What a network structural model would you advise to be employed by the company in this case? Explain why. Support your conclusion by drawing an example of such network.
Question 4
(ii) The point-to-point link which is a part of a more complex network connects two hosts, H1 and H2, via two routers R1 and R2, as is shown in the Figure 3.1 below. Both hosts H1 and H2 use the IPv4 protocol. The packets are transmitted between H1 and H2 over the non-IPv4 links in frames with a 24-byte header. The link between the Host 1 and the router R1 has the MTU of 600 bytes (including the 24-byte frame header), the link R1 - R2 has the MTU of 512 bytes (including the 24-byte header), and the link between R2 and Host 2 has the MTU of 800 bytes (including the 24-byte header). The transport layer at the Host 1 passes to its IPv4 Network Layer a datagram which contains 1300 bytes of the data and 20 bytes of the TCP header for transmission to the Host 2. Calculate the sizes of all fragments for each link, (Host 1 - R1), (R1 - R2), and (R2 - Host 2), assuming that the network operates in a transparent fragmentation mode.

Figure 3.1.
Question 5
(i) A business has been assigned by its ISP a class B network address space and requires 20 subnets. It is necessary to have as many addresses available as possible for hosts in each subnet. Find what subnet mask should be used, and state how many hosts are possible in each subnet.
(ii) The value of IHL field in a particular IPv4 datagram is 10 (in decimal system). How many Option bytes are present in the datagram?
Question 6
(i) The class C network is going to be sub-netted using the subnet mask 255.255.248.0. Find the maximum possible number of subnets, and thus calculate the maximum total number of hosts that can be supported by the sub-netted network.
(ii) A company has been allocated the 168.135.0.0/16 class B network address space. It is necessary to support maximum 900 hosts per subnet and accommodate the maximum number of subnets possible. Find the subnet mask which should be used.
(iii) Find the number of subnets supported by the mask you obtained in the part (ii).
Question 7
(i) Explain what are advantages and disadvantages of CIDR. Compare the router's operation in networks with and without CIDR.
(ii) A router has received the following new IP Addresses: 102.23.96.0/21, 102.23.104.0/21, 102.23.112.0/21, and 102.23.120.0/21. Assuming that all these addresses use the same outgoing link, can they be aggregated? If yes, to what aggregation address? If not, explain why not.
Question 8
(i) Explain what is the congestion control in computer networks, and how it differs from the flow control.
(ii Explain operation of the ECN (Explicit Congestion Notification) and the CWR (Congestion Window Reduced) algorithms.
(iii) A transport layer of a sender transmits 20 kB of data in 4-kB segments to the receiver. The receiver uses a buffer of 8 kB size. Explain and show schematically how the sliding window (SW) is managed in this transmission.
(iv) Consider the LLC which uses the flag bits with bit stuffing method for data framing. If the sending LLC receives the stream of data shown below, write down the stream of the data as they appear on the line after the framing with the bit stuffing.
Question 9
(i) The current estimate of the RTT (round-trip time) is RTT0 = 10.0 ms and the initial value of the mean deviation (dispersion) D0 = 1.0 ms. The further measurements resulted in the following values for RTT: M1 = 8.0 ms; M2 = 8.0 ms; M3 = 8. ms; M4
= 8.0 ms; M5 = 8.0 ms; M6 = 8.0 ms; M7 = 8.0 ms. Using the Jacobson algorithm cal- culate the RTO corresponding to each measurement (assume the smoothing factor ? = 0.875 for calculation of both the RTT and D).
(ii) Explain what the Retransmission Ambiguity Problem is in connection with dynamic estimation of RTT, and how the problem is resolved in the Karn's algorithm.
(iii) Why does User Datagram Protocol (UDP) exist? Would it not be simpler to just let user processes send raw IP packets without using UDP?
Question 10
(i) A client host sends a W = 1,200-byte file to a server which is L = 1,500 km away over a B = 2.5 Gb/s optical fibre network. Calculate the upper bound of the link efficiency ( LEUB ) for this transmission assuming that the speed of light in optical fibre is c = 200,000 km/s.
(ii) Calculate the
B = 2.5 Mb/s?
LEUB
for the same link as in the part (i) when transmission speed is
Question 11
(i) What is a purpose of Dijksra algorithm? Apply Dijkstra algorithm to compute the shortest path from any one node of your choice to each other node in the network shown in Figure 10.1. The numbers on each line shows the cost of the corresponding line. Show in a table or describe in the text each step undertaken in the calculations. The final routing table should show the obtained routes and their costs.
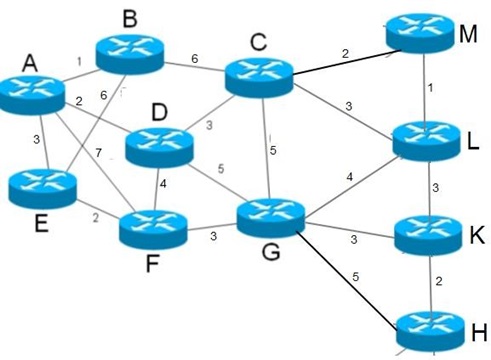
Figure
(ii) Explain the concepts of Autonomous System (AS) and Area in global internetworking. State why is it necessary to have hierarchy in Internet routing through use of ASs, showing why, for example OSPF could not be used over the entire Internet.
(iii) In what particular respect is Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) similar in its fundamental means to RIP? State the major difference between them that overcomes "count-to-infinity" problem of RIP.
Question 12
(i) Explain what is a role of Extension Headers in IPv6 packets and list the six types of Extension Header and state their use. What are the positions of Extension Headers with respect to the Main Header in IPv6 packet?
(ii) The IPv6 uses 16-byte addresses. Assume that a block of 1 billion addresses is allocated every nanosecond (10-9 s). Calculate how long it will take to allocate all IPv6 addresses.
(iii) Explain what is IPSec and where it is used?
(iv) When IPV6 protocol is introduced, does the ARP protocol have to be changed? If so, are the changes conceptual or technical?
(v) What are the Iterative and Recursive Name Resolution protocols? Explain how they are utilised.
Attachment:- Reassessment.rar