Reference no: EM13782437
Problem 1
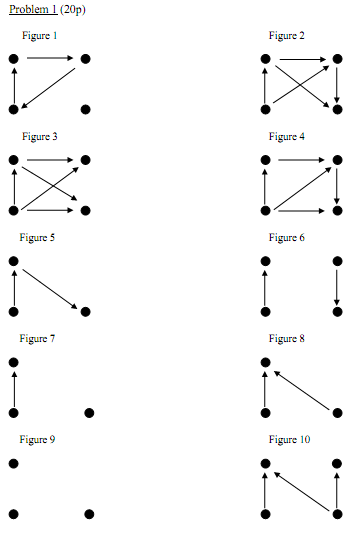
Figures 1-10 above depict preference and indifference relations of ten different people on a set of three or four alternatives. (For each decision maker her set of alternatives constitutes the entire domain of choice.) Alternatives are marked as dots and preferences are marked with arrows: the direction of an arrow is the direction of the preference relation, no arrow between two dots means that an individual is indifferent between these two alternatives.
In each of the ten figures preference relation either is or is not transitive and also, independently of the transitivity of the preference relation, the indifference relation is or is not transitive.
In the following table put "true" or "false" in each of the 20 empty cells.
Problem 2
Assume a voter has a strict preference over any two candidates in the set of Clinton, Obama and Edwards; in other words, it is not the case that he is indifferent between some two candidates in this set. In addition, assume that the voter is not rational.
(1) Prove that a voter who prefers Obama over Clinton has to prefer Edwards over Obama and Clinton over Edwards. Present your reasoning.
(2) Prove that if all voters are not rational then either (i) all of them have identical preferences or (ii) the set of all voters is split into two subsets such that in each subset all voters have identical preferences.
Problem 3
Let's see now how likely would we observe a rational outcome if a decision maker acted randomly. Consider the case of three alternatives X, Y and Z. Assume that deciding between any two of these alternatives, e.g., X and Y, the decision maker rolls a die and depending on the outcome decides Y < X or X < Y or Y ~ X, each with equal probability.
(More specifically, assume that a decision maker takes any two alternatives, say X and Y, and rolls a die; if one or two dots come up he decides that he is indifferent between X and Y, if three or four dots come up he decides that he prefers X over Y and if five or six dots come up he decides that he prefers Y over X. Then he does the same for X and Z and for Y and Z.)
Problem 4
Let's go back to explaining the survey data in which 60% chose Edwards over Obama, 60% chose Edwards over Clinton, 60% chose Clinton over Obama and then when asked to cast a single vote for one of the three candidates, 45% chose Clinton, 30% Obama, and 25% Edwards.
(1) Prove that it is not possible that all voters are rational (have transitive preferences.)
(2) Suppose now that the distribution of votes was not 45% chose Clinton, 30% Obama, and 25% Edwards but 38% Clinton, 32% Obama and 30% Edwards; pair-wise data remains unchanged. Prove that it is possible now that all voters are rational (have transitive preferences) and calculate the percentage of votes for each of the six different orderings of the three candidates.
|
Analyze the crime of burglary
: How has the definition of burglary changed from the old common law definition? Analyze the crime of burglary, including the actus reus and mens rea of burglary
|
|
Examine major issues of conflict and their causes
: Define the context of the conflict, providing relevant history and limitations of study. Examine major issues of conflict and their causes in that context (identifiable from the literature)
|
|
Home and its contents insured under Homeowners policy
: Paul has his home and its contents insured under a Homeowners 3 (special form)policy. He carries $160,000 of insurance on the home, which has a replacement cost of $200,000. Explain the extent to which each of the following losses is covered. (Ignore..
|
|
Lack of intercultural communication and interaction
: What is the cultural phenomenon at play here (what is it called/ term)? How do you explain the lack of intercultural communication and interaction?
|
|
Different orderings of the three candidates
: Prove that a voter who prefers Obama over Clinton has to prefer Edwards over Obama and Clinton over Edwards. Present your reasoning.
|
|
Principles of risk management and insurance
: Michael went deer hunting with Ed. After seeing bushes move, Michael quickly fired his rifle at what he thought was a deer. However, Ed caused the move- ment in the bushes and was seriously injured by the bullet. Ed survived and later sued Michael on..
|
|
Issue for supply chains and transport service providers
: We have all experienced highway congestion and "bumper-to-bumper" traffic, but congestion is a bigger issue for supply chains and transport service providers. Why?
|
|
Implementing the new ccdbg law effectively
: What program impacts or outcomes would you like to see accomplished in the next year based on new provisions within the CCDBG law?
|
|
Biggest challenges from the nigerian case for democracy
: Discuss whether you believe democracy will and can take hold in developing countries of Africa. What are the biggest challenges from the Nigerian case for democracy? When there are many competing interest & ethnic groups in a country such as Niger..
|