Reference no: EM131797042
Effects of Parental Education on Girls' Education Refer to Exercise 10.8. The data table compares 15-year-old girls who are either attending school or have dropped out, in order to understand the impact of parental education on them. Report the observed value of the chi-square statistic.
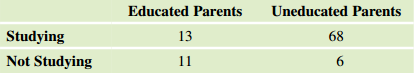
Exercise 10.8
Effects of Parental Education on Girls' Education Refer to Exercise 10.7. This data table compares 15-year-old girls who are either attending school or have dropped out, in order to understand the impact of parental education on them. The table shows the relationship between girls' education and parental education.

a. Find the row, column, and grand totals, and prepare a table showing these values as well as the counts given.
b. Find the percentage of girls who are studying.
c. Find the expected number of girls having educated parents who would study, if the variables are independent. Multiply the proportion overall that were studying times the number of girls having educated parents. Do not round off to a whole number. Round to two decimal digits.
d. Find the other expected counts. Report them in a table with the same orientation as the one for the data.
Exercise 10.7
Effects of Parental Education on Boys' Education A study done by the IZA Journal of Labour Economics in the United Kingdom in 2013 compared 15-year-old boys who are either attending school or have dropped out, in order to understand the impact of parental education on them. The table shows the relationship between boys' education and parental education.
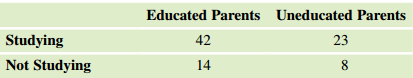
a. Find the row, column, and grand totals, and prepare a table showing these values as well as the counts given.
b. Find the percentage of boys who are studying.
c. Find the expected number of boys having educated parents who would study, if the variables are independent. Multiply the proportion overall that were studying times the number of boys having educated parents. Do not round off to a whole number. Round to two decimal digits.
d. Find the other expected counts using your knowledge so that the expected counts must add to the row and column totals. Report them in a table with the same orientation as the one given for the data.
|
What is the cost of capital for the stock to your firm
: Your firm is planning to issue preferred stock. The stock sell for Rm120; What is the cost of capital for the stock to your firm?
|
|
Variable manufacturing overhead costs
: During its first year of operations, the company produced 54,000 units and sold 47,000 units. The company's only product is sold for $256 per unit.
|
|
Current fair value of the plants
: The current fair value of the plants is $500 million. The plants will be recorded and reported as assets at
|
|
Prepare shetlands journal entry to record taxes
: Shetland Inc. had pretax financial income of $162,420 in 2014. Prepare Shetland's journal entry to record 2014 taxes, assuming a tax rate of 30%.
|
|
Calculate the percentage of girls who are studying
: Find the row, column, and grand totals, and prepare a table showing these values as well as the counts given.
|
|
Use of debt and the interests
: Firms HD and LD are identical except for their use of debt and theinterests rates they pay-- HD has more debt and thus must pay ahigher
|
|
Product cost markup percentage
: Magna Lighting Inc. and sells lighting fixtures. An entry light has a total cost of $125 per unit, of which $80 is selling and administrative expenses.
|
|
Prepare a cash budget for september
: a. Prepare a cash budget for September, October, November, and December b. Are the four monthly budgets that are presented prepared as static or flexible budget
|
|
Find the percentage of boys who are studying
: Find the expected number of boys having educated parents who would study, if the variables are independent.
|