Reference no: EM13910244
1. (a) For the mechanism shown in FIGURE 1 determine for the angle
θ = 45°:
(i) the velocity of the piston relative to the fixed point O (VBO)
(ii) the angular velocity of AB about point A (i.e. ωAB)
(iii) the acceleration of point B relative to A (aBA).
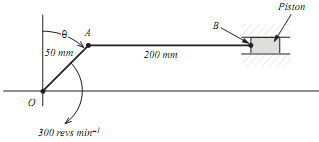
Note: Link AB is horizontal when θ = 45°
(b) Determine the value of the angle θ (measured from vertical) when:
(i) the velocity of point B = 0
(ii) the angular velocity of link AB a maximum.
(c) What is the maximum angular velocity of link AB?
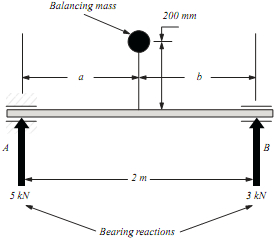
2. (a) A shaft 2 m long rotates at 1500 revs min-1 between bearings as shown in FIGURE 2. The bearings experience forces of 5 kN and 3 kN acting in the same plane as shown. A single mass is to be used to balance the shaft, so that the reactions are zero. The mass is to be placed at a radius of 200 mm from the shaft centre, 180° from the direction of the bearing reactions. Determine the size and position (a and b) of the mass to be used.
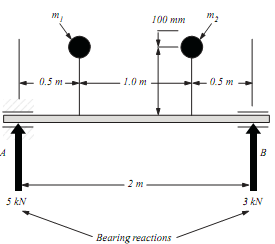
(b) The shaft in part (a) is to be balanced using two masses (m1 and m2) placed 0.5 m and 1.5 m from end A and 180° from the direction of the bearing reactions, each on radius arms 100 mm long. Calculate the sizes of m1 and m2.
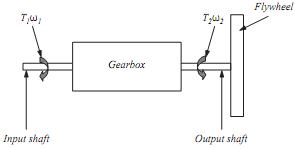
3. A gearbox and flywheel are as shown in FIGURE 4. The output shaft rotates in the opposite direction to the input shaft at 5 times its speed. The gearbox has an efficiency of 92%.
If the flywheel is solid, has a mass of 50 kg, a diameter of 1.5 m and is to accelerate from rest to 300 revs min-1 in 1 minute:
(a) Calculate the torque required at input T1.
(b) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the torque required to hold the gearbox stationary (holding torque Th). Show the direction of the holding torque applied to the shaft with the aid of a sketch.
(c) Plot a graph of the input power against time when taking the flywheel from rest to 300 revs min-1.
|
Paramagnetic behaviour of oxygen
: Explain the paramagnetic behaviour of oxygen on the basis of molecular orbital theory. Give reasons for a large difference in melting and boiling points between oxygen and sulphur.
|
|
Calculate the expected returns, standard deviations
: Calculate the expected returns, standard deviations and coefficient of variations for stocks i and j. Which stock would be preferred by the average investor? Explain why in your own words.
|
|
Observing the chemical reaction
: In this experiment, you will be observing the chemical reaction that takes place when steel wool is exposed to oxygen and other corrosive agents.
|
|
How probabilities are used in the situation you chose
: Explain in detail how probabilities are used in the situation you chose. What makes probabilities useful in this situation? Do these probabilities affect decision making in this situation? Explain your answer.
|
|
Calculate the magnitude and direction of the torque
: Calculate the magnitude and direction of the torque required to hold the gearbox stationary (holding torque Th). Show the direction of the holding torque applied to the shaft with the aid of a sketch.
|
|
Carbonyl group and terminal carbonyl group
: How is 18-electrone rule helpful in determining the number of metal-metal bonds in Fe3(co)12 and Co4(Co)12 ? explain with example that 18-electrone rule is not useful in distinguishing between bridging carbonyl group and terminal carbonyl group?
|
|
The cereal project proposal
: PROJECT 2Congratulations, your consulting company has been awarded the cereal project proposal and you are to begin immediately gathering relevant data on the identified segments introduced in your initial proposal.
|
|
Distinguishing between bridging carbonyl group
: How is 18-electron rule helpful in determining the number of metal-metal bonds in Fe3(CO)12 and Co4(Co)12 ? explain with example that 18-electron rule is not useful in distinguishing between bridging carbonyl group and terminal Carbonyl group?
|
|
What was revolutionary in the new attitudes toward natural
: What was revolutionary in the new attitudes toward the natural world?
|