Reference no: EM13811067
Problem 1:
Consider Hall's experiment indicated in Fig. 1. The material is a metal with a density n of charge carriers each with charge q and mass m. The Hall voltage VH is measured for a given applied field B current I and conductor thickness t. From these variables the so called Hall coefficient for the material is determined:
RH = VHt/IB
(a) For negative charge carriers, indicate on a sketch the carrier drift velocity v→ and which side of the conductor has positive and negative Hall voltage.
(b) For negative charge carriers, indicate on a sketch the carrier drift velocity and which side of the conductor has positive Hall voltage.
(c) Show that the Hall coefficient RH = 1/nq . To do this you may need the following formulae that you should derive or argue for: v = E=B, I = Jωt, and J→ = nqv→.
(d) Calculate the Hall voltage for an experiment on a conductor where n = 3.7x �1022 cm3, q = 1.602 x 10-19C. The current I = 100 mA, the conductor thickness t = 0:1 mm, and the magnetic field B = 0.5 Tesla.
Problem 2:
Consider the Helmholtz coil configuration shown in Fig. 2. Here R = 0.2 m, I = 10 A, and there are N = 100 windings in each coil. You can neglect the thickness of each coils windings so that its dimensions are fully specified by R.
(a) Use Biot and Savart's law to derive an expression for the magnetic field as a function of displacement x from the center of the coils.
(b) Calculate the strength of the magnetic field in Tesla at the central point between the coils where x = 0 and for x = ±R/2 and make a plot of B(x).
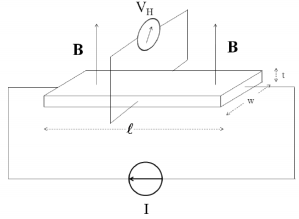
Figure 1: Experimental setup to measure the Hall coefficient for copper
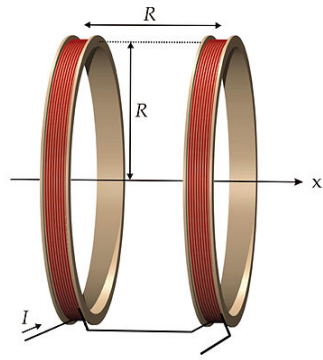
Figure 2: Helmholtz coil configuration.
Problem 3:
Consider the coaxial conductor shown in Fig. 3. Assume the current I flows in opposite directions in the inner and outer conductor respectively. You can assume the current is uniformly distributed in the inner and outer conductors.
(a) Use Ampere's law to determine the magnetic field B within the inner conductor, between the conductors, and outside the outer conductor. Make a plot of B as a function of displacement from the center of the coax cable.
(b) Considering the Lorentz force on moving charge in a magnetic field, sketch the direction of forces acting on points along the circumference of the inner and outer conductor where current is owing.
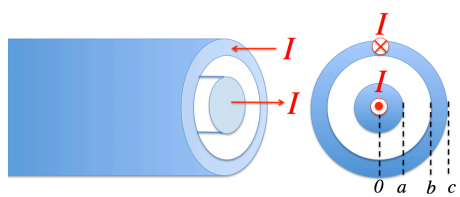
Figure 3: Coaxial cable with an inner and an outer.
|
Crime and education writing assignment
: Crime and Education Writing Assignment
|
|
Explain codification and personalization
: Briefly explain codification and personalization as they relate to knowledge management. How does the sort of knowledge management strategy a company has relate to its' business strategy? How should one pick a knowledge management strategy?
|
|
Analyze the rationale and purpose of the exclusionary rule
: analyze the rationale and purpose of the exclusionary rule, and identify exceptions. In your analysis, state the ramifications of the exclusionary rule
|
|
What is the exclusionary rule and what is an example
: What is the Exclusionary Rule and what is an example. What are the exceptions of the rule. How does the Exclusionary Rule apply to criminal procedure
|
|
Calculate the hall voltage for an experiment
: Calculate the Hall voltage for an experiment on a conductor where n = 3.7x �1022 cm3, q = 1.602 x 10-19C. The current I = 100 mA, the conductor thickness t = 0:1 mm, and the magnetic field B = 0.5 Tesla.
|
|
Which announces whether or not the player has won the game
: 2D graphics, instead of text, to display the Xs and Os in the grids of the square- shaped buttons decision logic or recursion in order to determine whether or not a player wins the games. Display a message which announces whether or not the player ha..
|
|
Implement and test a generic binary search
: Implement and test a generic binary search. Note that your test program must use at least 2 types of data to prove that bsearch is generic
|
|
Discuss how government intervention promotes efficiency
: Discuss how government intervention promotes efficiency and equity in the economy. Be sure that you include restraint of trade, indirect costs, deregulation, and overregulation within your analysis.
|
|
Conflicts as competition intensifies for water
: How will we counter the rapid rise of resource conflicts as competition intensifies for water and arable land. How should governments respond to this impending crisis of a diminished food supply
|