Reference no: EM13321427
Production and Operations Management
1. As the administrative manager in a law office, you have been asked to develop a system for evaluating the productivity of the 15 lawyers in the office. What difficulties are you going to have in doing this, and how are you going to overcome them?
2. List and explain the four basic global operations strategies. Give an example of each strategy.
3. For what type of organization might the location decision area be the least important of its ten decision areas? For what type of organization might the location decision be the most important of the ten decision areas? Discuss, augment your response with examples
4. Describe the differences between a Gantt chart and a PERT/CPM network.
5. A network consists of the following list. Times are given in weeks.
|
Activity
|
Preceding
|
Optimistic
|
Probable
|
Pessimistic
|
|
A
|
--
|
5
|
11
|
14
|
|
B
|
-
|
3
|
3
|
9
|
|
C
|
--
|
6
|
10
|
14
|
|
D
|
A, B
|
3
|
5
|
7
|
|
E
|
B
|
4
|
6
|
11
|
|
F
|
C
|
6
|
8
|
13
|
|
G
|
D, E
|
2
|
4
|
6
|
|
H
|
F
|
3
|
3
|
9
|
a. Draw the network diagram.
b. Calculate the expected duration and variance of each activity.
c. Calculate the expected duration and variance of the critical path.
d. Calculate the probability that the project will be completed in less than 28 weeks.
6. What is a tracking signal? How is it calculated? Explain the connection between adaptive smoothing and tracking signals.
7. Briefly explain how Product Lifecycle Management impacts product design. Cite an example.
8. List four quantitative forecasting methods and give examples on how it is used/implemented.
9. Discuss the advisability of using modular assemblies in manufacturing. (What are the advantages and disadvantages?) To what extent can these arguments be utilized in service products?
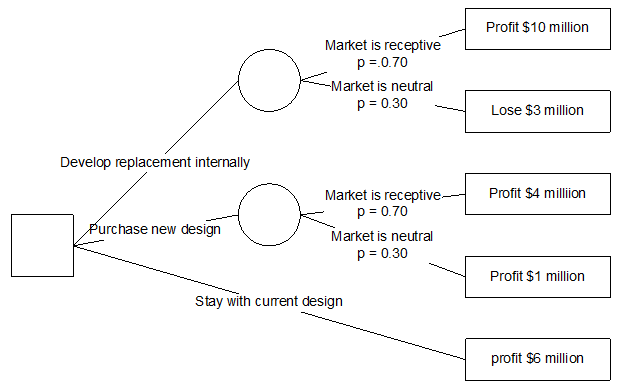
10. A company manufactures specialty pollution-sensing devices for the offshore oil industry.
One particular device has reached maturity, and the company is considering whether to replace it with a newer model. Technologies have not changed dramatically, so the new device would have similar functionality to the existing one, but would be smaller and lighter in weight. The firm's three choices are: keep the old model; design a replacement device with internal resources; and purchase a new design from a firm that is one of its suppliers. The market for these devices will be either "receptive" or "neutral" of the replacement model.
The financial estimates are as follows: Keeping the old design will yield a profit of $6 million dollars. Designing the replacement internally will yield $10 million if the market is "receptive," but a $3 million loss if the market is "neutral."
Acquiring the new design from the supplier will profit $4 million under "receptive," $1 million under "neutral." The company feels that the market has a 70 percent chance of being "receptive" and a 30 percent chance of being "neutral." Draw the appropriate decision tree. Calculate expected value for all courses of action. What action yields the highest expected value?