Reference no: EM131293230
Question 1. Demand in a market is given by P = 360 - 0.25Q, where Q is the total amount of output. There are N firms that compete as in Stackelberg competition: they move sequentially, and after observing the actions of any previous players, choose a quantity of output to produce. Each firm has a constant marginal cost of MC = 10.
(a) Suppose N = 2. (This is our baseline version of Stackelberg competition.) Solve for the equilib¬rium strategies and the outcome of the game.
(b) Suppose N = 3. Solve for the equilibrium strategies and the outcome of the game.
(c) Suppose that N = 3. Firm 1 moves first, but now suppose that Firms 2 and 3 move simultaneously (they compete in Cournot competition). What are the equilibrium strategies and outcome of this game? How does this compare to your answer from the previous part?
Question 2. [Multiple NE, Multiple Options] Consider the following two-player stage game.
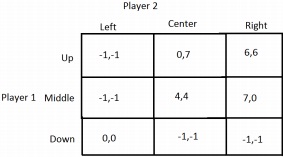
(a) Find all of the Nash Equilibria of the one-shot version of this game.
(b) Suppose this game is repeated indefinitely, and that the firms want to collude and choose (Up, Right) to earn a payoff of 6 in each period. What is the minimum probability-weighted discount factor required in order to sustain collusion using a Grim Trigger strategy in equilibrium?
(c) Again suppose the game is repeated indefinitely. What is the minumum probability-weighted discount factor required to support the best cooperative outcome, using the other Nash equilibrium as the punishment phase of the Grim Trigger strategy?
(d) Suppose that the game is repeated indefinitely and that the firms want to use a Grim Trigger strategy to support collusion, but they want to alternate between the two Nash equilibrium strategies (of the stage game) as the punishment, starting with the equilibrium with the higher payoffs. What is the minimum probability-weighted discount factor needed to support collusion using this strategy?
Question 3. [Trust Busting] Demand in the market for blenders is given by P = 100 - Q/2. The blender market is supplied by two firms, each of which has a constant marginal cost MC = 12. These two firms compete with each other in an indefinitely repeated game, and each firm has the same probability-weighted discount factor ρ.
(a) At first, the government is afraid of the mighty blender industry, and does not dare to interfere in the market for blenders. Solve for the minimum level of p needed to support collusion at the monopoly level of output in the blender market, assuming that if they collude the two firms split production and profits equally. If they don't collude, they compete as Cournot firms.
(b) At some point, the government grows bold, and is considering busting up this cartel, for the sake of the people. They suspect that the blender companies have formed a cartel, but they cannot prove it yet, so they are considering forming a special investigative unit to look into the matter. However, they have to be careful about how they proceed - if they raise the fine for cartel formation too high, it will look like they are unfairly targeting the blender companies. Accordingly, they cannot raise the fine that they can charge the blender companies above F = 1000. They can, however, hire a lot of economists, lawyers, and private detectives to catch the (potentially) colluding firms at work. That is, they can choose the probability of catching the firms q. Suppose that the maximum value of q that they can achieve is 0.40, and the maximum fine they can impose is F = 1000. What is the highest value of p such that they could potentially prevent the firms from forming a cartel?
(c) Suppose that p = 0.95, and the plucky government agents are clever enough to learn this. The government would really like to avoid a scandal - that is, they would like to prevent the cartel from forming, rather than catch the cartel, and have to have a messy trial. What is the lowest level of q they would have to commit to, in order to prevent the cartel?
(d) This is a government of the people, for the people. That is, they care about consumer surplus in the blender market, although they have to weigh that against the cost of preventing the cartel. Given that the cost to the government of setting a level of q is C(q) = 40000q2, is it worth it to them to prevent the cartel? Why or why not?
Question 4. [Dixit] In the Dixit model we saw in class, we discussed two benchmark values of K1, which we referred to as M1 and V1. Assuming the same production function for output, for generic demand P = A- BQ , wage rate w, and rental rate of capital r, what condition on A, B, w, and r must be true for it to be possible for Firm 1 to prevent Firm 2 from enterering for some values of F2? How does this condition change if we instead needed two units of capital and one unit of labor to produce one unit of output? For a given w and r, is this new condition more or less restrictive?
Question 5. [Entry Prevention] Q5 in PRN, Ch12. Two firms must decide whether to enter a new industry. Industry demand is described b y P = 900 - Q, where Q = q1 + q2. To enter the industry, a firm must build a production facility of one of two types: small or large. A small facility requires an investment of $50,000 and allows the firm to produce up to 100 units at a unit cost of zero. Alternatively the firm can pay $175,000 and build the large facility, which allows them to produce any amount of output at a marginal cost of zero per unit. A firm with a small production facility is capacity constrained, whereas a firm with the large facility is not. Firm 1 makes the entry decision first. It must choose whether to enter, and if it enters, what kind of facility to build. After observing F1's action, F2 chooses from the same set of alternatives. If only one firm chose to enter, it selects a quantity of output and sells it at the market price. If both firms chose to enter, they compete as Cournot firms. All output decisions are subject to capacity constraints of the production facilities. The market lasts for only one period.
(a) Draw the extensive form game tree that represents the entry game being played between the firms.
(b) What is the equilibrium outcome? Does Fl enter and at what size? Does F2 enter and at what size?
Question 6. [Auctions: 1st and 2nd Price] Consider an auction with two bidders, in which each bidder's valuations are private valuations, known only to them, and are independently drawn from the uniform distribution on the [0,1] interval. Bidders are risk-neutral.
(a) Calculate the equilibrium of the first-price auction, assuming that equilibrium strategies are linear. That is, each player's bid is b(V) = a1/ for some constant a.
(b) Calculate the equilibrium of the second-price auction, assuming that equilibrium strategies are linear.
(c) Show that the first and second price auctions yield the same expected revenue to the auctioneer.