Reference no: EM131135844
This exercise asks you to work through the Salop (1979) model of product differentiation, which differs from the Dixit-Stiglitz model in that equilibrium markups are declining in the number of firms. Imagine that consumers are located uniformly around a circle with perimeter equal to 1. The circle indexes both the preferences of heterogeneous consumers and the types of goods. The point where the consumer is located along the circle corresponds to the type of product that he most prefers. When a consumer at point x around the circle consumes a good of type z, his utility is R - t |z - x| - p, while if he chooses not to consume, his utility is 0. Here R can be thought of as the reservation utility of the individual, while t parameterizes the "transport" costs that the individual has to pay in order to consume a good that is away from his ideal point along the circle. Suppose that each firm has a marginal cost of ψ per unit of production.
(a) Imagine a consumer at point x, with the two neighboring firms at points z1 > x > z2. As long as the prices of these firms are not much higher than those farther away, the consumer will buy from one of these two firms. Denote the prices of these two firms by p1 and p2. Show that the price difference that would make the consumer indifferent between purchasing from the two firms satisfies p1 - p2 = (2x - z1 - z2)t, with t(z1 - x) + p1 ≤ R.
(b) Suppose that p1 and p2 satisfy the above relationships. Then show that all x ∈ [z2,x) strictly prefer to buy from firm 2, and all x ∈ (x, z1] strictly prefer to buy from firm 1.
(c) Now assume that there are three firms along the circle at locations z1 > z2 > z3. Show that firm 2's profits are given by
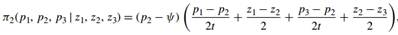
and calculate its profit-maximizing price.
(d) Suppose that p1 = p3. Show that firm 2 would like to locate half way between z1 and z3. Prove that an equilibrium with N firms charging the same price must have the distance between any two firms equal to 1/N.
(e) Show that when there are N equidistant firms, it is an equilibrium for all firms to charge p = ψ + t/N. Explain why the markup here is a decreasing function of the number of firms, whereas it was independent of the number of firms in the Dixit-Stiglitz model.
|
Print the minimum cost of conversion
: Print the minimum cost of conversion for each string to super ascii string
|
|
Determine the conditions on the function u
: In the Dixit-Stiglitz model in Section 12.4.1, determine the conditions on the function u(., .) in (12.7) such that an increase in N raises the profits of a monopolist.
|
|
Define herzberg theory
: Define Herzberg's Theory. Identify specific proactive steps supervisors can take to influence employee motivation according to the theory. Discuss how different generations might or might not be motivated according to the theory.
|
|
Using the customer traffic data and matching sales
: 1. I am stuck on this assignment. I have started it but I don't know how to figure out the formula. I don't know if the formula I am supposed to use is y=mx+b or something else. Need to figure out the figures missing from both charts and draw the ..
|
|
Calculate its profit-maximizing price
: Show that when there are N equidistant firms, it is an equilibrium for all firms to charge p = ψ + t/N. Explain why the markup here is a decreasing function of the number of firms, whereas it was independent of the number of firms in the Dixit-Sti..
|
|
Develop your composition based on area of interest in arts
: Trace some of the major contributions of an ethnic or "minority" group to U.S. culture, for example, to music, the arts, dance, or theater. There are many other possibilities! Develop your composition based on an area of interest to you in the art..
|
|
Describe the situation and advise the owner
: The owner has a chance to get another territory from the dealer but is cash constrained.- Describe the situation and advise the owner on what he should do.
|
|
Register of the audible spectrum
: A recording/playback system at 22,050 Hz would be missing most of the brilliance register of the audible spectrum
|
|
State the null and alternative hypotheses
: Brand managers become concerned if they discover that customers are aging and gradually moving out of the high-spending age groups. For example, the average Cadillac buyer is older than 60, past the prime middle years that typically are associated..
|