Reference no: EM132687112
Scenario One:
Greenland Manufacturing Co. produces lawnmowers. After five years, the once successful line is no longer selling well, so the company is considering production of an improved line of machines incorporating solar technology. This can be done by buying needed production equipment. There is a six-month manufacturing, delivery, setup, and training delay before the equipment will be ready for production. The company wants to start producing the new line of lawn mowers in January next year to be ready for peak selling season. Two options are available - lease or buy.
Buy Option - The entire purchase price of the production equipment is $900K and is due at the time of the order. The cost of capital for this purchase is 7.5%. Assume: (1) the equipment has no residual value at the end of the fifth year and (2) there are no taxes.
Lease Option - The total lease cost is $900K. A $160K deposit is due at the time of the order. The remaining portion of the first year's lease payment ($85K) is due in January next year. The other four annual lease payments ($147K each) are due in January of production years 2, 3, 4, and 5. The cost of capital for leasing is 17%. Assume no taxes.
Revenue from sales of the new line of solar powered mowers is expected to be:
• Year 1 - $900,000
• Year 2 - $640,000
• Year 3 - $327,000
• Year 4 - $235,000
• Year 5 - $115,000
1. Calculate the net present value of both the new purchase option and the lease option. Show all work. Determine the best option for Jones and justify your answer.
2. Calculate IRR for each option.
3. Assuming projected inflows and outflows are accurate, under what conditions can Jones expect to see a return equal to IRR? Is this realistic?
Other Related Questions:
4. Based on the NPV profile shown below, what is the approximate internal rate of return (IRR)?
5. You work for a company whose primary long term financial goal is to undertake projects that maximize company value. You have been asked to provide a recommendation with respect to ranking three mutually exclusive projects. The first project has a NPV of $200K and an IRR of 10%; the second has a NPV of $180K and an IRR of $12%; the third has a NPV of 220K and an IRR of 9%. How would you rank the projects? Explain.
6. Using appropriate financial analysis tools (e.g., NPV, IRR, and payback analyses), your company has already identified several independent projects that will add value to the company. Unfortunately, the company has an insufficient capital budget to undertake all of the projects and management has declined additional debt or equity financing efforts to increase the capital budget. What recommendation would you make for selecting the appropriate projects?
Scenario Two:
Your company experienced some cash flow issues during your last project that caused the project to be terminated early without achieving all its original objectives. Despite being told there is nothing to worry about, you decide to investigate the company's financial status.
7. What three financial statements should you look at first? What will they tell you?
8. You find the company has assets of $22M, total equity of $12M, and net cash flow of $6M per month, what are the company's total liabilities?
9. You also note the company depreciated an asset, purchased for $6M, over seven years using the straight-line method. What is the total depreciation expense (to the nearest dollar) at the end of year 4?
10. Based on the depreciation notes, you conclude that depreciation expense is:
A. A cash expense
B. Equal each year the asset is depreciated
C. A non-cash expense
D. A and B above
Note: Disregard question 10 when answering question 11.
11. You calculate the company's Current Ratio and find it to be 3.5. What specifically does this tell you?
12. You calculate Return on Assets (ROA) and find it to be 5.39% based on net income (available to common stockholders) of $350,000 and total assets of $6,500,000. You dig further and find that sales were $10,000,000. What does this information tell you about the company's net profit margin and total asset turnover? Provide values to support your assessment.
Scenario Three:
You are evaluating a work breakdown structure for adherence to WBS core characteristics. The WBS is decomposed to the work package level, i.e., work packages are not decomposed into component parts. You note that work packages are described as indicated in the project Scope Management Plan: WP - [description of the work to be performed]. You decide work package descriptors DO NOT violate core characteristics.
13. From a WBS core characteristics perspective, what is wrong with the following WBS sequence and how would you correct it?
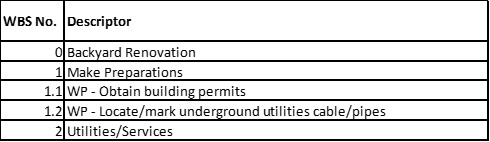
14. From a WBS core characteristics perspective, what is wrong with the following WBS sequence and how would you correct it?
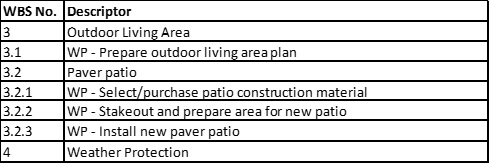
15. From a WBS core characteristics perspective, what is wrong with the following WBS sequence and how would you correct it?
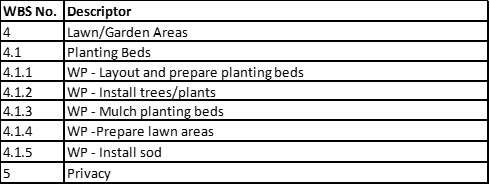
16. From a WBS core characteristics perspective, what is wrong with the following WBS sequence and how would you correct it?
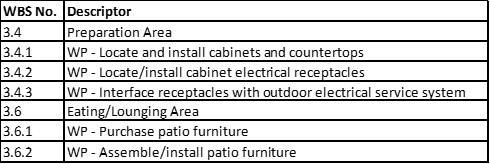
Scenario 4:
Project UMUC is to produce 325 widgets and is scheduled to take five weeks. Each unit is planned to cost $81.50. The project is severely cost constrained; the project budget does not include any contingency or management reserves. Performance data for the project at the end of week four is presented below:
• 247 total units were planned to be produced
• 271 units have actually been produced
• The financial manager reported that the business had actually spent $22,677 on the project by the end of week four.
You calculate, PV, EV, and BAC as follows:
PV = 242 units X $81.50 per unit = $19,723
EV = 267 units X $81.50 per unit = $21,761
BAC = 325 units x $81.50 per unit = $26,488
17. Calculate cost variance (CV). Based on this information, is the project over or under budget? Explain.
18. Calculate schedule variance (SV). Based on this information, is the project ahead or behind schedule? Explain.
19. Calculate cost performance efficiency to three digits. Based on this information, is the project performing better or worse than planned? Explain.
20. Calculate schedule performance efficiency to three digits. Based on this information, is the project performing better or worse than planned? Explain.
21. What is the forecast of project cost at completion assuming remaining work will be performed according to plan? How much budget variance is expected at completion?
22. Assuming remaining work will be performed according to plan, what is the forecast of funding needed to complete the project (from this point forward)?
23. What cost performance efficiency would be required for the remainder of the project to complete the project within the original budget?
24. As the project financial manager, what recommendations would you make?
Other Related Questions:
25. You are responsible for analyzing and quantifying cost and schedule performance on an Agile life cycle development project. During planning for the first sprint, the development team decided on a sprint duration of 15 days and estimated they could complete 30 story points during the sprint. The development teams consists of five people with an aggregate daily cost of $500. Assume this is the daily sprint cost.
Note: Story points represent about equal amounts of work and are a way of estimating the scope of a product backlog item based on size and complexity. A large and/or complex product backlog item is worth more story points than a smaller and/or less complex product backlog item.
At the end of 10 days, the development team has completed only 17 story points. What is the equivalent EVM Schedule Variance (SV), Schedule Performance Index (SPI), Cost Variance (CV), and Cost Performance Index (CPI)?
Attachment:- PMAN.rar