Reference no: EM13841678
Homework:
You may work together, but turn in your own individual answers.
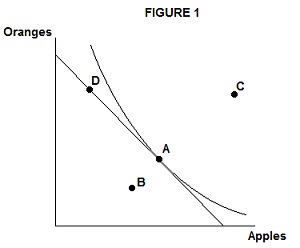
1. Figure 1 above shows a consumer's budget constraint for buying apples and oranges, as well as the indifference curve passing through the utility-maximizing bundle A.
a. Explain why the consumer does not choose bundle B.
b. Explain why the consumer does not choose bundle C.
c. Explain why the consumer does not choose bundle D. Hint: draw a bundle on the same indifference curve as A, but with both more apples and more oranges than D.
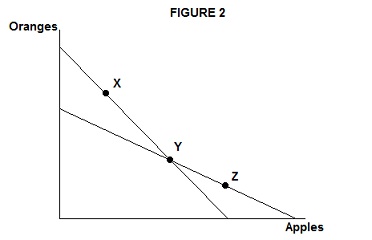
2. Figure 2 above shows 2 different budget constraints faced by a consumer choosing bundles of apples and oranges. Suppose that when both X and Y are affordable (on the steeper budget constraint), the consumer chooses Y. When both Y and Z are affordable (on the flatter budget constraint), the consumer chooses Z.
a. Based on revealed preference, explain why the consumer must prefer Z over X.
b. Draw two indifference curves, one passing through Y and another passing through Z, that are consistent with these choices.
c. Now suppose instead that the consumer always chooses Y, regardless of which of the two budget constraint is in effect. Is it possible to conclude, based on revealed preference, whether the consumer prefers Z over X or vice versa? Explain.
d. Redraw the graph in Figure 2, and draw an indifference curve passing through Y that is consistent with the choices the consumer made in part (c). Hint: Such an indifference curve must have a "kink" at bundle Y, similar to the indifference curves for perfect complements discussed in lecture.
e. Explain why the indifference curve in part (d) must be "kinked" and not "smooth" at bundle Y.
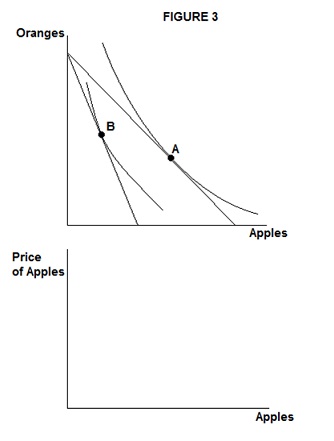
3. In the top panel of Figure 3, we see two budget constraints faced by a consumer choosing between apples and oranges. When the price of apples is $1 per unit, the consumer chooses bundle A. When the price of apples rises to $2 per unit, the consumer chooses bundle B. In the bottom panel of Figure 3, draw the consumer's individual demand curve for apples.
4. Suppose a consumer's marginal utility for beer is 2, and marginal utility for juice is 1. Beeris $3 per unit, while juiceis $1 per unit.
a. Find the consumer's marginal rate of substitution between beer and juice and the ratio of the price of beer to the price of juice. Also calculate the consumer's marginal utility per dollar spent on each good. Is the consumer maximizing utility?
b. Should the consumer increase consumption of beer or juice? Explain how increasing consumption of one of the goods by 1 unit (while decreasing consumption of the other good by an amount of equal cost) could increase the consumer's utility. As usual, assume the goods are perfectly divisible.
|
Order quantity-expected sales and expected overstock
: AspenWear, a retailer of ski wear needs to place an order for the Mirabelle, a designer ski jacket for the high-end market. Compute the following performance measures for the above order quantity: expected sales, expected overstock, and expected prof..
|
|
What is the total safety stock across all stores
: Suppose the 100 retail stores of a supermarket chain have identical weekly demand for a product (mean 200, standard deviation 120). There is zero correlation between the retailers’ demands. The lead time to replenish each retail store is 4 weeks. A c..
|
|
Which constraints are binding
: Stoneware Pottery Company wants to determine how many bowls and mugs should be produced per day in order to maximize profit given the labor and material constraints. The unit profit value for Bowls is $40 per unit, for mugs the unit profit value is $..
|
|
Determine the speed range required to give a frequency range
: Determine the speed range required to give a frequency range
|
|
Budget constraint for buying apples and oranges
: Figure 1 above shows a consumer's budget constraint for buying apples and oranges, as well as the indifference curve passing through the utility-maximizing bundle A.
|
|
Provide a summary on expanding your it unit
: Provide a Summary report on existing capability and capacity assessment, and discuss how these can address the problem on hand. Provide a summary on expanding your IT unit to meet the problem on hand.
|
|
Is there a payoff from top-team diversity
: Write 1-2 page summary each of the following articles- Is there a payoff from top-team diversity? Management intuition for the next 50 years
|
|
What is the profit that studio expects to make
: Top Gun Records and several movie studios have decided to sign a revenue-sharing contract for DVDs. Each DVD costs the studio $2 to produce. The DVD will be sold to Top Gun for $3. What is the profit that Top Gun expects to make? What is the profit t..
|
|
What order quantity maximizes borders expected profit
: A publisher sells books to Borders at $12 each. Borders prices the book to its customers at $24 and expects demand over the next two months to be normally distributed, with a mean of 20,000 and a standard deviation of 5,000. What order quantity maxim..
|