Reference no: EM133085710
COIT20247 Database Design and Development - Central Queensland University
PART A - Data Modelling Questions
Questions 1, 2 and 3 in this part relate to the ER model given below. The ER model illustrates the entities and relationships for modelling a financial service firm that has been engaged in stock research and trade. Assume the firm has two types of staff - trade managers and research analysts. Analysts make recommendations based on their research, whereas the manager's duty is to trade the stocks with consideration of the recommendations by analysts. Examine the ER model below and answer all the questions in thissection relate to the ER model given below.
ER model
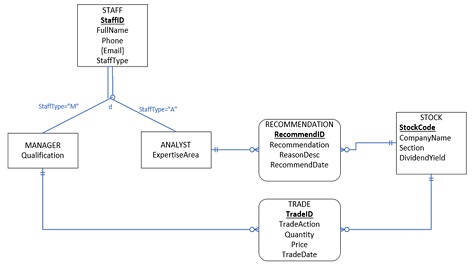
Question 1
Data Modelling
According to the ER model given above, answer either yes or no to the following questions:
(a) Can each manager have more than one email address?
(b) Is it possible for an analyst to recommend more than one stock?
(c) Is a manager required to trade at least one stock?
(d) Are there any other possible types of staff?
Question 2
(a) Explain the total or partial specialisations that have been used in the ER model.
(b)List the reasons for using disjoint classification in the ER model.
Question 3
Converting ER models
Convert the ER model given in Part A into a set of relations that satisfy Third Normal Form (3NF). You do not need to show your workings. You do not need to justifythat they are in 3NF at this stage. You do not need to show sample data. Just show your relations. You should write your relations in either format shown below:
Student (StudentID, StudentName, DateOfBirth)
Enrolment (EnrolmentID, StudentID, DateOfEnrolment)
or:
Student (StudentID, StudentName, DateOfBirth)
Enrolment (EnrolmentID, StudentID, DateOfEnrolment)
Foreign key (StudentID) references Student
Question 4
Relational model and Normalisation
The following table is designed to include customer, seller, and vehicle information for test drives in a car sale firm. But this relation has been wrongly designed. Ithas been assumed that the combination of CustomerID, SellerID,VehicleID and the date of test drive uniquely identifies each tuple in this relation.
VehicleTest
|
CustomerID
|
CustName
|
SellerID
|
SellerName
|
VehicleID
|
VehicleModel
|
TestDriveDate
|
|
C101
|
James Cook
|
S001
|
John Wells
|
V10022
|
Altise
|
12-1-2019
|
|
C101
|
James Cook
|
S002
|
Kylie Taylor
|
V10025
|
Hilux
|
15-1-2019
|
|
C102
|
Shirley Lin
|
S001
|
John Wells
|
V20443
|
Yaris
|
12-2-2019
|
|
C102
|
Shirley Lin
|
S003
|
Paul Walker
|
V20215
|
Corolla
|
18-3-2019
|
|
C103
|
David Johnson
|
S004
|
Andy Lin
|
V13535
|
Prius
|
19-2-2019
|
|
C104
|
Linda Coles
|
S002
|
Kylie Taylor
|
V23007
|
Aurion
|
26-2-2019
|
(a) On the above table, if deleting the test drive of Prius on 19/02/2019, justify what anomaly will happen.
(b) What is the highest normal form that this relation satisfies and why?
(c) Normalise the relation into a set of relations that satisfy 3NF using the format as follows:
Customer (CustomerID, CustomerName)
Order (OrderID, Amount, Date, CustomerID)
Foreign key (CustomerID) references Customer
Part B - Structured Query Language Questions
FormulateSQL queries to answer the following information requests. Use the relations CUSTOMER, BOOKING, ROOM, ROOMTYPE and BRANCH provided below. These relations describe the business activities in which customers book a room from a chain-motel in central Queensland area. The relevant data on customer, branch, room, roomtype and booking activities are stored in a database.
Relations
CUSTOMER(CustomerID, FirstName, LastName, Address,MobilePhone,
DateOfBirth,DriverLicenseNo)
ROOM(RoomID, MaxNumOfAccom, NumOfBed, BranchID, RoomTypeID)
Foreign Key (RoomTypeID) References ROOMTYPE
Foreign Key (BranchID) References BRANCH
ROOMTYPE(TypeID, TypeDescription,PricePerNight)
BRANCH(BranchID, BranchName, ManagerFirstName, ManagerLastName,
Address, Telephone)
BOOKING(BookingID, StartDate, EndDate, NumOfPeople, TotalCharge,
CustomerID, RoomID)
Foreign Key (CustomerID) References Customer
Foreign Key (RoomID) References Room
Note: The following E-R diagram may assist you to understand the relations as described as above.
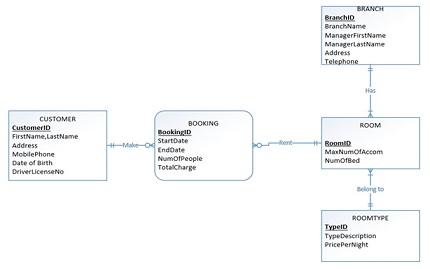
Tables
CUSTOMER
|
|
CustomerID
|
FirstName
|
LastName
|
Address
|
MobilePhone
|
DateOfBirth
|
DriverLicenseNo
|
|
1
|
John
|
Andersen
|
9 Bridge street,Gold Coast
|
0450099112
|
01/10/1977
|
099 888 700
|
|
2
|
Sydney
|
Shield
|
1 Adelaide road, Brisbane
|
0404332210
|
09/07/1989
|
120 990 044
|
|
3
|
William
|
Stallings
|
11 North street, Gold Coast
|
0449306300
|
27/01/2000
|
077 123 777
|
|
4
|
Cloud
|
Itchaya
|
541 Forest park, Sunshine Coast
|
0422901212
|
09/10/1988
|
077 809 012
|
|
5
|
Paul
|
Arthur
|
340 City road, Rockhampton
|
0458001919
|
09/01/1977
|
099 111 765
|
|
6
|
Amanda
|
Roseling
|
14 Coast road, Sydney
|
0453382222
|
17/07/1990
|
118 777 665
|
|
7
|
Kim
|
Pinkney
|
12 Gosford road, Gosford
|
0450910909
|
21/09/1999
|
186 776 900
|
BOOKING
|
|
BookingID
|
StartDate
|
EndDate
|
NumOfPeople
|
TotalCharge
|
CustomerID
|
RoomID
|
|
100
|
01/11/2020
|
02/11/2020
|
1
|
$100.00
|
1
|
10000
|
|
101
|
15/06/2020
|
17/06/2020
|
2
|
$800.00
|
2
|
10005
|
|
102
|
10/10/2020
|
13/10/2020
|
1
|
$450.00
|
6
|
10002
|
|
103
|
09/09/2020
|
11/09/2020
|
1
|
$200.00
|
7
|
20001
|
|
104
|
22/11/2020
|
23/11/2020
|
1
|
$100.00
|
1
|
10001
|
|
105
|
01/11/2020
|
02/11/2020
|
1
|
$100.00
|
1
|
20003
|
|
106
|
02/12/2020
|
05/12/2020
|
1
|
$450.00
|
6
|
10001
|
ROOM
|
|
RoomID
|
MaxNumOfAccom
|
NumOfBed
|
TypeID
|
BranchID
|
|
10000
|
3
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
|
10001
|
3
|
2
|
2
|
1
|
|
10002
|
3
|
2
|
2
|
1
|
|
10005
|
5
|
2
|
4
|
1
|
|
20001
|
3
|
1
|
1
|
2
|
|
20002
|
5
|
2
|
4
|
2
|
|
20003
|
3
|
1
|
1
|
2
|
|
20004
|
3
|
2
|
2
|
2
|
|
30001
|
3
|
1
|
1
|
3
|
ROOMTYPE
|
|
TypeID
|
TypeDescription
|
PricePerNight
|
|
1
|
Standard room
|
$100.00
|
|
2
|
Superior room
|
$150.00
|
|
3
|
Deluxe room
|
$200.00
|
|
4
|
Deluxe executive room
|
$400.00
|
BRANCH
|
|
BranchID
|
BranchName
|
Address
|
Phone
|
ManagerFirstName
|
ManagerLastName
|
|
1
|
Rockhampton Grand Motel
|
101 bruce highway, Rockhampton
|
49308811
|
Peter
|
Hogan
|
|
2
|
Gladstone Grand Motel
|
25 han street, Galdstone
|
49343023
|
Boris
|
Stallings
|
|
3
|
Mackay Grand Motel
|
18 river road, Mackay
|
48343524
|
Linda
|
Lumby
|
Note that:
• You are asked to provide a general solution to each request. If the database contents change, each of your queries should continue to answer the information requested correctly.
• Simple queries are preferred; if your queries are unnecessarily complex you may lose marks.
• For the given sample data, your queries should be able to generate the same data and column names as shown in the result table for each request.
• You are not required to sort the results in any order unless requested.
• State any assumption that you make to clarify your understanding of the information request.
Question 1 List the details of rooms that have never been booked. The details include roomID, room type and the price per night.
Question 2 How many rooms does each branch have? Show the manager's name, the branch name and the number of rooms. Order the list so that the manager who has managed the most rooms appears first.
Question 3 Identify the rooms of hotels in Gladstone with the daily rent no higher than $150 per night.
Question 4 Which customers have made more than one booking in last sixmonths? Show the customer names, mobile phones and the number of bookings.
Question 5 Find the details of the bookings that have the most total charges. The details include the customer name, the room ID, the start date, the end date, and the total charge.
PART C
Question 1 Briefly explain the referential integrity rule. Provide a suitable situation when the referential integrity constraint is violated.
Question 2 This question refers to the Part table as used in this unit lecture slides about the customers to order homeware parts. Using SQL DCL command to write a statement to permit a user with the log in ID of JOHNSON to access the Part table and update its UnitPrice value.
Question 3 Consider a relation named STUDENT_ ACCOMMODATION (StudentID, Building, AccommodationFee) as shown in the figure below, where StudentID is the primary key. Assume the value of Building is unique. Explain why this relation is in 2NF but not in 3NF.
Question 4 Explain the purpose of transaction logs and checkpoints.
Question 5 Compare and contrast Data Warehousing against Database.
Attachment:- Database Design and Development.rar